Methodology Report #11: Sample design of the 1997 MEPS Household Component
by Steven B. Cohen, Ph.D., Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
Select for more information on
Health Care Information and Electronic Ordering Through the AHRQ Web Site.
Abstract
The Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) is the third in a series of nationally representative surveys of medical care use and expenditures sponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). MEPS comprises four component surveys. The Household Component (HC) produces national and regional estimates of the health care use, expenditures, sources of payment, and insurance coverage of the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population. This report gives a detailed description of the 1997 HC. (The 1996 HC was described in an earlier report.) The survey's overlapping panel design is emphasized. The sample selection scheme implemented to oversample selected subgroups--functionally impaired adults, children with activity limitations, working-age adults predicted to incur high medical expenditures, and persons predicted to have low family income--is explained. The report also includes a summary of sample size specifications, survey response rates, and targeted precision levels for national population estimates and health care expenditure estimates for policy-relevant subgroups.
Select for information on The Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS).
Introduction
The Household Component of the 1997 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) was designed to produce national and regional estimates of the health care use, expenditures, sources of payment, and insurance coverage of the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population. MEPS includes surveys of medical providers, employers, and other health insurance providers to supplement the data provided by household respondents. The MEPS design permits both person-based and family-level estimates. Government agencies, legislative bodies, and health professionals need comprehensive national estimates to use in formulating and analyzing national health policies. The scope and depth of this data collection effort reflect this need.
MEPS collects data on the specific health services that Americans use, how frequently they use them, the cost of these services, and how they are paid for, as well as data on the cost, scope, and breadth of private health insurance held by and available to the U.S. population. MEPS is unparalleled for the degree of detail in its data. In addition, through MEPS, the medical expenditures and health insurance data of survey respondents can be linked to other characteristics, such as demographic variables, employment status, economic status, health status, and use of health services. Moreover, MEPS is the only national survey that provides a foundation for estimating the impact of changes in sources of payment for health services and insurance coverage on different economic groups or special populations of interest, such as the poor, the elderly, veterans, the uninsured, and racial and ethnic minorities.
MEPS is cosponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), formerly called the Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, and the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS).
MEPS reflects the first stage of implementation of the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) Survey Integration Plan, which provides directives targeted to improve the analytic capacity of programs, fill major data gaps, and establish a framework in which DHHS data activities are streamlined and rationalized. Through this effort, specifically through a linkage to the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), MEPS has achieved a number of significant design improvements and analytic enhancements (Arnett, Hunter, Cohen, et al., 1996; J. Cohen, 1997; S. Cohen, 1997; Hunter et al., 1995).
In this report, the sample design of the Household Component of the 1997 MEPS is described in detail. Particular emphasis is given to the overlapping panel design that characterizes the survey. Attention is given to the sample selection scheme implemented to facilitate an oversample of functionally impaired adults, children with activity limitations, working-age adults predicted to incur high medical expenditures, and individuals predicted to have incomes less than 200 percent of the poverty level. The report also includes a summary of sample size specifications, survey response rates, and targeted precision levels for national population estimates and health care expenditure estimates for policy-relevant population subgroups.
Return To Top
Sample Design
To fill major data gaps identified by DHHS, MEPS was specified as a continuous survey. The 1997 MEPS Household Component had an overlapping panel design. Health care data are collected for each new MEPS sample (panel) to cover a 2-year period, with the first two MEPS panels spanning 1996-97 and 1997-98, respectively. To produce health care estimates for calendar year 1997, the data are pooled across the two distinct nationally representative MEPS samples. More specifically, the 1997 design combines the second year of the first MEPS panel and the first year of the second MEPS panel. The National Health Interview Survey serves as the sampling frame for MEPS. NHIS is an ongoing annual household survey of approximately 42,000 households (109,000 individuals) conducted by NCHS to obtain national estimates on health care use, health conditions, health status, insurance coverage, and access to care for the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population. In addition to the cost savings achieved by using NHIS instead of an independent national screener sample as the MEPS sampling frame, this design feature enhances the analytic capacity of the resultant survey data. Use of the NHIS data in concert with the MEPS data provides a capacity for longitudinal analyses not available in the prior national medical expenditure surveys sponsored by AHRQ (S. Cohen, 1996).
Return To Top
The analytical goals of the 1997 MEPS and budget constraints required that the sample design for the Household Component meet the following requirements.
- The full series of interviews for the pooled MEPS samples covering calendar year 1997 should be completed in approximately 13,500 households.
- The sample should be spread over 195 separate areas to represent the civilian noninstitutionalized population of the 50 States and the District of Columbia.
- The sample should yield approximately unbiased national estimates of the health care parameters under study and estimates of adequate precision for the four Census regions.
- The sample should meet predesignated precision specifications for the following population subgroups of analytical interest: blacks, Hispanics, the functionally impaired, children with activity limitations, individuals predicted to have high medical expenditures, and persons predicted to have family income less than 200 percent of the poverty level.
The 1996 MEPS Household Component sample was selected from households that responded to the 1995 NHIS. NHIS is designed to permit the selection of nationally representative subsamples from any one of four panels. Furthermore, any individual panel or combination of panels will provide a nationally representative sample of households. Each NHIS panel subsample for a given quarter of a calendar year is nationally representative. The 1996 MEPS household sample was selected from two of the four 1995 NHIS panels during the second and third quarters of 1995. Consequently, the MEPS sample is an approximately one-quarter subsample of the overall 1995 NHIS sample.
Return To Top
The complete 1995 NHIS sample (panels 1-4) consists of 358 primary sampling units, or PSUs (which are counties or groups of contiguous counties), and approximately 42,000 responding households. The NHIS sample design is characterized by a stratified multistage area probability design, with the sample PSUs stratified by geographic area (Census region and State), metropolitan status, and sociodemographic measures (Judkins, Marker, and Waksberg, 1994). Within sample PSUs, a sample of blocks (segments) was selected after the blocks were stratified by measures of minority population density that allowed for an oversample of areas with high population concentrations of blacks and Hispanics. A nationally representative sample of approximately 71,000 addresses within sampled blocks was selected and targeted for further screening to facilitate an oversample of blacks and Hispanics as part of the 1995 NHIS interview.
