|
|
Font Size:
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
STATISTICAL BRIEF #421:
Differentials in the Concentration in the Level of Health Expenditures across Population Subgroups in the U.S., 2010
Highlights
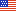
- In 2010, the top 1 percent ranked by their health care expenses accounted for 21.4 percent of total health care expenditures with an annual mean expenditure of $87,570. Overall, the top 50 percent of the population ranked by their expenditures accounted for 97.2 percent of overall health care expenditures while the lower 50 percent accounted for only 2.8 percent of the total.
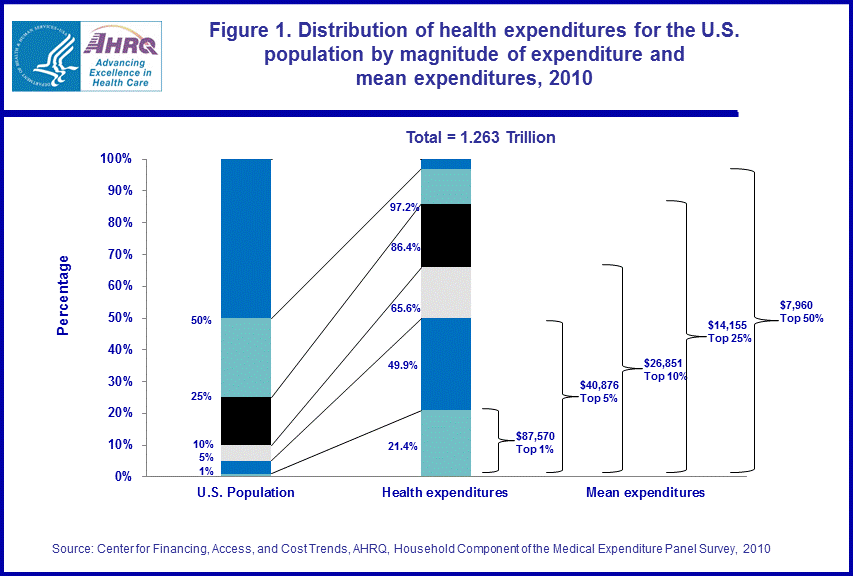
- Children under the age of 18 were characterized by substantially greater concentrated levels of health care spending relative to their older counterparts. Alternatively, the elderly had the highest mean levels of health care expenditures relative to younger population subgroups at the top quantiles of the expenditure distribution.
- The top 5 percent of the uninsured population under age 65 ranked by their health care expenses accounted for 67.3 percent of the health care expenditures incurred by this subpopulation with an annual mean of $17,453. Conditioned on insurance coverage status, the uninsured had the most concentrated levels of health care expenditures and the lowest annual mean expenses.
- The top 5 percent of individuals with four or more chronic conditions accounted for 29.7 percent of health care expenditures for this subpopulation with an annual mean of $81,790. Based on chronic condition status, persons with four or more chronic conditions had the lowest concentrated levels of health care expenditures and the highest annual mean expenses at the top quantiles of the expenditure distribution.
Introduction
Estimates of health care expenses for the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized (community) population are critical to policymakers and others concerned with access to medical care and the cost and sources of payment for that care. In 2010, health care expenses among the U.S. community population totaled $1.263 trillion. Medical care expenses, however, are highly concentrated among a relatively small proportion of individuals in the community population. As previously reported in 1996, the top 1 percent of the U.S. population accounted for 28 percent of the total health care expenditures and the top 5 percent for more than half. More recent data have revealed that over time there has been some decrease in the extent of this concentration at the upper tail of the expenditure distribution.Using information from the Household Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS-HC) for 2010, this Brief provides detailed estimates of the concentration in the level of health care expenditures for the nation, and further distinguishes them by specific population subgroups. Studies that examine the concentration of health care expenditures, their magnitude, and their respective differentials distinguished by specific population subgroups are essential to help discern the factors most likely to drive health care spending and the characteristics of the individuals who incur them. The MEPS-HC data are particularly well suited for measuring the population's distribution of health care expenditures. All differences between estimates discussed in the text are statistically significant at the 0.05 level unless otherwise noted.
