|
|
Font Size:
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
STATISTICAL BRIEF #115:
Health Service Use and Expenses for Migraines and Other Headaches, 2002-03 (Average Annual Estimates)
Highlights
- In 2002-03, an annual average of 3.5 percent of adults had ambulatory care visits and/or prescribed medicine purchases to treat migraines and/or other types of headaches. Among these persons, the average annual expenditure for these services was $566 (in 2003 dollars).
- The median expense per year for treatment of headaches was about 40 percent higher for migraines than for other headaches.
- Persons age 65 and over were less likely than younger adults, and females were more likely than males, to have treatment for a migraine or other headache.
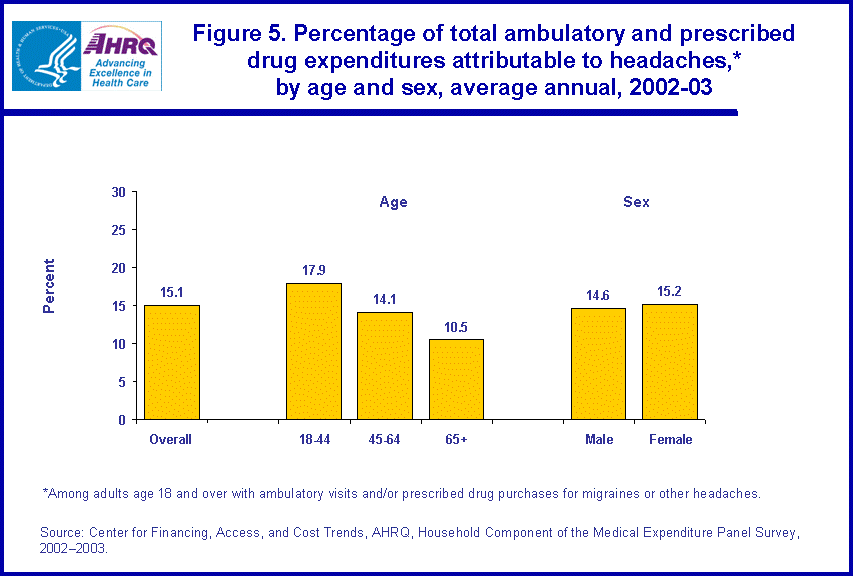
- Among adults who received treatment for migraines or other headaches, an annual average of 15.1 percent of all their expenditures for ambulatory care and prescribed medicines was for treatment of these conditions.
Introduction
Migraines and other headaches are common conditions among U.S. adults. For some, headaches can be treated using over-the-counter drugs, rest, and other means that do not require the involvement of health professionals. For others, however, substantial medical expenses are incurred from ambulatory visits to a physician or other health provider and the use of analgesics and other types of prescribed medications to treat headaches. Total expenditures for these services for the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population averaged $4.3 billion per year in 2002-03, with approximately 60 percent of the total for ambulatory visits and 40 percent for prescribed medicines.
This Statistical Brief presents estimates based on data from the Household Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS-HC) on health care use and expenditures to treat headaches among adults age 18 and over in the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population. Estimates include use and expenditures for ambulatory care services (including office-based, hospital outpatient, and emergency room settings) and prescribed medicines because these are the MEPS service categories that are most relevant to headache treatment.* Average annual estimates for the period from 2002-03 are shown for two categories of headaches: migraines and other headaches (facial pain, nonspecific reported pain in head, and tension headaches) as well as by age and sex. Data for two years were combined to improve the precision of the estimates, and expenditure data for 2002 were Consumer Price Index-adjusted to 2003 dollars. All differences between estimates noted in the text are statistically significant at the 0.05 level or better.
Findings
Health service use by type of headache
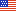
During 2002-03, an annual average of 3.5 percent of adults (about 7.5 million per year) were reported to have had an ambulatory care visit and/or a prescribed medicine purchase during the year to treat a migraine and/or other type of headache (figure 1), with a slightly higher percentage of adults having treatment for a migraine (1.9 percent) than for other types of headaches (1.6 percent).
