|
|
Font Size:
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
STATISTICAL BRIEF #136:
The Long-Term Uninsured in America, 2001-2004: Estimates for the U.S. Population under Age 65
Highlights
- Fully 16.9 million people, 6.6 percent of the population under age 65, were uninsured for the entire four-year period from 2001 through 2004.
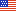
- During 2003 to 2004, young adults aged 18 to 24 were the most likely to be uninsured for at least one month (55.1 percent). Children under age 18 were the least likely to be uninsured for the entire 2001-2004 four-year period (2.6 percent).
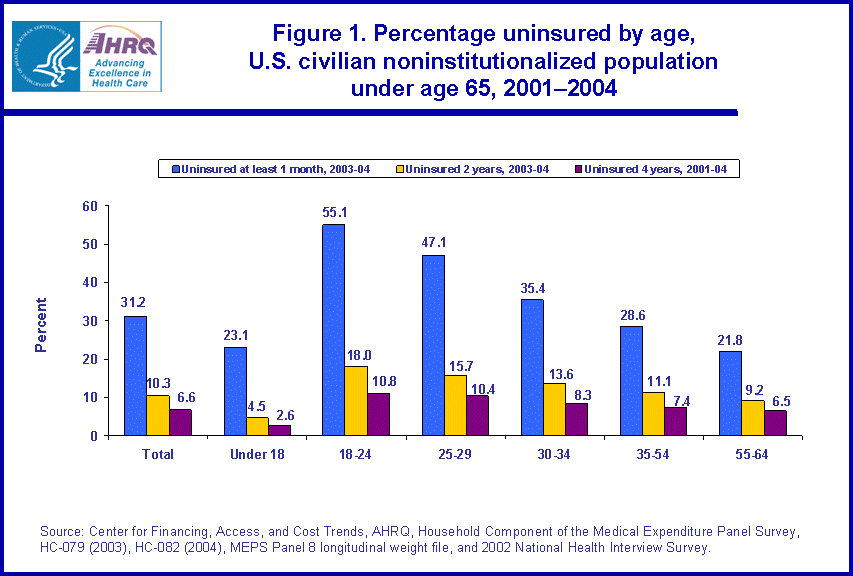
- Individuals reporting excellent or very good health status were the least likely to be uninsured for at least one month during 2003 to 2004 (27.1 and 30.1 percent, respectively). Those reporting good or fair/poor health were the most likely to be uninsured for the entire 2001-2004 four-year period (8.8 and 8.9 percent, respectively).