The 1995 NHIS subsample selected for the 1996 MEPS consists of 195 PSUs. In the two targeted quarters of 1995, these PSUs included 1,675 sample segments (second-stage sampling units) and 10,597 responding households. This NHIS sample reflects oversampling of households with Hispanics and blacks at a ratio of approximately 2.0:1 for Hispanics and 1.5:1 for blacks. This 1996 MEPS sample constitutes a panel that was surveyed to collect annual data for 2 consecutive years (S. Cohen, 1997).
A new 1997 MEPS panel sample was selected as a nationally representative subsample of households responding to the 1996 NHIS. More specifically, this 1997 MEPS sample was selected from the same two NHIS panels used for the 1996 MEPS, using a nationally representative subsample of the 1996 NHIS that also reflected an oversample of Hispanics and blacks at the same ratios as in the 1995 NHIS (Hispanics, 2.0:1; blacks, 1.5:1).
It should be noted that in 1996, NHIS was undergoing a transition from paper-and-pencil survey administration to computer-assisted personal interviewing. The subsample of NHIS reserved for the 1997 MEPS sample selection retained the paper-and-pencil survey administration mode to allow for smoother integration of the two national surveys.
The new 1997 MEPS sample was selected from the first three quarters of the 1996 NHIS subsample within the two panels reserved for MEPS. This NHIS nationally representative subsample was concentrated within the same 195 PSUs selected for the 1996 MEPS household sample and consisted of 14,706 responding NHIS dwelling units. A nationally representative subsample of 6,300 NHIS responding dwelling units (consisting of 6,480 reporting units) was selected to serve as the new 1997 MEPS sample. In addition to retaining the oversample of minorities that characterized the NHIS sample design, the 1997 MEPS was designed to oversample the following policy-relevant subgroups: functionally impaired adults, children limited in activities, adults predicted to have high medical expenditures, and persons predicted to have family income less than 200 percent of the poverty level. The new 1997 MEPS panel was designed to collect annual data for 2 consecutive years. Consequently, the full 1997 MEPS Household Component sample consists of the first year of the 1997 MEPS panel pooled with the second year of the 1996 MEPS sample.
Return To Top
Sampling Unit Definitions and Eligibility Criteria
The definitions for dwelling units and group quarters in the MEPS Household Component are generally consistent with the definitions employed for NHIS. More specifically, a dwelling unit is a house, apartment, group of rooms, or single room occupied as separate civilian noninstitutional living quarters or vacant but intended for occupancy as separate living quarters. Group quarters consist of a single civilian noninstitutional dwelling or structure in which nine or more unrelated persons reside and where inhabitants are not considered a part of any other dwelling unit. A reporting unit is a person or group of persons in the sampled dwelling unit who are related by blood, marriage, adoption, or other family associations and are to be interviewed at the same time in MEPS. Examples of discrete reporting units follow.
- A married daughter and her husband living with her parents in the same dwelling are considered one reporting unit.
- A husband and wife and their unmarried daughter, age 18, who is living away from home at college constitute one family, but two reporting units.
- Three unrelated persons living in the same dwelling unit would be three reporting units.
College students under 24 years of age who usually live in the sampled household but are currently living away from home and going to school are treated as separate reporting units for the purpose of data collection.
Return To Top
The new 1997 MEPS sample consisted of households (dwelling units) that responded to the 1996 NHIS in the two panels reserved for MEPS, with the basic unit of analysis defined as the person. This mirrored the 1996 MEPS design. Analysis is planned using both the individual and the family as units. Through the reenumeration section of the Round 1 questionnaire for each MEPS panel, the status of each individual sampled at the time of the NHIS interview is classified as "key" or "non-key," "in-scope" or "out-of-scope," and "eligible" or "ineligible" for MEPS data collection. For an individual to be in scope and eligible for person-level estimates derived from the MEPS household survey, he or she must be a member of the civilian noninstitutionalized population for some period of time in the calendar year of analytic interest. Because a person's eligibility for the survey may change after the NHIS interview, sampling renumeration takes place in each subsequent reinterview for persons in all households selected into the core survey. The keyness, in-scope, and eligibility indicators, together, define the target sample to be used for person-level national estimates. Only persons who are key, in scope, and eligible for data collection are considered in the derivation of person-level national estimates from MEPS.
Return To Top
Key Persons
Key survey participants are defined as all civilian noninstitutionalized individuals who resided in households that responded to the nationally representative NHIS subsample reserved for MEPS (e.g., 6,300 households from the 1996 NHIS), with the exception of college students interviewed at dormitories. Members of the Armed Forces who are on full-time active duty are also defined as key persons if they reside in responding NHIS households that include other family members who are civilian noninstitutionalized individuals. However, they are out of scope for person-level estimates derived from the survey.
All individuals who join the NHIS reporting units that define the 1997 MEPS household sample (in Round 1 or later MEPS rounds) and were not available for selection during the time of the NHIS interview are also considered key persons. These include newborn babies, individuals who were in an institution or outside the country, and military personnel previously residing on military bases.
College students under 24 years of age interviewed at dormitories in the 1996 NHIS are not included in the 1997 MEPS sample, since this population subgroup will be targeted through their parents during the MEPS interview. The same rule applied to the 1996 MEPS sample selected from the 1995 NHIS. Furthermore, any unmarried college student under 24 years of age who responded to the 1996 NHIS interview while living away at school (not in a dormitory) is excluded from the sample if it is determined in the MEPS Round 1 interview that the person is unmarried, under 24 years of age, and a student who has parents living elsewhere and who resides at his or her current housing only during the school year. If, on the other hand, the person's status at the time of the MEPS Round 1 interview is no longer that of an unmarried student under 24 years of age living away from home, then the person is retained as a key person.
Additionally, during the MEPS Round 1 interview with NHIS sample respondents, a determination is made whether there are any related college students under 24 years of age who usually live in the sampled household but are currently living away from home and going to school. These college students are considered key persons and are identified and interviewed at their college address but linked to the sampled household for family analyses. Some of these college students will have been identified as living in the sampled household at the time of the 1995 NHIS interview. The remainder are identified at the time of the MEPS Round 1 interview.