Health service expenditures by type of headache
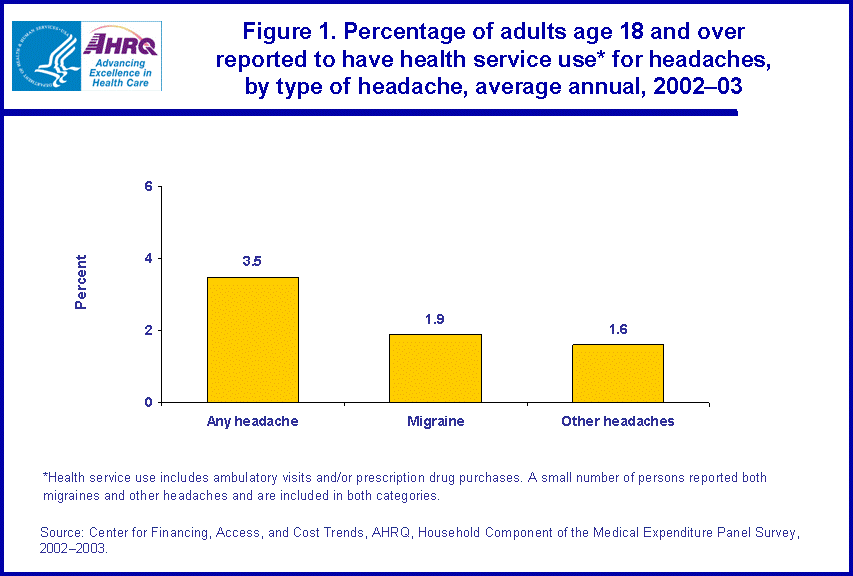
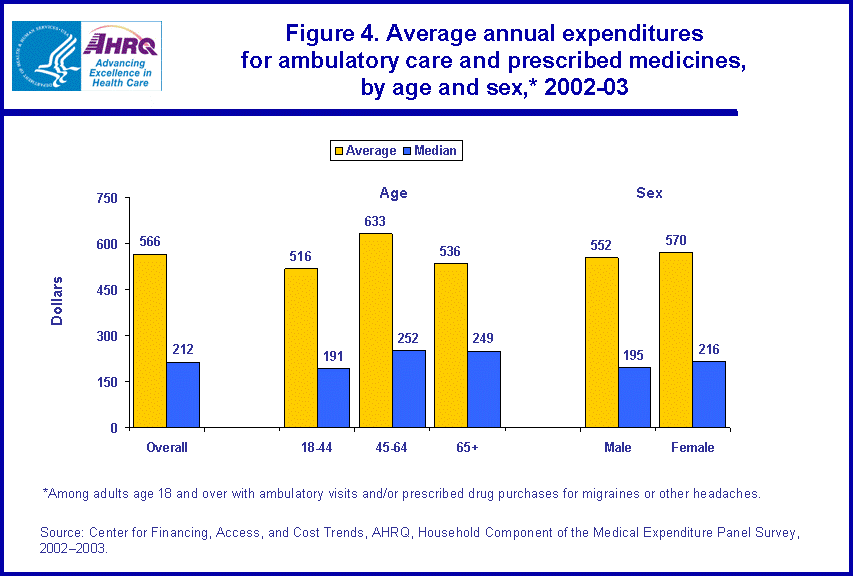
In 2002-03, adults with ambulatory care and/or a prescribed medicine to treat migraines or other headaches had average annual expenditures of $566 for these services (figure 2). Since persons with the highest expenses have a disproportionate impact on the average, the median annual expense of $212 per user was substantially lower than the per user average.
Among those with ambulatory visits and/or prescribed medicine purchases to treat headaches in 2002-03, the median expense per year was about 40 percent higher for persons with migraines than for persons with other headaches ($243 versus $172). However, the difference in average expenses between the two headache categories was not significantly different ($577 versus $530).
