MEPS
HC-036BRR: 1996-2009 Replicates for Variance Estimation File
December 2011
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends
540 Gaither Road
Rockville, MD 20850
(301) 427-1406
TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. Data Use Agreement
B. Background
1.0 Household Component
2.0 Medical Provider Component
3.0 Survey Management
C. Technical and Programming Information
1.0 General Information
2.0 Data File Information
3.0 Linking Instructions
4.0 Other Considerations
5.0 Further Information
A. Data Use Agreement
Individual identifiers have been removed from the micro-data contained in these files. Nevertheless, under sections 308 (d) and 903 (c) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 242m and 42 U.S.C. 299 a-1), data collected by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) and/or the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) may not be used for any purpose other than for the purpose for which they were supplied; any effort to determine the identity of any reported cases is prohibited by law.
Therefore in accordance with the above referenced Federal Statute, it is understood that:
- No one is to use the data in this data set in any way except for statistical reporting and analysis; and
- If the identity of any person or establishment should be discovered inadvertently, then (a) no use will be made of this knowledge, (b) the Director Office of Management AHRQ will be advised of this incident, (c) the information that would identify any individual or establishment will be safeguarded or destroyed, as requested by AHRQ, and (d) no one else will be informed of the discovered identity; and
- No one will attempt to link this data set with individually identifiable records from any data sets other than the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey or the National Health Interview Survey.
By using these data you signify your agreement to comply with the above stated statutorily based requirements with the knowledge that deliberately making a false statement in any matter within the jurisdiction of any department or agency of the Federal Government violates Title 18 part 1 Chapter 47 Section 1001 and is punishable by a fine of up to $10,000 or up to 5 years in prison.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality requests that users cite AHRQ and the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey as the data source in any publications or research based upon these data.
Return to Table of Contents
B. Background
1.0 Household Component
The Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) provides nationally representative estimates of health care use, expenditures, sources of payment, and health insurance coverage for the U.S. civilian non-institutionalized population. The MEPS Household Component (HC) also provides estimates of respondents' health status, demographic and socio-economic characteristics, employment, access to care, and satisfaction with health care. Estimates can be produced for individuals, families, and selected population subgroups. The panel design of the survey, which includes 5 Rounds of interviews covering 2 full calendar years, provides data for examining person level changes in selected variables such as expenditures, health insurance coverage, and health status. Using computer assisted personal interviewing (CAPI) technology, information about each household member is collected, and the survey builds on this information from interview to interview. All data for a sampled household are reported by a single household respondent.
The MEPS-HC was initiated in 1996. Each year a new panel of sample households is selected. Because the data collected are comparable to those from earlier medical expenditure surveys conducted in 1977 and 1987, it is possible to analyze long-term trends. Each annual MEPS-HC sample size is about 15,000 households. Data can be analyzed at either the person or event level. Data must be weighted to produce national estimates.
The set of households selected for each panel of the MEPS HC is a subsample of households participating in the previous year’s National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics. The NHIS sampling frame provides a nationally representative sample of the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population and reflects an oversample of blacks and Hispanics. In 2006, the NHIS implemented a new sample design, which included Asian persons in addition to households with black and Hispanic persons in the oversampling of minority populations. MEPS further oversamples additional policy relevant sub-groups such as low income households. The linkage of the MEPS to the previous year’s NHIS provides additional data for longitudinal analytic purposes.
Return to Table of Contents
2.0 Medical Provider Component
Upon completion of the household CAPI interview and obtaining permission from the household survey respondents, a sample of medical providers are contacted by telephone to obtain information that household respondents can not accurately provide. This part of the MEPS is called the Medical Provider Component (MPC) and information is collected on dates of visit, diagnosis and procedure codes, charges and payments. The Pharmacy Component (PC), a subcomponent of the MPC, does not collect charges or diagnosis and procedure codes but does collect drug detail information, including National Drug Code (NDC) and medicine name, as well as date filled and sources and amounts of payment. The MPC is not designed to yield national estimates. It is primarily used as an imputation source to supplement/replace household reported expenditure information.
Return to Table of Contents
3.0 Survey Management
MEPS HC and MPC data are collected under the authority of the Public Health Service Act. Data are collected under contract with Westat, Inc. Data sets and summary statistics are edited and published in accordance with the confidentiality provisions of the Public Health Service Act and the Privacy Act. The National Center for Health statistics (NCHS) provides consultation and technical assistance.