Return To Top
Non-Key Persons
Persons who were not living in the original sampled dwelling unit at the time of the relevant NHIS interview and who had a non-zero probability of selection for that survey are considered non-key. (The 1996 NHIS interview is the relevant interview for the 1997 MEPS sample; the 1995 NHIS interview is the relevant interview for the 1996 MEPS sample.) If such persons happen to be living in sampled households in Round 1 or later rounds, MEPS data are collected for the period of time they are part of the sampled unit to permit family analyses. Non-key persons who leave any sampled household are not recontacted for subsequent interviews. Non-key individuals are not part of the target sample used to obtain person-level national estimates.
A key person from the NHIS sampled household selected for MEPS may move out in Round 1 or later rounds and join or create another family. Data on all members of this new household who are related by blood, marriage, adoption, or foster care to the person from the NHIS sampled household are obtained from the time that the sampled person joined the household. Keyness status (key or non-key) is determined for these new members based on their probability of selection for NHIS. If it is positive, they are classified as non-key. Similarly, data are collected in Round 1 and later rounds on all related persons who join NHIS sampled households selected into MEPS.
Persons in NHIS sampled households selected in MEPS may subsequently enter an institution, thus no longer qualifying as a member of the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population. For those who enter nursing homes, data collection continues during the nursing home stay. For those who enter other institutions, data collection is suspended while they are institutionalized, but their whereabouts are monitored during the field period. If they rejoin the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population, HC data collection resumes. (This is also the procedure for those entering military service away from home or moving out of the United States.)
Return To Top
MEPS Data Collection Eligibility
In order for a MEPS reporting unit to be eligible for data collection, it must include at least one individual who is key and in scope for some period of time during the reference period for a given round of data collection. If this condition holds, the persons who are key and in scope and all other individuals who are members of the reporting unit (living together and related by blood, marriage, adoption, or other family associations) are eligible for data collection in a given round of MEPS.
Return To Top
Sample Selection for 1997 MEPS Panel
Sample Size Targets and Precision Requirements
An overall precision requirement for the 1997 MEPS was the achievement of an average design effect of 1.7 for survey estimates of the policy-relevant population subgroups. The precision requirements for the 1997 HC are presented in Table 1. They are presented in terms of relative standard errors for the following survey estimates.
- A 20-percent population estimate at the person level for each specified domain (e.g., a percent population estimate such as the rate of uninsured for the population under age 65).
- Mean estimates of the following measures of health care utilization and expenditures at the person level (precision requirement specified as an average relative standard error):
-- Total health expenditures.
-- Utilization and expenditure estimates for inpatient hospital stays.
-- Utilization and expenditure estimates for ambulatory physician visits.
-- Utilization and expenditure estimates for dental visits.
-- Utilization and expenditure estimates for prescribed medicines.
Return To Top
The 1997 MEPS person-level precision requirements are specified for estimates derived from individuals who are considered full-year respondents (individuals with responses for their entire period of eligibility in 1997). Consequently, in the determination of sample sizes necessary to achieve the precision requirements, additional adjustments must be made for survey nonresponse to obtain the targeted number of full-year respondents. Approximately 34,000 persons completing the three core MEPS household interviews to cover calendar year 1997 (Rounds 1-3 for the new 1997 MEPS sample; Rounds 3-5 for the carryover 1996 MEPS sample) were targeted for sample selection to achieve the desired precision specifications for national population estimates. Assuming 2.5 persons per original sampled reporting unit, it was estimated that approximately 13,600 families were needed to complete the three rounds in 1997 to meet precision specifications. Table 2 indicates the number of persons in the various subpopulations of interest needed to satisfy the survey precision requirements for the pooled 1996 and 1997 MEPS samples to permit 1997 population estimates.
Precision requirements for the 1997 MEPS HC were stated in terms of national estimates at the person level. To meet these requirements, the survey must include a minimum number of persons in each domain of interest. The prior 1996 MEPS sample was also selected to satisfy distinct precision requirements at the person level for overall population estimates and for subgroup analyses of blacks and Hispanics for calendar year 1996 (S. Cohen, 1997). To satisfy precision requirements for the pooled 1997 MEPS sample, the Panel 1 MEPS yields were derived and projected into 1997. Additional sample sizes necessary to satisfy the precision requirements for the analytical domains were determined (after adjusting for estimated survey nonresponse). These projected yields informed the specification of the final sample selection rates for the new 1997 Panel 2 MEPS sample.
Return To Top
For both the 1996 and 1997 MEPS, the unit of interviewing and subsampling was the household. To facilitate the sample selection of the new 1997 MEPS sample, the 1996 NHIS households were selected on the basis of the characteristics of the persons they included. There were seven sample domains of interest. An NHIS dwelling unit was assigned to one or more sample domains based on having at least one household member with the characteristic of interest:
- Adults (age 18 and over) with functional impairments--at least one activity of daily living (ADL) for which assistance is needed.
- Children (under age 18) with limitations in activity.
- Individuals 18-64 years old with predicted high medical expenditures (predicted probability of .4 or more, using the MEPS prediction model to identify likely high-expenditure individuals).
- Individuals with family incomes likely to be below 200 percent of poverty level (predicted probability of .3 or more, using the MEPS prediction model to identify low-income households).
- Adults with other impairments--ages 18-69, at least one instrumental activity of daily living (IADL) and unable to work; age 70 and over, at least one IADL.
- Elderly individuals (age 65 and over).
- All remaining individuals.
These sampling domains are not mutually exclusive, but their order reflects the hierarchy of their sampling priority. For purposes of sampling, dwelling units containing members having these characteristics were hierarchically classified to form seven mutually exclusive and exhaustive sampling strata (DiGaetano, 1994).
Return To Top
Using Predictive Models for Domain Assignments
Poverty Status Model
Since a reporting unit's poverty status classification in 1997 was unknown at the time the 1996 NHIS interview was administered, a prediction model was used to determine whether a household was to be oversampled. More specifically, a logistic regression model was developed to estimate the probability that a reporting unit would have a family income less than 1.25 times the poverty level in a subsequent year, based on the poverty status classification and other predictive measures obtained during the NHIS interview. Households with predicted probabilities above a certain threshold value were to be oversampled. In addition to facilitating an oversample of individuals with family income less than 125 percent of the poverty level, use of this prediction model was expected to facilitate an oversample of individuals with family income less than 200 percent of the poverty level. Consequently, all reporting units with a predicted probability of .3 or greater were classified as households predicted to have family income less than 200 percent of the poverty level.