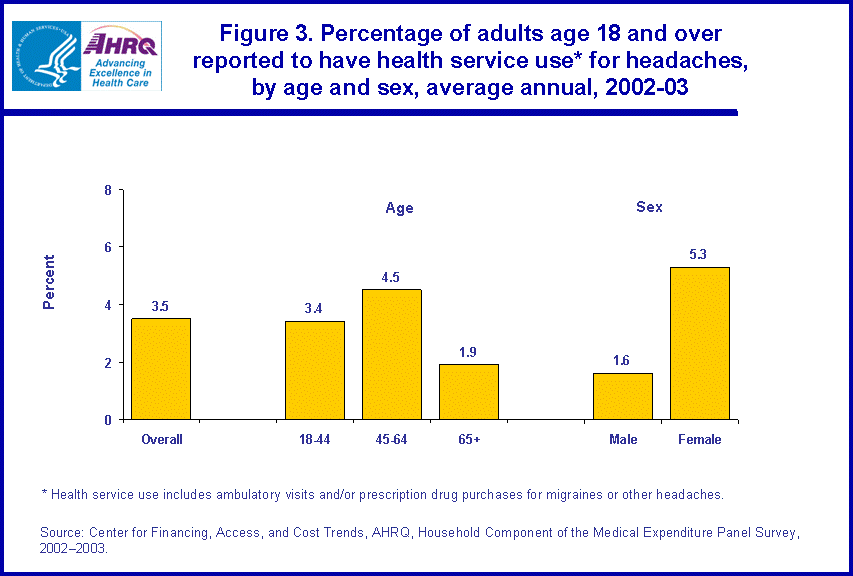
Health service use and expenditures for headaches by age and sex
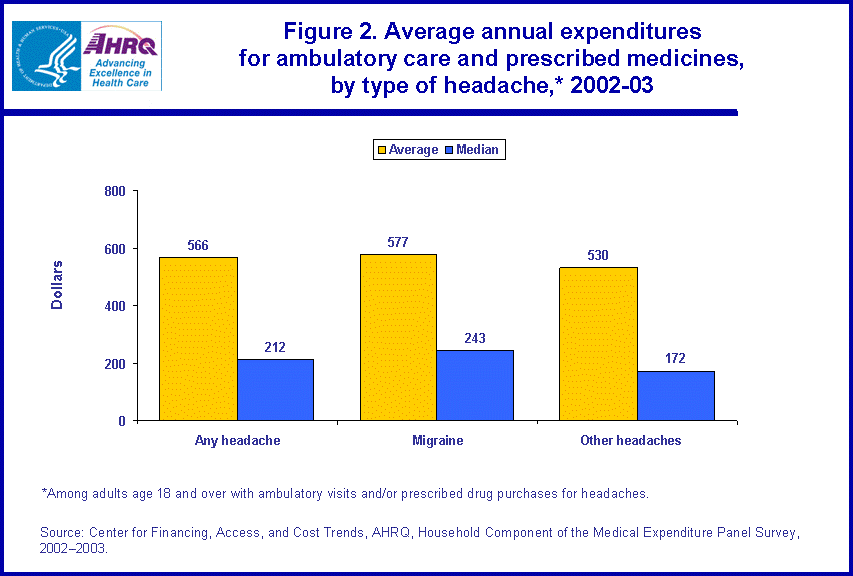
The percentage of persons with reported treatment for a migraine or other headache varies by age and sex (figure 3). Adults ages 45-64 were the most likely (4.5 percent) and adults 65 and older were the least likely (1.9 percent) to have treatment for migraines and other headaches. The percentage of young adults reporting treatment (3.4 percent) fell in between the other two age categories. Further, adult females were more than three times as likely as adult males to be treated for a migraine or other headache (5.3 versus 1.6 percent). Among adults with reported treatment for headaches, however, there were no significant differences by age or sex in the average or median annual expenditures for ambulatory visits and prescribed medicines to treat these conditions (figure 4).