Findings
In 2010, the top 1 percent ranked by their health care expenses accounted for 21.4 percent of total health care expenditures with an annual mean expenditure of $87,570 (figure 1). The top 5 percent of the population accounted for 49.9 percent of total expenditures with an annual mean expenditure of $40,876. In addition, the top 10 percent of the population accounted for 65.6 percent of total expenditures with an annual mean expenditure of $26,851. Overall, the top 50 percent of the population ranked by their expenditures accounted for 97.2 percent of overall health care expenditures while the lower 50 percent accounted for only 2.8 percent of the total. Those individuals ranked in the top half of the health care expenditure distribution had an annual mean expenditure of $7,960.Age
In 2010, the top 5 percent of children under the age of 18 ranked by their health care expenses accounted for 54.6 percent of the health care expenditures incurred by this subpopulation with an annual mean expenditure of $16,901 (figure 2). Among persons 18–44 years, the top 5 percent accounted for 50.5 percent of the health care expenditures incurred by this population subgroup with an annual mean of $24,871. The top 5 percent of individuals 45–64 were associated with 45.0 percent of the health care expenditures incurred by this age group with an annual mean of $51,881. Alternatively, the top 5 percent of the elderly aged 65 years and older accounted for 34.1 percent of the medical expenditures experienced by this domain, with an annual mean of $67,474. In summary, the youngest age cohort (under 18 years old) was characterized by the most concentrated levels of health care spending relative to their older counterparts. In contrast, the elderly had the highest mean levels of health care expenditures relative to younger population subgroups at the highest quantiles of the health care expenditure distribution.
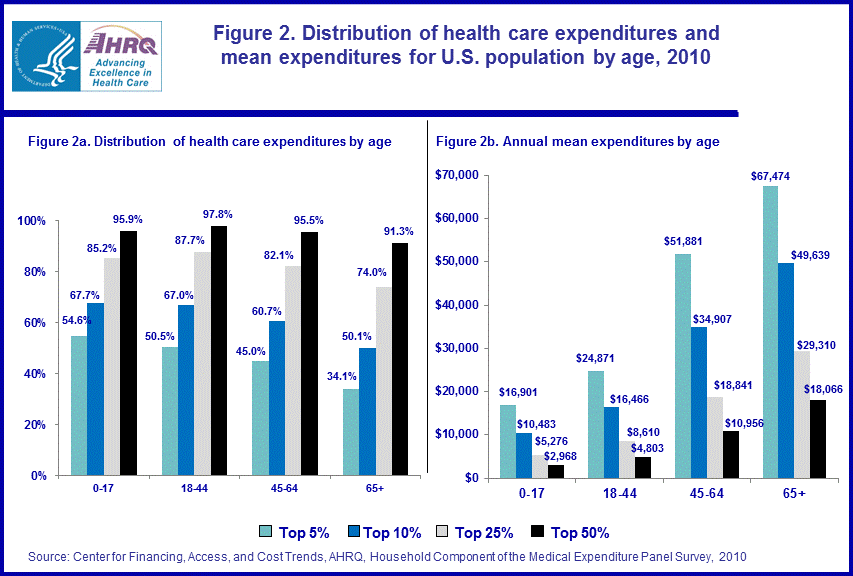
The top 5 percent of non-Hispanic whites and other races accounted for 46.2 percent of the health care expenditures incurred by this subpopulation with an annual mean of $43,236 in 2010 (figure 3). Among non-Hispanic black individuals, the top 5 percent accounted for 58.4 percent of the health care expenditures for this subgroup, with an annual mean of $47,329. For non-Hispanic Asians, the top 5 percent were associated with 55.1 percent of the health care expenditures incurred for this subpopulation, exhibiting a mean of $26,865. The top 5 percent of Hispanics accounted for 60.3 percent of health care expenditures by this subpopulation with an annual mean of $27,307. Non-Hispanic whites and other races had the lowest concentration of expenditures when controlling for race/ethnicity. Alternatively, non-Hispanic whites and other races and non-Hispanic blacks exhibited the highest mean levels of health care expenditures at the top quantiles of the expenditure distribution.