Data from the 1987 National Medical Expenditure Survey (NMES) were examined using a predicted probability of .3 or greater (derived from the logistic regression prediction model) as the criterion to target reporting units most likely to have members with family income less than 200 percent of the poverty level in 1996. Based on an evaluation of the model's performance at the reporting-unit level, the following results were observed.
- Among the 19.5 percent of reporting units predicted to have members with family income less than 200 percent of the poverty level, the expected prediction rate for true positives (family income less than 200 percent of the poverty level) is 83.1 percent.
- Among the 80.5 percent of reporting units predicted to have family income at or above 200 percent of the poverty level, the expected prediction rate for false negatives is 17.1 percent.
- Among the 30 percent of reporting units with family income less than 200 percent of the poverty level, 54 percent had been predicted to have members with family income less than 200 percent of the poverty level. Alternatively, among the 70 percent of reporting units with family income at or above 200 percent of the poverty level, 95.3 percent had been predicted to have members with family income above 200 percent of the poverty level.
Return To Top
The logistic regression model that was adopted was specified at the reporting unit level and required data on the following measures obtained in the NHIS interview (Moeller and Mathiowetz, 1994):
- Age of reference person.
- Home ownership.
- Reporting unit (RU) size.
- Whether children of specific ages (under 6, 6-15) are present in the RU.
- Whether someone in the RU other than the reference person is at least 65 years of age.
- Health status of reference person.
- Race/ethnicity of reference person.
- Census Division.
- Metropolitan statistical area (MSA) status of PSU.
- Education of reference person.
- Marital status and sex of reference person.
- Whether reference person or spouse was employed in the previous 3 months.
- Whether the family income of the reporting unit was less than 1.25 times the poverty level.
- Whether anyone in the RU was covered by Medicaid.
Return To Top
High-Expenditure Prediction Model
Among the sample domains to be oversampled in the main survey are individuals ages 18-64 who are predicted to be likely to incur high medical expenditures. An individual's medical care expenditures in a future year were unknown when the 1996 NHIS interview was administered. Therefore, a prediction model based on NMES data was used to determine whether a household should be oversampled as part of the high-medical-expenditures group because one or more of the family members were expected to incur high medical expenditures in the subsequent year. More specifically, a logistic regression model was developed to estimate the expected probability that an individual ages 18-64 will incur high medical expenditures (top 15 percent of the health expenditure distribution) in a subsequent year based on predictive measures obtained during the NHIS interview. Households with at least one person with a predicted probability above a certain threshold value were oversampled. The group was restricted to individuals ages 18-64, since persons 65 and over who were functionally impaired were separately targeted to be oversampled. For purposes of sampling, all individuals with a predicted probability of .4 or greater were classified as likely to incur high medical expenditures in the subsequent year. This threshold was selected as the value that was expected to best limit prediction errors.
The logistic regression model under consideration was specified at the person level and requires data on the following measures obtained in the NHIS interview (Moeller and Mathiowetz, 1994):
- Sex.
- Health status.
- Marital status.
- Poverty status.
- Whether the person lives alone.
- Age.
- Whether the person's health keeps him or her from working at a job, doing work around the house, or going to school.
- Whether the person is unable to do certain kinds or amounts of work, housework, or schoolwork because of health.
- The number of visits to a medical doctor or other medical care provider the person has had during the last 6 months.
- The number of times prescribed medicines were purchased or obtained for the person's use in the last 6 months. (An imputation strategy was used to derive this measure, since data were unavailable from the 1996 NHIS.)
- Census Division.
- MSA status of PSU.
Return To Top
The results listed below were observed based on an evaluation of the model's performance at the individual level, using data from NMES. A predicted probability of .4 or greater (derived from the logistic regression prediction model) was used as the criterion to target individuals who are age 18-64 and considered likely to incur high medical expenditures in the subsequent year.
- The expected prediction rate for true positives (computed at the RU level) is 37.7 percent among the 14.1 percent of individuals in RUs with members age 18-64 who are predicted to incur high medical expenditures in the subsequent year. It should be noted that when the evaluation is restricted to the subset of individuals predicted to incur high medical expenditures (8.1 percent), the expected prediction rate for true positives is 65.3 percent (computed at the person level).
- The expected prediction rate for false negatives (computed at the RU level) is 11.3 percent among the 85.9 percent of individuals in RUs with members age 18-64 predicted not to incur high medical expenditures in the subsequent year.
Return To Top
NHIS Sample Composition
In order to provide the 1997 MEPS sample to Westat and the National Opinion Research Center (the MEPS data collection organizations) in the timeframe specified to field the survey in February 1997, it was necessary to restrict the sample selection to the nationally representative NHIS subsample for the first three quarters of 1996 rather than the entire year. This NHIS sample of 14,706 responding dwelling units was then classified into seven mutually exclusive and exhaustive sampling classes based on the demographic characteristic of its "highest priority" individual. This was the household member requiring the highest sampling rate to meet sample size targets.
The sampling classes presented in Table 3 are arranged in order of priority. The table provides a distribution of the 14,706 responding NHIS dwelling units according to these sampling classes, the MEPS sampling rates, and the resultant sample of dwelling units selected for the 1997 MEPS. It should be noted that a dwelling unit with a higher order sampling classification may include members with a characteristic of interest that defines a lower sampling classification. More specifically, a dwelling unit with a sampling classification of 1, which indicates that the dwelling unit includes an adult (age 18 and over) with functional impairments (at least one ADL requiring personal assistance), may also include a member with any of the other characteristics targeted for oversampling: children (under age 18) with limitations in activity; individuals 18-64 years old with predicted high medical expenditures; individuals with family incomes likely to be below 200 percent of poverty level; adults with other impairments (age 18-69, at least one IADL, and unable to work; or age 70 and over and at least one IADL). However, dwelling units assigned to sampling classes with lower priority do not include members with a characteristic that defines a higher order classification.