Percentage of health service expenditures by age and sex
Among adults who received treatment for migraines or other headaches in 2002-03, an annual average of 15.1 percent of all ambulatory and prescribed medicines expenditures were for treatment of these conditions (figure 5). While there was no significant difference by sex, this percentage decreased with age, ranging from 17.9 percent for adults age 18-44 to only 10.5 percent for adults age 65 and over. This percentage was smallest for the elderly due to greater expenses for other types of conditions.
Data Source
The estimates in this Statistical Brief are based on data from the MEPS 2002 and 2003 Full Year Consolidated Files (HC-070 and HC-079), Medical Condition Files (HC-069 and HC-078), Office-Based Medical Provider Visits Files (HC-067G and HC-077G), Outpatient Department Visits Files (HC-067F and HC-077F), Emergency Room Visits Files (HC-067E and HC-077E), and Prescribed Medicines Files (HC-067A and HC-077A).
Definitions
Migraine or other headache
In MEPS, conditions are recorded in connection with reported health care utilization (i.e., a person who reports purchasing a drug will be asked what condition the drug was intended to treat). For the purposes of this brief, individuals who were reported to have a migraine or other headache associated with one or more ambulatory events (see definition below) or prescribed medicine purchases are analyzed. Conditions with an ICD9 code of 346 were classified as migraines while the ICD9 codes of 784.0 and 307.81 were used to identify other headaches. A small number of persons had both migraines and other headaches, and these persons are included in the estimates for both categories.
Ambulatory and prescribed medicine use
At least one visit to a medical provider and/or one prescribed medicine purchase during the year. Visits include those to office-based, hospital outpatient, and emergency department settings.
Expenditures
Payments from all sources for ambulatory care provided in offices, hospital outpatient, and emergency department settings, as well as prescribed medicine purchases reported by respondents in the MEPS-HC. Sources include direct payments from individuals, private insurance, Medicare, Medicaid, Workers' Compensation, and miscellaneous other sources. Expenditure data for 2002 were Consumer Price Index-adjusted to 2003 dollars.
About MEPS-HC
MEPS-HC is a nationally representative longitudinal survey that collects detailed information on health care utilization and expenditures, health insurance, and health status, as well as a wide variety of social, demographic, and economic characteristics for the civilian noninstitutionalized population. It is cosponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Center for Health Statistics.
For more information about MEPS, call the MEPS information coordinator at AHRQ (301-427-1656) or visit the MEPS Web site at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/.
References
For a detailed description of the MEPS survey design, sample design, and methods used to minimize sources of nonsampling error, see the following publications:
Cohen, J. Design and Methods of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 1. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0026. Rockville, Md.: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997.
Cohen, S. Sample Design of the 1996 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 2. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0027. Rockville, Md.: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997.
Cohen, S. Design Strategies and Innovations in the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. Medical Care, July 2003: 41(7) Supplement: III-5-III-12.
Suggested Citation
Machlin, S. R. and Miller, G. E. Health Service Use and Expenses for Migraines and Other Headaches, 2002-03 (Average Annual Estimates). Statistical Brief #115. February 2006. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, Md. http://meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st115/stat115.shtml
AHRQ welcomes questions and comments from readers of this publication who are interested in obtaining more information about access, cost, use, financing, and quality of health care in the United States. We also invite you to tell us how you are using this Statistical Brief and other MEPS data and tools and to share suggestions on how MEPS products might be enhanced to further meet your needs. Please e-mail us at mepspd@ahrq.gov or send a letter to the address below:
Steven B. Cohen, PhD, Director
Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
540 Gaither Road
Rockville, MD 20850
Footnotes
* Purchases of over-the-counter medications are not recorded in the MEPS, and inpatient hospital and home health care services were rarely used in the treatment of headaches.
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||