|
|
Font Size:
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
STATISTICAL BRIEF #101:
Variations in Smoking by Selected Demographic, Socioeconomic, Insurance, and Health Characteristics, United States, 2003
Highlights
- In 2003, 21.7 percent of the adult U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population (46.3 million persons) currently smoked.
- White non-Hispanics (23.2 percent) and black non-Hispanics (22.5 percent) were nearly three times more likely to smoke than Asians (7.9 percent) and about one and a half times more likely to smoke than Hispanics (15.6 percent).
- About one-quarter of all adult males currently smoked (24.4 percent) compared to 19.1 percent of females.
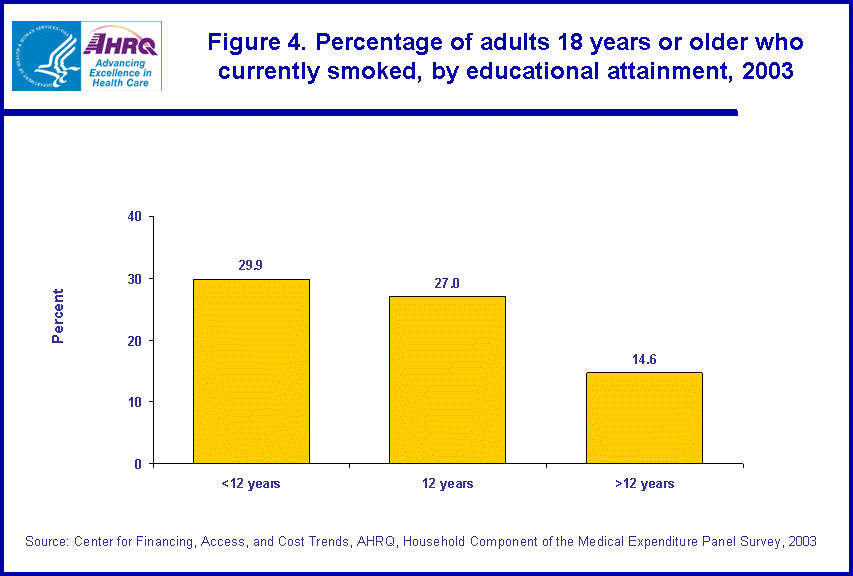
- Adults with fewer than 12 years of education were about twice as likely to smoke as adults with more than 12 years of education (29.9 percent versus 14.6 percent).
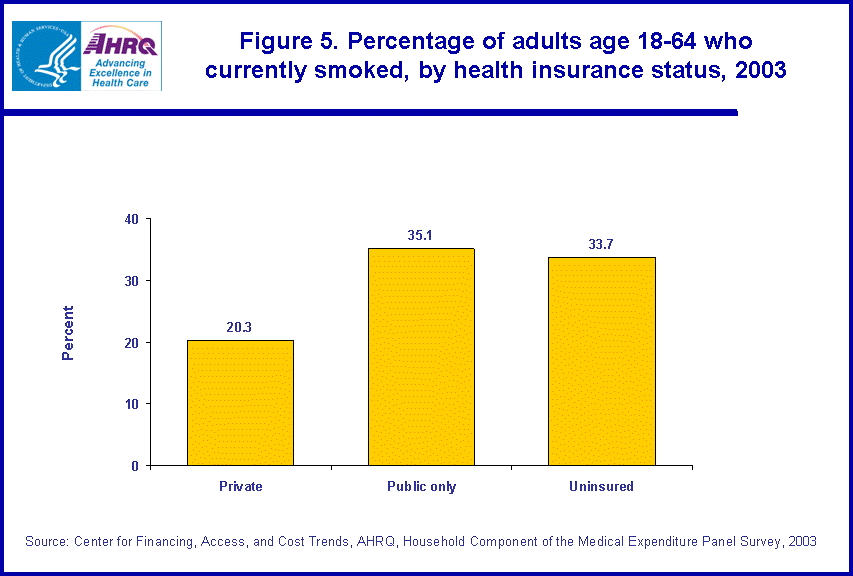
- Persons age 18-64 with public only insurance (35.1 percent) or who were uninsured (33.7 percent) were considerably more likely to smoke than those 18-64 with any private insurance (20.3 percent).