As soon as data collection and editing are completed, the MEPS survey data are released to the public in staged releases of summary reports, micro data files, and tables via the MEPS web site: www.meps.ahrq.gov. Selected data can be analyzed through MEPSnet, an on-line interactive tool designed to give data users the capability to statistically analyze MEPS data in a menu-driven environment.
Additional information on MEPS is available from the MEPS project manager or the MEPS public use data manager at the Center for Financing Access and Cost Trends, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, 540 Gaither Road, Rockville, MD 20850 (301-427-1406).
Return to Table of Contents
C. Technical and Programming Information
1.0 General Information
Due to the complex survey design of the MEPS-HC, special methods must be used to calculate the standard errors of MEPS-HC estimates. To facilitate the calculation of design-based standard errors, MEPS-HC annual public use datasets contain stratum and PSU variables which can be utilized by the survey procedures that implement the Taylor series linearization method of variance estimation. There is also a public use file, HC-036, which provides a standardized set of pooled linkage variance estimation units over all years of MEPS-HC so that estimates can be made with datasets created by pooling over multiple years of annual MEPS-HC data.
Although useful, the linearization method is limited in the number of survey estimators for which variances can be calculated, including population totals, simple proportions and regression parameters. It is not possible, for instance, to calculate the variances of a median or the ratio between two medians using a Taylor series expansion. For these types of estimators, users may calculate a proper design based standard error using either the PSU bootstrap or balanced repeated replication (BRR) method of variance estimation.
This dataset, HC-036BRR, contains the information necessary to construct the BRR replicate samples that are necessary to calculate the BRR variances. It contains the unique person-level identifier (DUPERSID and PANEL) of every MEPS respondent appearing in any of the 1996-2009 annual full year samples: HC‑012 (1996), HC‑020 (1997), HC‑028 (1998), HC‑038 (1999), HC‑050 (2000), HC‑060 (2001), HC-070 (2002), HC-079 (2003), HC-089 (2004), HC-097 (2005) , HC-105 (2006), HC-113 (2007), HC-121 (2008), and HC-129 (2009). It also contains a set of 128 flags (BRR1—BRR128), each of which is coded 0 or 1 to indicate whether the person should or should not be included in that particular replicate sample. These flags should be used in conjunction with the sample weights from the full-year sample files to construct the BRR replicate weights needed to calculate BRR variances.
Return to Table of Contents
2.0 Data File Information
Released as an ASCII data file (with SAS® and SPSS® user statements) and in SAS Transport version, the HC-36BRR file contains 241,212 records. These records contain the standard MEPS person‑level ID variables (DUID, PID, DUPERSID and PANEL), as well as the 1996‑2009 replicate indicator variables BRR1-BRR128.
There is a record for each person who appears on any of the 1996‑2009 MEPS full‑year person level public use files: HC‑012, HC‑020, HC‑028, HC‑038, HC‑050, HC‑060, HC-070, HC-079, HC-089, HC-097, HC-105, HC-113, HC-121, and HC-129. These fourteen datasets have a combined total of 441,268 records. However, because each person may appear in one or two of these datasets the number of unique persons (241,212) is fewer than the combined total number of records on the annual files.
Return to Table of Contents
3.0 Linking Instructions
The following steps should be taken to create a file containing persons from any one or more of the fourteen years of MEPS HC data.
- Create a dataset for each year containing the person- and/or event-level records of all persons to be included in the analysis. Keep the unique person identifier (DUPERSID and PANEL), the person-level sampling weight, any classification variables (e.g., sex, race/ethnicity) and response variables (e.g., total expenditure amount, number of prescription drug purchases, etc) to be used in the data analysis.
- Reconcile the discrepancies in variable names. For all years, most variable names on the annual public use files contain a 2-digit year suffix. For instance, in the 1997 consolidated person-level file (HC-020) the panel variable is called PANEL97, the total annual expenditure amount variable is called TOTEXP97 and the sampling weight variable is called WTDPER97. But in the 2003 dataset (HC-079) these same variables are named PANEL03, TOTEXP03 and PERWT03F, respectively, and in the 1996 dataset (HC-012) the total expenditure and sampling weight variables are named TOTEXP96 and WTDPER96, respectively, and the panel variable is missing (users should assign a value of 1 for each record in HC-012). As illustrated below, the variable names must be made consistent before pooling the data. Note: starting in 2005, the panel variable is called simply PANEL (no year suffix).