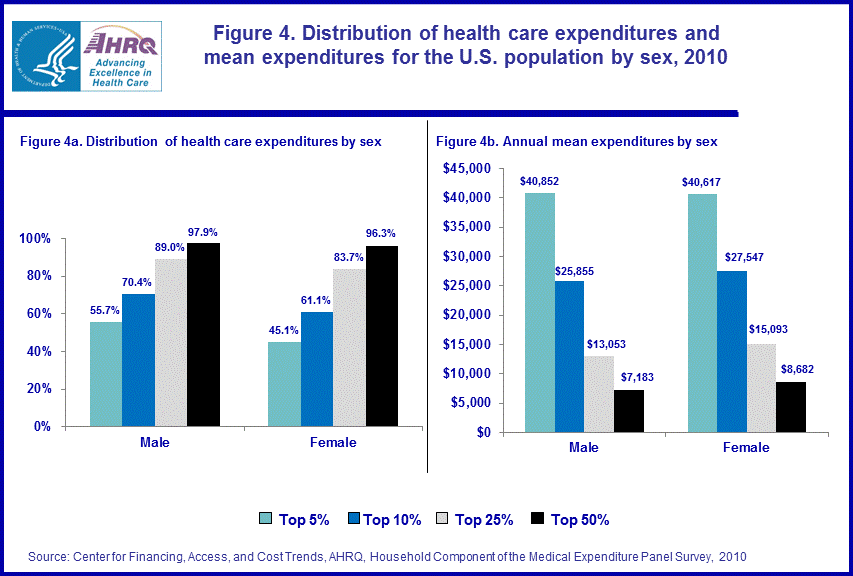
Sex
In 2010, the top 5 percent of males accounted for 55.7 percent of health care expenditures incurred by this subpopulation with an annual mean of $40,852 (figure 4). Among females, the top 5 percent were associated with 45.1 percent of health care expenditures for this subgroup, with mean expenditures of $40,617. Conditioned on sex, males had a more concentrated level of health care expenditures.
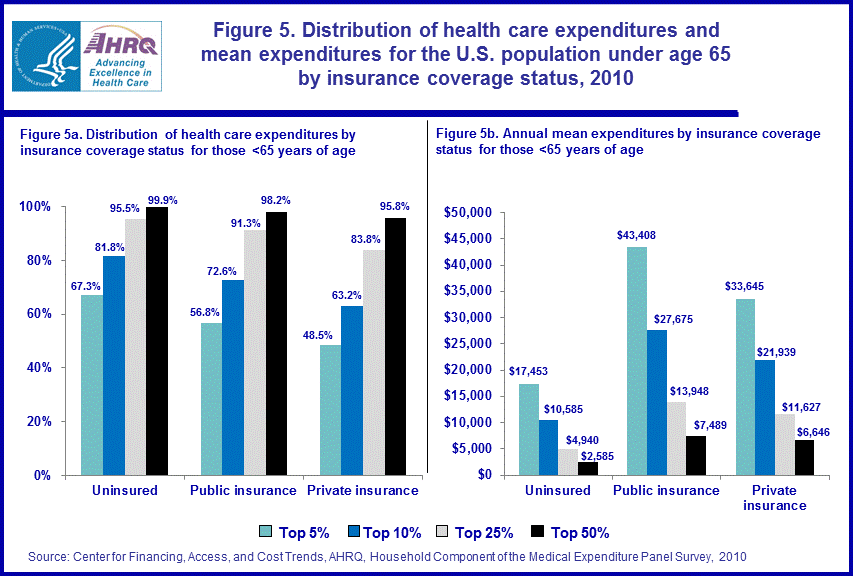
Insurance status
The top 5 percent of the uninsured population under age 65 ranked by their health care expenses accounted for 67.3 percent of the health care expenditures incurred by this subpopulation with an annual mean of $17,453 in 2010 (figure 5). Among non-elderly persons with public coverage only, the top 5 percent accounted for 56.8 percent of health care expenditures for this subgroup, with mean expenditures of $43,408. For those non-elderly with any private coverage, the top 5 percent were associated with 48.5 percent of this group's overall health care expenses, exhibiting a mean of $33,645. Conditioned on insurance coverage status, the uninsured had the most concentrated levels of health care expenditures and the lowest annual mean expenses.