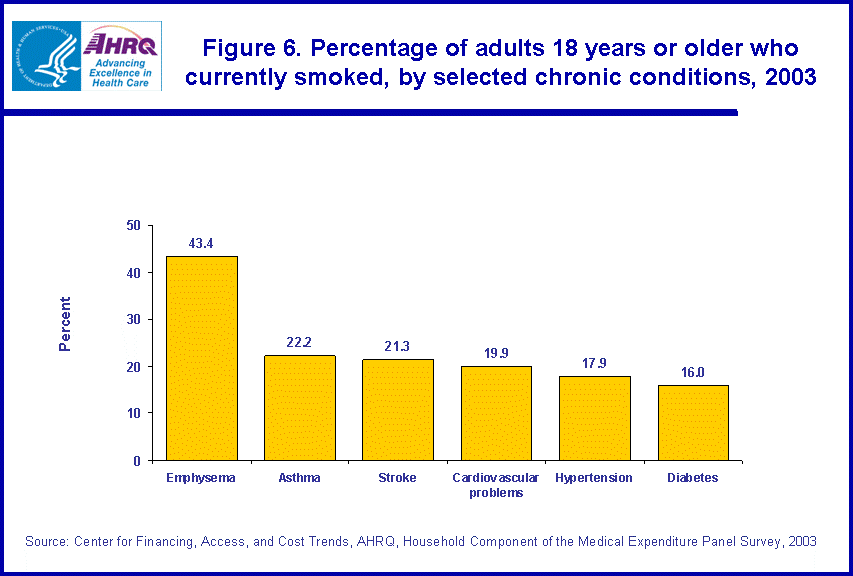
- Over two-fifths (43.4 percent) of persons with emphysema were current smokers.
- In 2003, 63.6 percent of smokers who had a routine check-up in the last 12 months were counseled by a physician to stop smoking.
Introduction
Since 1965, the percentage of adults in the United States who smoke has declined by nearly half.* Moreover, the percentage of smokers with a routine check-up who were advised by their doctor to quit smoking rose in recent years from 57 percent in 2000 to about 64 percent in 2003. Despite these improvements, the smoking status of adults remains a serious concern to citizens, health care providers, and policy makers, as smoking is one of the leading causes of preventable death and disease. Data from the Household Component of the 2003 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS-HC) indicate that more than one-fifth of the adult U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population currently smoked and that smokers were more likely to be in fair or poor health than non-smokers (about 18.0 versus 11.6 percent).
This Statistical Brief presents estimates on the smoking status of adults, age 18 or older, in the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized (community) population in 2003 by selected characteristics, including age, race/ethnicity, sex, education, insurance coverage, and health conditions. Additional estimates are provided on routine check-ups and smoking cessation counseling. The national estimates are derived from the MEPS-HC self-administered questionnaire (SAQ) in conjunction with data obtained from the core MEPS-HC questionnaire. All differences between estimates discussed in the text are statistically significant at the 0.05 level or better.
Findings
Age
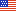
In 2003, 21.7 percent of the adult U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population (46.3 million persons) currently smoked. Persons in the 18-24 year (22.5 percent), 25-44 year (24.4 percent), and 45-64 year (23.7 percent) age categories were more than twice as likely to smoke as adults age 65 and over (figure 1). The differences among the subgroups under 65 were not significant.