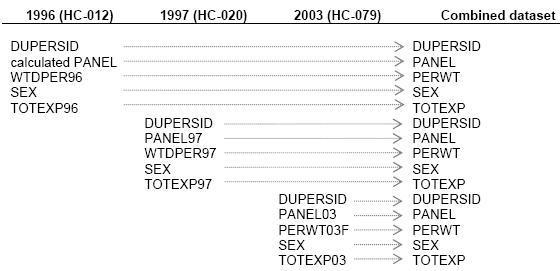
- Create a pooled analysis dataset by combining the individual-year datasets by row; that is, append the records from the 1996 dataset with those from the 1997 and 2003 datasets.
- Attach the BRR replicate flags to the pooled analysis dataset by column; that is, merge the variables BRR1-BRR128 from this HC-036BRR file to the pooled analysis dataset by DUPERSID and PANEL keeping all records in the pooled analysis dataset and only those records in HC-036BRR dataset that match. Depending on the software being used to manage the datasets, the pooled analysis dataset may need to be sorted by DUPERSID and PANEL prior to merging.
- To calculate a standard set of 128 BRR replicates, multiply each BRR replicate flag by 2 by the sample weight (PERWT, if using the example above). That is, BRR1wt = BRR1 * 2 * PERWT and BRR2wt = BRR2 * 2 * PERWT, …, BRR128wt = BRR128 * 2 * PERWT. This method creates a set of balanced replicates whereby half the sample in each replicate will have a replicate weight equal to two times sample weight (if the BRR flag is 1) or 0 (if the BRR flag is 0). Users interested in implementing Fay’s BRR method may chose different multipliers than 0 and 2 against which to factor the sample weights in each replicate. For instance, they may chose to multiply the sample weights by 0.5 if the BRR flag is 0 and multiply them by 1.5 if the BRR flag is 1.
Return to Table of Contents
4.0 Other Considerations
When working with pooled data, analysts should consider whether they need to adjust the survey weights from the annual public use files to account for the reprojection of survey estimates to a multi-year time period. The survey weights provided in the 1996 annual dataset (HC-012) project the HC-012 sample to the US population in 1996, and the survey weights in the 1997 dataset (HC-020) project the HC-020 sample to the US population in 1997. When combining two years of annual MEPS data (e.g., 1996 and 1997), these single-year weights over-represent the population in the new two-year period (1996 and 1997) by a factor of 2. Likewise, when combining three years of MEPS data, the single-year weights over-represent the new three-year population by a factor of 3.
This over-representation will only affect the estimates of totals but not the estimates of proportions. That is, all estimates of total expenditures and their standard errors will be twice as high as they should be if using the annual weights on the annual public use files pooled over two years without adjustment; these same estimates will be three times too high if pooling over three years. Ratio estimates, such as the mean expenditure or the percent of expenditures paid out of pocket, will not be too high when using the annual weights after pooling several years of MEPS datasets together. Users wishing to estimate totals have two options to account for the multi-year period: they may factor the weights before they make any estimates or they may factor the estimates themselves (they should not do both).
- To illustrate the first method (factoring the weights), users who pool two years of MEPS data should divide the sampling weight (variable PERWT if following the example above) by 2 prior to constructing the BRR replicate weights. They would divide the sampling weight by three if pooling three years of MEPS data together. With this adjustment to the sampling weight, all estimates of totals (and their standard errors) will reflect the new multi-year period. Estimates of proportions (and their standard errors) will also be correct after this adjustment.
- To illustrate the second method (factoring the estimates themselves), users would make the estimates of totals (and optionally their proportions) with the annual weights as is. They would then factor the estimates of the totals (as well as their standard errors) by the number of years that were pooled. If the estimates were made with two years of data, the totals and their standard errors would be divided by 2, if they were made with three years of data, the totals and their standard errors would be divided by 3. Users would only adjust the estimates and standard errors of totals, not those of proportions.
Return to Table of Contents
5.0 Further Information
For any question regarding the HC-036BRR file or pooling of data, please contact
Sadeq Chowdhury by email at: sadeq.chowdhury@ahrq.hhs.gov or
Fred Rohde by email at: frederick.rohde@ahrq.hhs.gov.
Return to Table of Contents
|