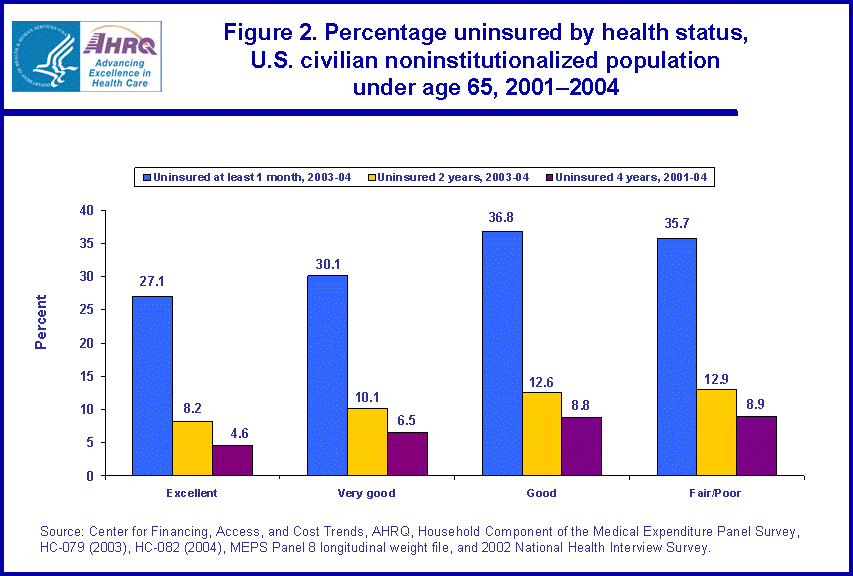
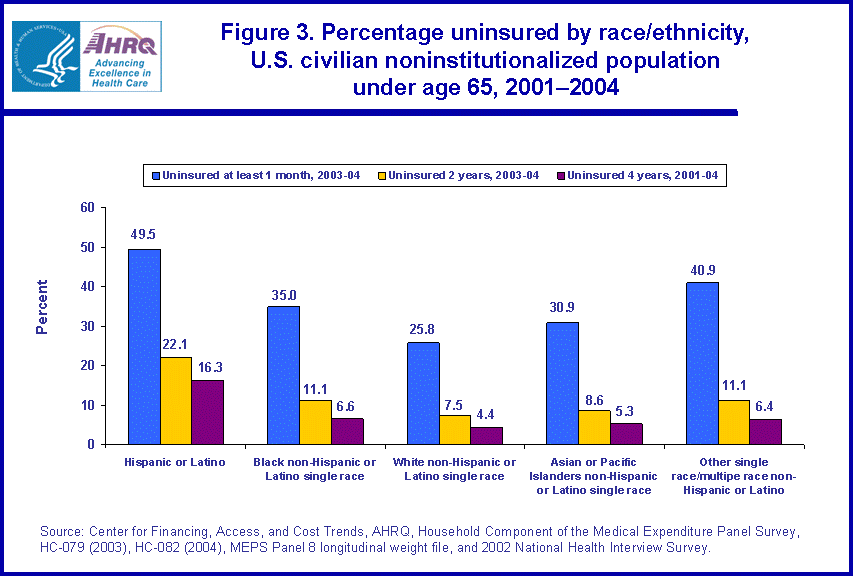
- Hispanics were the most likely to be uninsured for at least one month during 2003 to 2004 (49.5 percent) and for the entire 2001-2004 four-year period (16.3 percent).
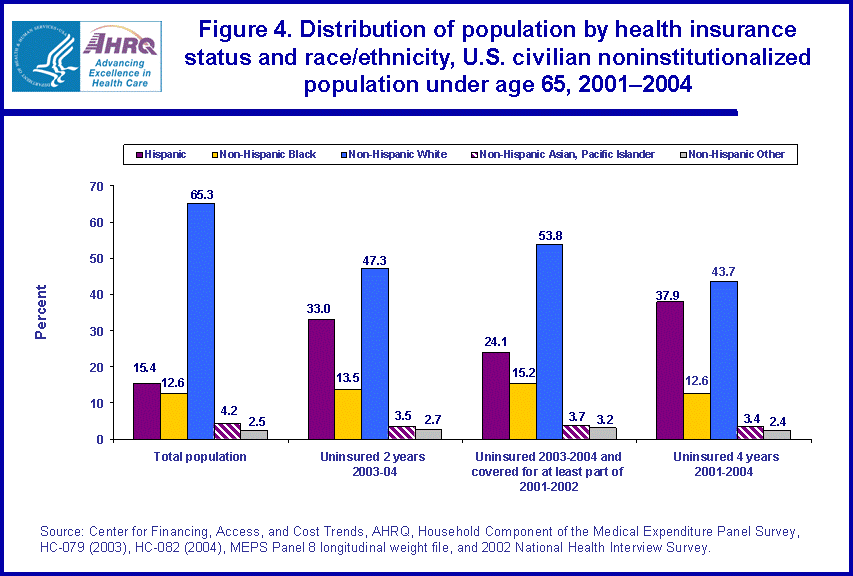
- Hispanics or Latinos single race were disproportionately represented among the long-term uninsured. While they represented 15.4 percent of the population under age 65, they represented 37.9 percent of the long-term uninsured for the period 2001-2004.
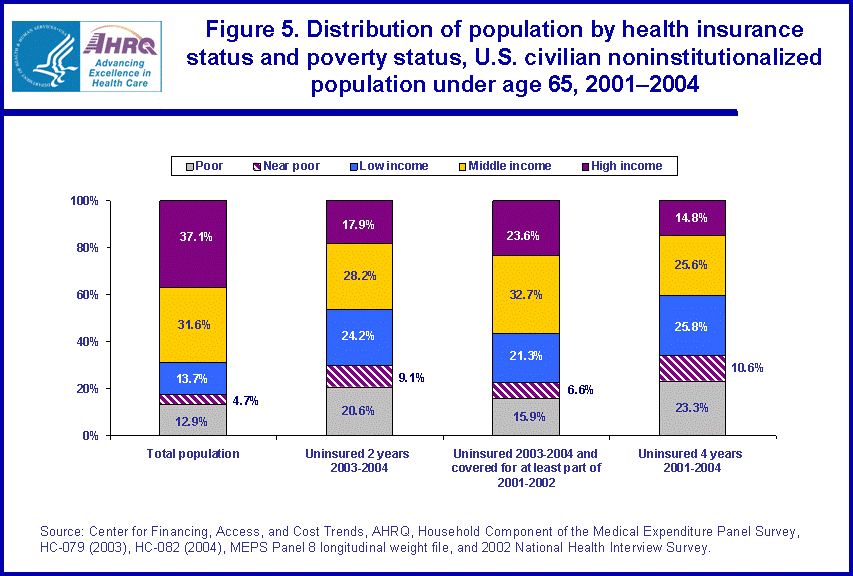
- Individuals who were poor were disproportionately represented among the long-term uninsured. While they represented 12.9 percent of the population under age 65, they represented 23.3 percent of those uninsured for the entire four-year period.