Race/ethnicity
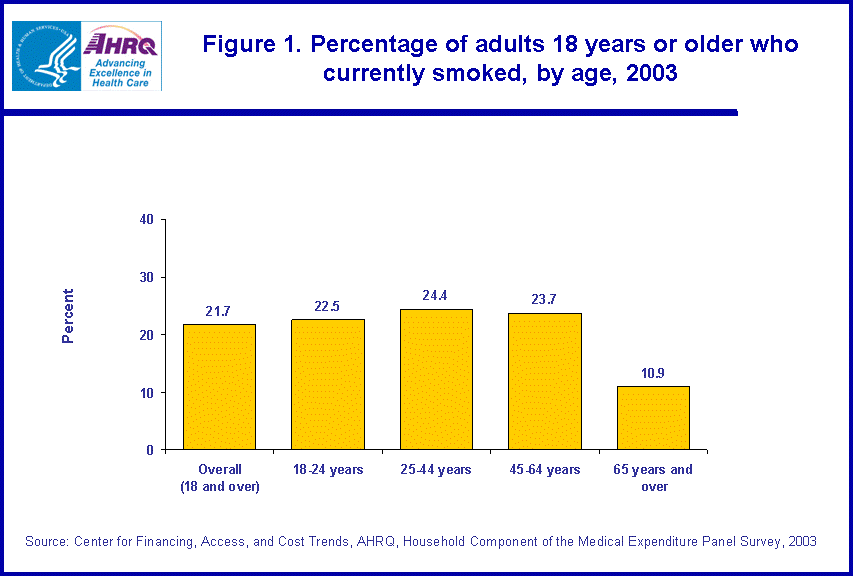
White non-Hispanics (23.2 percent) and black non-Hispanics (22.5 percent) were nearly three times more likely to smoke than Asians (7.9 percent) and almost 1.5 times more likely to smoke than Hispanics (15.6 percent) (figure 2).
Sex
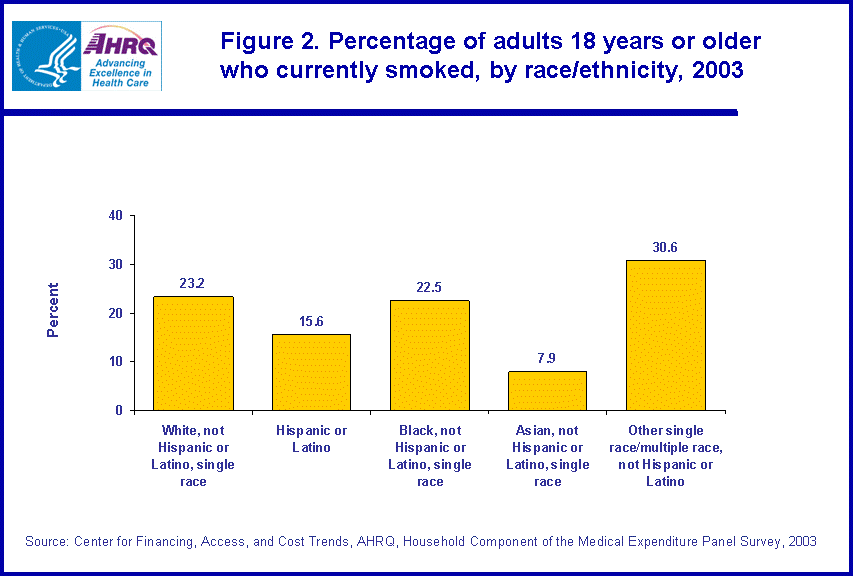
In 2003, about one-quarter of all adult males smoked (24.4 percent) compared to 19.1 percent of females (figure 3). While men in the 18-64 age group were more likely to smoke than women in the same age group (26.5 percent versus 21.2 percent), the difference between the rates of smoking of males and females in the 65 and over age category were not significant.
Education
Adults with fewer than 12 years of education were about twice as likely to smoke as adults with more than 12 years of education (29.9 percent versus 14.6 percent) (figure 4). Persons with 12 years of education were slightly less likely to smoke than those with fewer than 12 years of education (27.0 percent versus 29.9 percent) but were nearly twice as likely to smoke as persons with more than 12 years of education (27.0 percent versus 14.6 percent).
Insurance status
Persons 18-64 years of age with public only insurance (35.1 percent) or who were uninsured (33.7 percent) were considerably more likely than persons in the same age group with private insurance (20.3 percent) to smoke (figure 5).
Chronic conditions
A significant number of persons with reported physician-diagnosed chronic conditions currently smoked. Of the six chronic conditions examined, persons with emphysema were most likely to currently smoke (43.4 percent) (figure 6). About 22.2 percent of persons with asthma, 21.3 percent of persons who had a stroke, 19.9 percent of persons with cardiovascular problems, 17.9 percent of persons with hypertension, and 16.0 percent of persons with diabetes reported that they currently smoked.