Return To Top
For sampling purposes, a person was classified as having at least one ADL requiring personal assistance if there was an affirmative answer to the following question in the 1996 NHIS: "Because of any impairment or health problem, does ___ need the help of other persons with personal care needs, such as eating, bathing, dressing, or getting around this home?" Similarly, a person was classified as having at least one IADL requiring assistance if there was an affirmative answer to the following question in the 1996 NHIS: "Because of any impairment or health problem, does ___ need the help of others in handling routine needs, such as everyday household chores, doing necessary business, shopping, or getting around for other purposes?"
Rates of selection were specified to satisfy sample size targets for the pooled 1997 sample for individuals with specific characteristics. All NHIS dwelling units assigned to the first three sampling classes ordered by sampling priority--adults with functional impairments (at least one ADL requiring personal assistance), children (under age 18) with limitations in activity, and individuals 18-64 years old predicted to incur high levels of medical expenditures--were selected with certainty for inclusion in the 1997 MEPS sample. Dwelling units associated with the next highest priority sampling classes--individuals with family incomes predicted to be below 200 percent of poverty level and adults with other impairments (at least one IADL)--were then selected at a sampling rate of 0.6. All remaining dwelling units associated with the remaining sampling classes were selected with a rate of 0.3.
Return To Top
Prior to sample selection, dwelling units within each of the sampling classes were hierarchically sorted by the following measures:
- Quarter of calendar year 1996.
- Week within applicable calendar quarter of 1996.
- Census Division.
- State.
- MSA classification.
- NHIS primary sampling unit.
- NHIS segment within primary sampling unit.
- Minority classification of dwelling unit (Hispanic, black non-Hispanic, other).
A random systematic sample of dwelling units was then selected from each sampling class, using the specified sample selection rate (Table 3). Table 4 shows the distribution of the 15,067 responding NHIS reporting units within the dwelling units according to these sampling classes. It also shows the resultant sample of 6,480 reporting units selected for the 1997 MEPS. Table 5 shows the distribution of the 38,418 responding NHIS individuals within the dwelling units assigned to the hierarchically defined sampling classes, in addition to the subsample of 17,063 individuals selected for the 1997 MEPS sample. Since individuals may be classified in more than one category based on the sampling domains under consideration, the sample yields for the 1997 MEPS sample, allowing for multiple classifications, are presented in Table 6. (Note that the sample distributions presented in Tables 3-6 are confined to the new panel of MEPS introduced in 1997.)
Return To Top
Procedures for Data Collection
The preliminary contact with households responding to NHIS and subsampled as part of a MEPS panel is described in S. Cohen (1997). Procedures in the rounds of data collection are described below.
Five interviews are conducted with each NHIS panel selected for MEPS at 4- to 5-month intervals over an approximately 24-month field period. The first three rounds (Panel 1, Rounds 1-3) define the 1996 MEPS Household Component and collect the main body of annual use and expenditure data for calendar year 1996. Rounds 3-5 of the 1996 MEPS panel (Panel 1, Rounds 3-5) are combined with Rounds 1-3 of the 1997 MEPS panel (Panel 2, Rounds 1-3) to yield the sample base for the 1997 MEPS Household Component and the source of annual estimates for that calendar year. All interviews are conducted in person through a computer-assisted personal interview (CAPI). Round 1 asks about the period from January 1 of the MEPS year to the date of that interview, Round 2 asks about the time from the Round 1 interview through the date of the Round 2 interview, and Round 3 asks about the time from the date of the Round 2 interview through the date of the Round 3 interview in 1997.
Questionnaires for these field rounds parallel those used in the 1987 NMES but include some modifications implemented for a 1992 feasibility study and further changes stemming from the feasibility study and a MEPS pretest. The instruments contain items that are asked once in the life of the study, items that are asked repeatedly in each round, and items that are updated in later rounds. Questions asked only once include basic sociodemographic characteristics. Core questions asked repeatedly include health status, health insurance coverage, employment status, days of restricted activity due to health problems, medical use, hospital admissions, and purchase of medicines. For each health encounter identified, data are obtained on the nature of health conditions, characteristics of the provider, services provided, associated charges, and sources and amounts of payment.
Permission forms for medical providers are collected in the field. A sample of medical providers identified by MEPS respondents is contacted in the survey of medical providers--the MEPS Medical Provider Component, or MPC--to verify and supplement information provided by the family respondent in the household interview. Employers and other health insurance providers are contacted in the survey of health insurance providers--the MEPS Insurance Component, or IC--to collect other information on insurance characteristics that household respondents would not typically know.
Return To Top
Sample Yields and Survey Response Rates
Data to cover a 2-year period are collected for each MEPS panel. The first two MEPS panels spanned 1996-97 and 1997-98, respectively. This section provides a summary of the sample yields for deriving national person-based estimates from the 1997 MEPS: both point-in-time estimates (first part of calendar year 1997) and annual estimates. Attention will first be given to the point-in-time estimation capacity of the survey, followed by an emphasis on the sample yields for producing calendar year health care estimates.
Point-in-Time Estimates for First Part of 1997
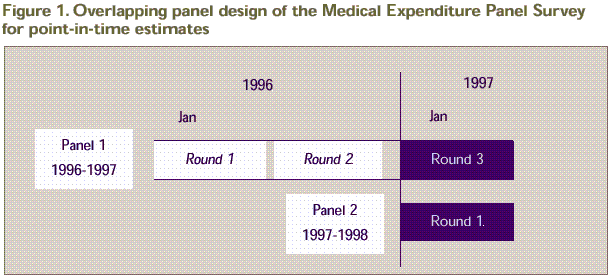
To produce point-in-time health care estimates for the first part of 1997 based on the MEPS sample design, data need to be pooled from the first two MEPS national samples, with data covering approximately the first half of calendar year 1997. More specifically, data from the 1997 portion of the third round of data collection for the MEPS Panel 1 sample are pooled with data from the first round of data collection for the MEPS Panel 2 sample (Figure 1). This feature of the MEPS design supports the derivation of health insurance coverage estimates covering the first half of calendar year 1997.