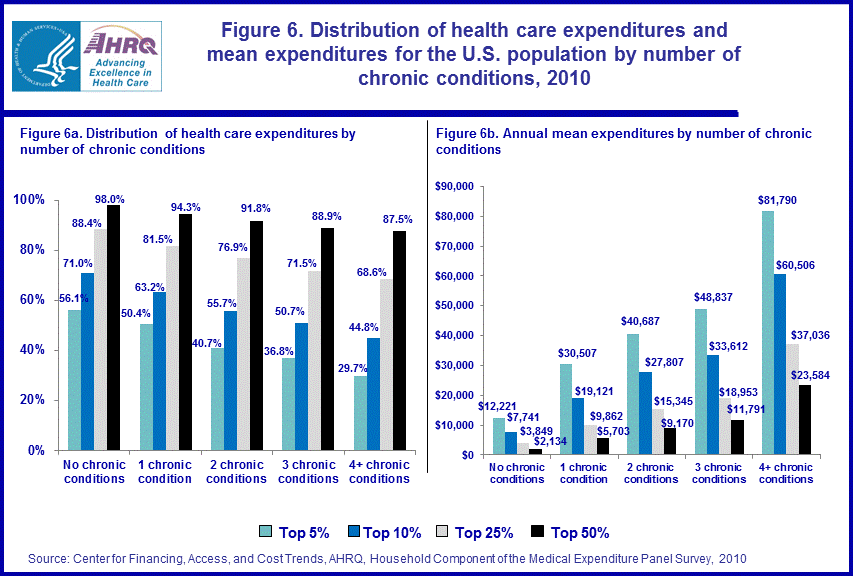
Chronic conditions
In 2010, the top 5 percent of individuals without a chronic condition accounted for 56.1 percent of health care expenditures for this subpopulation with an annual mean of $12,221 (figure 6). For persons with a single chronic condition, the top 5 percent comprised 50.4 percent of health care expenditures incurred by this subgroup, exhibiting a mean of $30,507. Among individuals with two chronic conditions, the top 5 percent accounted for 40.7 percent of health care expenditures for this subgroup, with a mean expenditure of $40,687. For those persons with three chronic conditions, the top 5 percent were associated with 36.8 percent of this group's overall health care expenses, exhibiting a mean of $48,837. The top 5 percent of individuals with four or more chronic conditions accounted for 29.7 percent of health care expenditures for this subpopulation with an annual mean of $81,790. Based on chronic condition status, persons with four or more chronic conditions had the lowest concentrated levels of health care expenditures and the highest annual mean expenses at the top quantiles of the expenditure distribution.
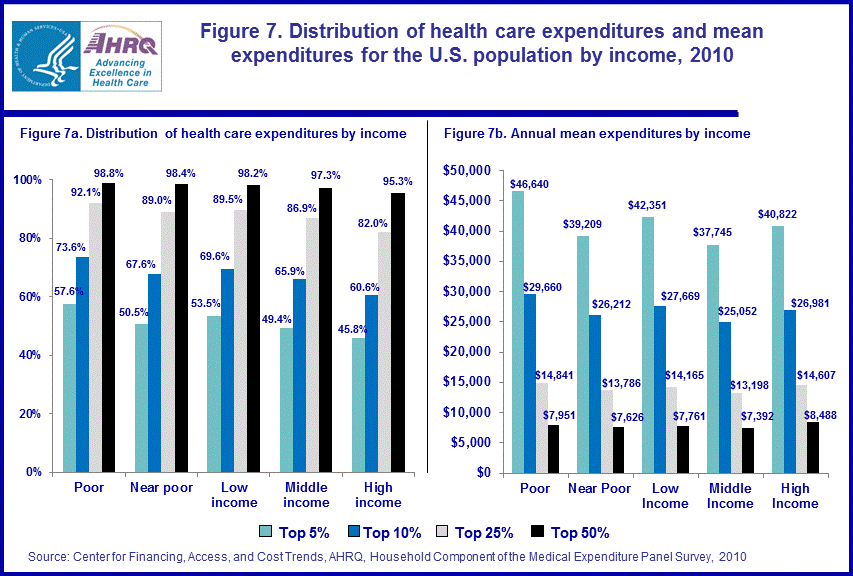
Income
In 2010, the top 5 percent of the poor accounted for 57.6 percent of health care expenditures incurred by this subgroup with an annual mean of $46,640 (figure 7). For near poor individuals, the top 5 percent were associated with 50.5 percent of health care expenses for this subpopulation, exhibiting a mean of $39,209. Among low income persons, the top 5 percent accounted for 53.5 percent of this groups overall health care expenditures, with an annual mean of $42,351. The top 5 percent of the middle income subgroup accounted for 49.4 percent of health care expenditures and an annual mean of $37,745. For those persons in the high income subgroup, the top 5 percent were associated with 45.8 percent of health care expenditures, exhibiting a mean of $40,822. Conditioned on income, the poor had a significantly more concentrated level of health care expenditures than their high income counterparts.