Routine check-ups/counseling
Slightly less than half of smokers (47.8 percent) had a routine check-up within the last year compared to 61.1 percent of non-smokers (estimates not shown in a figure). Nearly two-thirds (63.6 percent) of smokers who had a routine check-up in the last year were counseled by a physician to stop smoking.
Data Source
The estimates in this Statistical Brief are based upon data from the MEPS 2003 Full Year Population Characteristics data file (HC-073).
Definitions
Racial and ethnic classifications
Classification by race and ethnicity is based on information reported for each family member. Respondents were asked if each family member's race was best described as American Indian, Alaska Native, Asian or Pacific Islander, black, white, or other. They also were asked if each family member's main national origin or ancestry was Puerto Rican; Cuban; Mexican, Mexicano, Mexican American, or Chicano; other Latin American; or other Spanish. All persons whose main national origin or ancestry was reported in one of these Hispanic groups, regardless of racial background, were classified as Hispanic. Since the Hispanic grouping can include black Hispanic, white Hispanic, Asian and Pacific Islanders Hispanic, and other Hispanic, the race categories of black, white, Asian and Pacific Islanders, and other do not include Hispanic. MEPS respondents who reported other single or multiple races and were non-Hispanic were included in the other category.
Health insurance status
Individuals under age 65 were classified in the following three insurance categories, based on household responses to health insurance status questions:
- Any private health insurance: Individuals who, at any time during the year, had insurance that provides coverage for hospital and physician care (other than Medicare, Medicaid, or other public hospital/physician coverage) were classified as having private insurance. Coverage by TRICARE (Armed Forces-related coverage) was also included as private health insurance. Insurance that provides coverage for a single service only, such as dental or vision coverage, was not included.
- Public coverage only: Individuals were considered to have public coverage only if they met both of the following criteria: 1) they were not covered by private insurance at any time during the year, 2) they were covered by one of the following public programs at any point during the year: Medicare, Medicaid, or other public hospital/physician coverage.
- Uninsured: The uninsured were defined as people not covered by private hospital/physician insurance, Medicare, TRICARE, Medicaid, or other public hospital/physician programs at any time during the entire year or period of eligibility for the survey.
Information on chronic conditions was obtained from responses to questions asked in the Priority Conditions section of the MEPS-HC questionnaire. For each of the priority conditions, the following question was asked: "(Have/Has) PERSON ever been told by a doctor or other health professional that PERSON had [condition]."
About MEPS-HC
MEPS-HC is a nationally representative longitudinal survey that collects detailed information on health care utilization and expenditures, health insurance, and health status, as well as a wide variety of social, demographic, and economic characteristics for the civilian noninstitutionalized population. It is cosponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Center for Health Statistics.
For more information about MEPS, call the MEPS information coordinator at AHRQ (301-427-1656) or visit the MEPS Web site at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/.
References
For a detailed description of the MEPS survey design, sample design, and methods used to minimize sources of nonsampling error, see the following publications:
Cohen, J. Design and Methods of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 1. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0026. Rockville, Md.: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997.
Cohen, S. Sample Design of the 1996 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 2. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0027. Rockville, Md.: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997.
Cohen, S. Design Strategies and Innovations in the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. Medical Care, July 2003: 41(7) Supplement: III-5-III-12.
Suggested Citation
Carper, K. and Machlin, S. R. Variations in Smoking by Selected Demographic, Socioeconomic, Insurance, and Health Characteristics, United States, 2003. Statistical Brief #101. October 2005. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, Md. http://meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st101/stat101.shtml
AHRQ welcomes questions and comments from readers of this publication who are interested in obtaining more information about access, cost, use, financing, and quality of health care in the United States. We also invite you to tell us how you are using this Statistical Brief and other MEPS data and tools and to share suggestions on how MEPS products might be enhanced to further meet your needs. Please e-mail us at mepspd@ahrq.gov or send a letter to the address below:
Steven B. Cohen, PhD
Director
Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
540 Gaither Road
Rockville, MD 20850
Footnote
* National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2004, with Chartbook on Trends in the Health of Americans. Hyattsville, Maryland: 2004. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/hus.htm
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||