Return To Top
Panel 1
Initially, in 1996, the MEPS Panel 1 sample consisted of 10,639 households, a nationally representative subsample of the households responding to the 1995 National Health Interview Survey. The 1995 NHIS sampled households with Hispanic members and households with black members at approximately 2.0 and 1.5 times the rate of other households, respectively. These oversampling rates are also reflected in the MEPS sample of households. The 1995 NHIS response rate for MEPS-eligible households was 94 percent. Of 10,639 responding NHIS dwelling units eligible for MEPS, 99.6 percent were identified with enough information to allow MEPS data collection. Of the 11,424 eligible reporting units targeted for interviews in Round 1, 9,488 (83.1 percent) responded. Overall, the joint (NHIS and MEPS Round 1) response rate for the 1996 MEPS household survey was 77.7 percent (.939 x .996 x .831). Conditioned on participation in MEPS, 90.33 percent of the sample participants provided data for their entire period of eligibility in 1996 and through the early part of 1997 (Round 3). Consequently, the overall MEPS Panel 1 response rate at the end of Round 3 (which collects data for the first part of 1997) was 70.2 percent, reflecting response to the 1995 NHIS interview and the MEPS interviews for Rounds 1-3 (S. Cohen, 1997). Overall, the Round 3 MEPS Panel 1 sample consisted of 21,411 survey participants. Panel 2
The 1997 MEPS Panel 2 sample initially consisted of 6,300 eligible NHIS dwelling units serving as a nationally representative subsample of the households responding to NHIS. Like Panel 1, the Panel 2 sample reflects the oversampling of Hispanic and black households in NHIS. However, the sample allocation for Panel 2 of MEPS differed from that for Panel 1 because of the additional oversampling of targeted policy-relevant groups. The 1996 NHIS response rate achieved for MEPS-eligible households was 93.8 percent. In Round 1, 6,196 eligible dwelling units were targeted for interviews, and 5,182 dwelling units (consisting of 5,536 responding reporting units) responded, for a rate of .831. The overall MEPS Panel 2 response rate at the end of Round 1 (when data were collected for the first part of 1997) was 77.9 percent. This overall rate reflects response to both the 1996 NHIS interview and the MEPS Round 1 interview and consists of a total sample of 14,505 survey participants.
Return To Top
Combined Response Rates for Point-in-Time Estimates
Each panel was given equal weight in the development of sampling weights to produce national estimates. Therefore, a pooled response rate for the survey respondents in this data set can be obtained by taking an average of the panel-specific response rates. This pooled response rate for the combined panels is 74.1 percent, consisting of a total of 35,916 survey participants within 14,147 family and single-person analytical units in MEPS. The weighted MEPS population estimate for the civilian noninstitutionalized population as of March 1997 was 265,926,692, based on poststratification to population estimates produced from the March 1997 Current Population Survey. The weighted estimate of the number of family units (family and single-person units) as of March 1997 was 112,106,153, based on data from the same source.
Using data from the 1997 MEPS Panel 1 Round 3/Panel 2 Round 1 public use file (MEPS HC-005), estimates of the proportion of the population that was uninsured were produced for the overall population and for a representative set of analytical domains, which included several of the population subgroups targeted for oversampling (shown in Table 7). The low-income and high-expenditure population subgroups were not included in this analysis because 1997 MEPS full-year data were not available at the time this report was prepared. Table 7 includes sample yields for the full 1997 MEPS sample, in addition to the level of precision achieved for the survey estimates as measured by the relative standard error and the respective survey design effects.
Return To Top
The 1997 MEPS point-in-time sample includes an oversample of minorities, with 7,960 Hispanic sample participants and 5,301 black non-Hispanic sample participants, which reflects the oversampling rates for minorities inherent in the NHIS sample (Hispanics, 2.0:1; blacks, 1.5:1). Alternatively, the overall sample yield for the elderly, consisting of 4,104 sample participants and 11.4 percent of the sample, is quite consistent with their proportional representation in the population, as anticipated by the MEPS sample selection rates applied to the eligible NHIS sample. As can be observed in Table 7, the sample yields achieved for the pooled 1997 MEPS point-in-time sample were consistent with targeted sample yields for the full-year 1997 MEPS after adjusting for survey nonresponse. After factoring in the anticipated sample size reductions attributable to survey attrition for the point-in-time 1997 estimates of the uninsured, it is evident that precision levels for the full-year 1997 MEPS were largely realized when considering comparable population estimates. It should be noted that some of the estimates of the uninsured obtained from the 1997 MEPS were less than 20 percent (the value used to set precision targets). This partially explains some of the observed differentials from the precision targets, which were also specified as average relative standard errors.
More specifically, there were 638 adults in the MEPS sample who, because of an impairment or a physical or mental problem, received help or supervision with the ADLs of bathing, dressing, or getting around the house (Table 7). This subset of ADLs is less inclusive than the set of ADLs considered in NHIS for oversampling purposes and indicates the lower bound in terms of sample size yields for this target population. In addition, a design effect of 1.8 was achieved for the survey estimate of the uninsured for this policy-relevant population subgroup. There were also 1,131 adults in the MEPS sample who, because of an impairment or a physical or mental problem, received help or supervision with IADLs, which were using the telephone, paying bills, taking medications, preparing light meals, doing laundry, and going shopping (Table 7). This sample yield is convergent with sample size targets for this policy-relevant population subgroup. A survey design effect of 1.8 was achieved for the associated survey estimate.
An examination of the efficacy of the sample design in achieving design goals for children with physical limitations, households with low incomes, and individuals with high levels of medical expenditures is planned. The results will inform future oversampling efforts in MEPS for these target population subgroups. A similar analysis will be conducted to examine the level of precision realized for survey estimates of health care utilization and expenditures.