Data Source
The estimates shown in this Statistical Brief are drawn from analyses conducted by the MEPS staff from the following public use file: MEPS HC-138, 2010 Full Year Consolidated Data File.Definitions
ExpendituresMEPS-HC defines total expense as the sum of payments from all sources to hospitals, physicians, other health care providers (including dental care), and pharmacies for services reported by respondents in the MEPS-HC. Sources include direct payments from individuals and families, private insurance, Medicare, Medicaid, and miscellaneous other sources.
Age
Age was defined as age at the end of the year 2010.
Race/ethnicity
Classification by race and ethnicity was based on information reported for each family member. Respondents were asked if each family member's race was best described as American Indian, Alaska Native, Asian or Pacific Islander, black, white, or other. They also were asked if each family member's main national origin or ancestry was Puerto Rican; Cuban; Mexican, Mexicano, Mexican American, or Chicano; other Latin American; or other Spanish. All persons whose main national origin or ancestry was reported in one of these Hispanic groups, regardless of racial background, were classified as Hispanic. Since the Hispanic grouping can include black Hispanic, white Hispanic, Asian and Pacific Islanders Hispanic, and other Hispanic, the race categories of black, white, Asian and Pacific Islanders, and other only include non-Hispanics for the race/ethnicity classifications. MEPS respondents who reported other single or multiple races and were non-Hispanic were included in the other category. For this analysis, the following classification by race and ethnicity was used: Hispanic (of any race), non-Hispanic blacks single race, non-Hispanic whites single race and others, and non-Hispanic Asian and Pacific Islanders single race.
Health insurance status
Individuals under age 65 were classified into the following three insurance categories based on household responses to the health insurance status questions:
- Any private health insurance: Individuals who, at any time during the year, had insurance that provided coverage for hospital and physician care (other than Medicare, Medicaid, or other public hospital/physician coverage) were classified as having private insurance. Coverage by TRICARE (Armed Forces-related coverage) was also included as private health insurance. Insurance that provided coverage for a single service only, such as dental or vision coverage, was not included.
- Public coverage only: Individuals were considered to have public coverage only if they met both of the following criteria: 1) they were not covered by private insurance at any time during the year, and 2) they were covered by one of the following public programs at some point during the year: Medicare, Medicaid, or other public hospital/physician coverage.
- Uninsured: The uninsured were defined as people not covered by private hospital/physician insurance, Medicare, TRICARE, Medicaid, or other public hospital/physician programs at any time during the entire year or their period of eligibility for the survey.
The identification of sample persons with one or more chronic conditions was based on application of the AHRQ Healthcare Utilization Project Chronic Condition Indicator (CCI) (http://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/toolssoftware/chronic/chronic.jsp#overview) and Clinical Classification Software (http://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/toolssoftware/ccs/ccs.jsp) tools to the MEPS medical condition files. These files contain coded information on conditions reported by MEPS respondents as being associated with medical events, disability days and/or were bothersome during the year (http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_stats/download_data_files_detail.jsp?cboPufNumber=HC-120). The CCI categorizes all ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes as chronic or not chronic, with chronic conditions defined as those lasting 12 months or longer that also place limitations on self-care, independent living, and social interactions or result in the need for ongoing intervention with medical products, services, and special equipment (Perrin et al., 1993). The CCI algorithm originated with work by a physician panel that reviewed diagnosis codes appearing in MEPS data (Hwang et al., 2001).