Return To Top
Annual Estimates for 1997
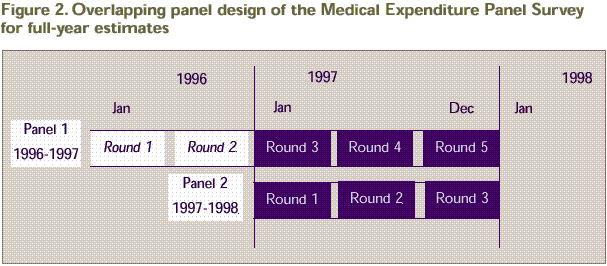
In order to produce annual health care estimates for calendar year 1997 based on the full MEPS sample, data need to be pooled across the first two MEPS national samples. More specifically, full calendar year 1997 data collected in Rounds 3-5 for the MEPS Panel 1 sample are pooled with data from the first three rounds of data collection for the MEPS Panel 2 sample (Figure 2). Overall, the full 1997 MEPS household sample consists of approximately 13,000 reporting units that include 32,636 individuals who completed the full series of MEPS interviews for their entire period of eligibility, providing the necessary information to produce national use and expenditure estimates for calendar year 1997. Panel 1
Conditioned on response to Rounds 1-3 of MEPS Panel 1, 19,622 (90.44 percent) of 21,696 key and in-scope individuals eligible for data collection in 1997 provided data for their entire period of eligibility. After factoring in the impact of survey attrition, the overall Panel 1 MEPS person-level response rate for deriving annual estimates was 63.5 percent (.702 x .9044). Of these full-year respondents for calendar year 1997, 19,407 were in scope on December 31, 1997. Panel 2
Conditioned on response to Round 1 of MEPS Panel 2, 13,014 (88.87 percent) of 14,644 key and in-scope individuals eligible for data collection in 1997 provided data for their entire period of eligibility. After factoring in the impact of survey attrition, the overall Panel 2 MEPS person-level response rate for deriving annual estimates was 69.2 percent (.779 x .8887). Of these full-year respondents for calendar year 1997, 12,819 were in scope on December 31, 1997.
Combined Response Rates for Full-Year Estimates
Each panel was given equal weight in the development of sampling weights to produce annual national estimates. Therefore, a pooled response rate for the survey respondents in this data set can be obtained by taking an average of the panel-specific response rates. This pooled response rate for the combined panels is 66.4 percent, and it consists of a total of 32,636 survey participants. The weighted MEPS population estimate for the civilian noninstitutionalized population as of December 31, 1997, was 267,704,802, based on poststratification to population estimates produced from the December 1997 Current Population Survey. Sample yields for the subset of the 32,636 survey participants who were in scope as of December 31, 1997 (32,226), controlling for sex, race/ethnicity, region, MSA status, and age, are presented in Table 8.
Return To Top
Summary
This report has provided a summary of the sample design features of the 1997 Household Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. Particular attention has been given to the sample selection scheme implemented for the new 1997 MEPS sample panel. The report also provides a summary of the precision specifications for the survey, sample yields, and the level of precision in survey estimates. The details of the probabilistic models that were used to select an expected oversample of low-income households and households with individuals likely to incur high levels of medical expenditures in 1997 were also presented, in addition to measures of the predictive capacity of the respective models. Both the panel-specific and pooled survey response rates were summarized for the 1997 MEPS Panel 1 Round 3/Panel 2 Round 1 point-in-time sample (first half of 1997) and for annual estimates.
The MEPS data serve as the primary source of information for research efforts examining how health care use and expenditures vary among different sectors of the population (such as the elderly, veterans, children, disabled persons, minorities, the poor, and the uninsured) and how health insurance coverage varies by demographic characteristics, employment status and characteristics, geographic locale, and other factors. The MEPS data are providing and will continue to provide answers to questions about private health insurance costs and coverage. These data are helpful in evaluating the growing impact of managed care on health care expenditures and enrollment in different types of managed care plans.
Return To Top
References
Arnett RA, Hunter E, Cohen S, et al. The Department of Health and Human Services' Survey Integration Plan. In: Proceedings of the American Statistical Association (ASA). Section on Government Statistics; 1996 Aug; Chicago. Alexandria (VA): American Statistical Association; 1996.
Cohen JW. Design and methods of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. Rockville (MD): Agency for Health Care Policy and Research; 1997. MEPS Methodology Report No. 1. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0026.
Cohen SB. The redesign of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, a component of the DHHS Survey Integration Plan. In: Proceedings of the Council of Professional Associations on Federal Statistics (COPAFS) Seminar on Statistical Methodology in the Public Service. 1996 Nov; Bethesda (MD).
Cohen SB. Sample design of the 1996 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. Rockville (MD): Agency for Health Care Policy and Research; 1997. MEPS Methodology Report No. 2. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0027.
DiGaetano R. Sample design of the Household Component of the National Medical Expenditure Survey (NMES-3). Unpublished report. Rockville (MD): Westat, Inc.; 1994. Contract No. 282-94-200.
Hunter E, Arnett R, Cohen S, et al. HHS Survey Integration Plan: Background materials [unpublished report]. Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, Rockville (MD), and National Center for Health Statistics, Hyattsville (MD); 1995.
Judkins D, Marker D, Waksberg J. National Health Interview Survey: research for the 1995 redesign [unpublished report]. Prepared under contract for the National Center for Health Statistics. Rockville (MD): Westat, Inc.; 1994.
Moeller J, Mathiowetz N. Low income and high expenditure prediction models [internal memos]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Health Care Policy and Research; 1994.
Return To Top
Tables
Table 1. Targeted average relative standard errors (RSEs) for subpopulations of analytic interest in the 1997 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component
| .020 |
.035 |
| .040 |
.070 |
| .042 |
.070 |
| .080 |
.135 |
| .080 |
.135 |
| .080 |
.135 |
| .015 |
.023 |
a Need help in 1 or more activities of daily living (ADLs), such as bathing and dressing.
b Need help in 1 or more instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs), such as shopping or paying bills.
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component, 1997.
Return To Top
Table 2. Targeted sample yields at the end of three core data collection rounds for 1997 for subpopulations of analytic interest: 1997 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey
Household Component
| 15,000 |
| 4,000 |
| 3,700 |
| 1,000 |
| 1,000 |
| 1,000 |
| 34,000 |
a Need help in 1 or more activities of daily living (ADLs), such as bathing and dressing.
b Need help in 1 or more instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs), such as shopping or paying bills.
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component, 1997
Return To Top
Table 3. National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) dwelling unit sample classifications available for the 1997 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS)
Household Component
| 478 |
478 |
1.0 |
| 601 |
601 |
1.0 |
| 596 |
596 |
1.0 |
| 2,064 |
1,238 |
0.6 |
| 324 |
194 |
0.6 |
| 2,157 |
647 |
0.3 |
| 8,486 |
2,546 |
0.3 |
| 14,706 |
6,300 |
— |
Source: National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National Health Interview Survey, 1996.