Income
Sample persons were classified according to the total yearly income of their family. Within a household, all people related by blood, marriage, or adoption were considered to be a family. Poverty status categories are defined by the ratio of family income to the Federal income thresholds, which control for family size and age of the head of family. Poverty status was based on annual income in 2010.
Poverty status categories are defined as follows:
- Poor: Persons in families with income less than or equal to the poverty line; includes those who had negative income.
- Near poor: Persons in families with income over the poverty line through 125 percent of the poverty line.
- Low income: Persons in families with income over 125 percent through 200 percent of the poverty line.
- Middle income: Persons in families with income over 200 percent through 400 percent of the poverty line.
- High income: Persons in families with income over 400 percent of the poverty line.
About MEPS-HC
MEPS-HC is a nationally representative longitudinal survey that collects detailed information on health care utilization and expenditures, health insurance, and health status, as well as a wide variety of social, demographic, and economic characteristics for the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population. It is cosponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Center for Health Statistics.For more information about MEPS, call the MEPS information coordinator at AHRQ (301-427-1406) or visit the MEPS Web site at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/.
References
Cohen, J. Design and Methods of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 1. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0026. Rockville, MD. Agency for Healthcare Policy and Research, 1997. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/mr1/mr1.shtmlCohen, S. Design Strategies and Innovations in the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. Medical Care, July 2003: 41(7) Supplement: III-5–III-12.
Cohen, S. and Yu, W. The Concentration and Persistence in the Level of Health Expenditures over Time: Estimates for the U.S. Population, 2008–2009. Statistical Brief #354. December 2010. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st354/stat354.shtml
Cohen, S. and Yu, W. The Concentration and Persistence in the Level of Health Expenditures over Time: Estimates for the U.S. Population, 2006–2007. Statistical Brief #278. March 2010. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st278/stat278.shtml
Cohen, S. and Yu, W. The Persistence in the Level of Health Expenditures over Time: Estimates for the U.S. Population, 2004–2005. Statistical Brief #191. November 2007. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st191/stat191.shtml
Ezzati-Rice, T.M., Rohde, F., Greenblatt, J. Sample Design of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component, 1998–2007. Methodology Report No. 22. March 2008. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/mr22/mr22.shtml
Hwang, W., Weller, W., Ireys, H., Anderson, G. "Out-of-Pocket Medical Spending for Care of Chronic Conditions," Health Affairs, vol. 20, November/December 2001.
Perrin, E.C., Newacheck, P., Pless, I.B., Drotar, D., Gortmaker, S.L., Leventhal, J., Perrin, J.M., Stein, R.E., Walker, D.K., Weitzman, M. "Issues Involved in the Definition and Classification of Chronic Health Conditions," Pediatrics. 1993; 91: 787–793.
Yu, W. and Ezzati-Rice, T.M. Concentration of Health Care Expenditures in the U.S. Civilian Noninstitutionalized Population. Statistical Brief #81. May 2005. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st81/stat81.shtml
Suggested Citation
Cohen, S. and Uberoi, N. Differentials in the Concentration in the Level of Health Expenditures across Population Subgroups in the U.S., 2010. Statistical Brief #421. August 2013. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st421/stat421.shtmlAHRQ welcomes questions and comments from readers of this publication who are interested in obtaining more information about access, cost, use, financing, and quality of health care in the United States. We also invite you to tell us how you are using this Statistical Brief and other MEPS data and tools and to share suggestions on how MEPS products might be enhanced to further meet your needs. Please email us at MEPSProjectDirector@ahrq.hhs.gov or send a letter to the address below:
Steven B. Cohen, PhD, Director
Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
540 Gaither Road
Rockville, MD 20850
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||