Return To Top
Table 4. National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) reporting unit sample classifications available for the 1997 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS)
Household Component
| 481 |
481 |
| 601 |
601 |
| 600 |
600 |
| 2,126 |
1,274 |
| 326 |
194 |
| 2,163 |
652 |
| 8,770 |
2,678 |
| 15,067 |
6,480 |
Source: National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National Health Interview Survey, 1996.
Return To Top
Table 5. National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) person-level sample classifications available for the 1997 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS)
Household Component
| 506 |
506 |
| 723 |
723 |
| 701 |
701 |
| 6,304 |
4,181 |
| 393 |
253 |
| 3,234 |
1,109 |
| 26,557 |
9,590 |
| 38,418 |
17,063 |
Source: National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National Health Interview Survey, 1996.
Return To Top
Table 6. National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) person-level sample selected for the 1997 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS)
Household Component
| 506 |
| 723 |
| 755 |
| 7,990 |
| 900 |
| 4,600 |
Source: National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National Health Interview Survey, 1996.
Return To Top
Table 7. 1997 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey sample yields
| Demographic subgroup |
1996 unweighted sample |
1997 unweighted sample |
Pooled (Panel 1 and 2) |
| Unweighted sample |
Percent uninsured |
SE (percent) |
Relative SE (percent) |
Design effect |
| Overall population |
21,411 |
14,505 |
35,916 |
16.76 |
0.389 |
2.321 |
3.89 |
| Sex |
|---|
| Male |
10,191 |
6,842 |
17,033 |
18.51 |
0.472 |
2.550 |
2.52 |
| Female |
11,220 |
7,663 |
18,883 |
15.09 |
0.414 |
2.744 |
2.53 |
| Race/ethnicity |
|---|
| Hispanic |
4,610 |
3,350 |
7,960 |
32.94 |
1.118 |
3.394 |
4.51 |
| Black non-Hispanic |
2,819 |
2,422 |
5,301 |
21.45 |
0.985 |
4.592 |
3.05 |
| Other |
13,922 |
8,733 |
22,655 |
13.63 |
0.392 |
2.876 |
2.95 |
| Age in years |
|---|
| Under 6 |
1,989 |
1,450 |
3,439 |
14.27 |
0.895 |
6.272 |
2.25 |
| 6-17 |
4,265 |
3,160 |
7,425 |
15.72 |
0.679 |
4.319 |
2.58 |
| 18-44 |
8,296 |
5,428 |
13,724 |
23.36 |
0.579 |
2.479 |
2.57 |
| 45-64 |
4,392 |
2,832 |
7,224 |
14.84 |
0.587 |
3.956 |
1.97 |
| 65 and over |
2,469 |
1,635 |
4,104 |
1.02 |
0.194 |
19.020 |
1.53 |
| Activity limitations |
|---|
| 1 or more ADL (18 years and over) |
292 |
346 |
638 |
4.81 |
4.137 |
23.638 |
1.80 |
| 1 or more IADL (18 years and over) |
528 |
603 |
1,131 |
5.97 |
0.937 |
15.695 |
1.77 |
| Region |
|---|
| Northwest |
4,238 |
2,752 |
6,990 |
14.20 |
0.639 |
4.500 |
2.34 |
| Midwest |
4,637 |
2,941 |
7,578 |
12.51 |
0.728 |
5.819 |
3.67 |
| South |
7,442 |
5,150 |
12,592 |
19.62 |
0.745 |
3.797 |
4.43 |
| West |
5,094 |
3,662 |
8,759 |
18.93 |
0.921 |
4.855 |
4.84 |
Source: National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National Health Interview Survey, 1996.
Return To Top
Table 8. 1997 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) sample yields for full-year
respondents as of December 31, 1997 - Panels 1 and 2 combined
| Demographic subgroup |
Unweighted MEPS count |
Weighted Current Population Survey count |
| Sex |
|---|
| Male |
15,239 |
130,734,620 |
| Female |
16,987 |
136,970,181 |
| Race/ethnicity |
|---|
| Hispanic |
7,440 |
30,600,491 |
| Black non-Hispanic |
4,743 |
33,578,472 |
| Other |
20,043 |
203,445,838 |
| Region |
|---|
| Northwest |
6,144 |
51,118,238 |
| Midwest |
6,763 |
62,426,339 |
| South |
11,309 |
93,820,483 |
| West |
8,010 |
60,339,742 |
| Metropolitan statistical area (MSA) |
| MSA |
25,119 |
215,387,710 |
| Non-MSA |
7,107 |
52,317,091 |
| Age in years |
|---|
| Under 1 |
479 |
3,819,437 |
| 1-4 |
2,028 |
15,840,700 |
| 5-9 |
2,854 |
20,404,149 |
| 10-14 |
2,807 |
19,563,172 |
| 15-19 |
2,532 |
19,452,449 |
| 20-24 |
1,913 |
17,531.979 |
| 25-29 |
1,998 |
18,827,116 |
| 30 34 |
2,335 |
20,322,814 |
| 35-44 |
4,963 |
44,120,234 |
| 45-54 |
3,963 |
33,907,056 |
| 55-59 |
1,419 |
11,896,295 |
| 60-64 |
1,198 |
9,956,233 |
| 65-69 |
1,046 |
9,413,817 |
| 70-74 |
1,017 |
8,532,698 |
| 75-79 |
776 |
6,842,152 |
| 80 and over |
898 |
7,274,502 |
| Under 1 |
479 |
3,819,437 |
| 1-19 |
10,221 |
75,260,469 |
| 20-29 |
3,911 |
36,359,005 |
| 30-44 |
7,298 |
64,443,048 |
| 45-64 |
6,580 |
55,759,584 |
| 65 and over |
3,737 |
32,063,169 |
| Total |
32,226 |
267,704,802 |
Source: National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National Health Interview Survey, 1996.
Return To Top
Figures
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
Return To Top
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
Return To Top
Suggested Citation:
Methodology Report #11: Sample Design of the 1997 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. November 2000. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD.
http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/data_files/publications/mr11/mr11.shtml
|
|