Introduction
Estimates of the health insurance status of the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population are critical to policymakers and others concerned with access to medical care and the cost and quality of that care. Health insurance helps people get timely access to medical care and protects them against the risk of expensive and unanticipated medical events. When estimating the size of the uninsured population, it is important to consider the distinction between those uninsured for short periods of time and those who are uninsured for several years.
This Statistical Brief provides detailed estimates for the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized non-elderly (under age 65) population that was uninsured for the entire 2001-2004 period and identifies groups most at risk of lacking any coverage over that four-year period. Estimates are based on information from the Household Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS-HC) for 2003 and 2004, additional questions in MEPS to determine health insurance coverage for 2001 and 2002, and health insurance profiles from the National Health Interview Survey for 2002. All differences between estimates discussed in the text are statistically significant at the 0.05 level unless otherwise noted.
Findings
According to the MEPS-HC for 2003 and 2004, 31.2 percent (79.8 million people, estimate not shown) of the under-65 population were uninsured for at least one month during the full two-year period (calendar years 2003 and 2004), and 10.3 percent (26.4 million people, estimate not shown) were uninsured for the entire two-year period. Approximately two-thirds of those individuals lacking coverage for all of 2003-2004 were also without coverage for the entire prior 2001-2002 two-year period. This translates to 6.6 percent (16.9 million people, estimate not shown) of the total population under age 65 being uninsured for the entire four-year period from 2001 through 2004.
The age group 18 to 24 was the most likely to be uninsured for some time during 2003 to 2004. For the age group 18 to 24, 55.1 percent were uninsured for at least one month or more (figure 1).
Conversely, children age less than 18 were the least likely to be uninsured for same two-year period as well as for the entire 2001-2004 four-year period. Only 2.6 percent of children were uninsured for the entire 2001-2004 four-year period.
Individuals reporting excellent or very good health status were the least likely to be uninsured for some time during 2003 to 2004. For those reporting excellent health, 27.1 percent were uninsured at least one month; while for those reporting very good health, 30.1 percent were uninsured at least one month over the same time period (figure 2). Those reporting good or fair/poor health were the most likely to be uninsured for the entire two-year period, 12.6 and 12.9 percent, respectively. Approximately 70 percent of those individuals in fair or poor health lacking coverage for all of 2003-2004 were also without coverage for the entire prior two-year period from 2001 to 2002. This translates to 8.9 percent of the total population under age 65 in fair or poor health being uninsured for the entire 2001-2004 four-year period.
Among people under age 65, Hispanics or Latinos were substantially more likely than black non-Hispanics or Latinos single race, white non-Hispanics or Latinos single race, Asian or Pacific Islander non-Hispanics or Latinos single race, or other single race/multiple race non-Hispanics or Latinos to lack health insurance during the time intervals under consideration. Among Hispanics or Latinos under age 65, 49.5 percent were uninsured for at least one month, while 22.1 percent were uninsured for the entire 2003-2004 two-year period (figure 3). Approximately three-fourths of those Hispanic individuals lacking coverage for all of 2003-2004 were also without coverage for the entire prior two-year period from 2001 to 2002. This translates to 16.3 percent of the total Hispanic population under age 65 being uninsured for the entire 2001-2004 four-year period.
Hispanics or Latinos single race were disproportionately represented among the long-term uninsured. While Hispanics and Latinos single race represented 15.4 percent of the population under age 65, they represented 37.9 percent of the long-term uninsured for the period 2001-2004 (figure 4). Alternatively, while white non-Hispanics or Latinos single race represented 65.3 percent of the under 65 population, they represented only 43.7 percent of the long-term uninsured for the period 2001-2004. Furthermore, for individuals with no coverage for the entire 2003-2004 period, Hispanics were less likely to be represented in the subgroup that had acquired some health insurance coverage in the prior period 2001-2002 (24.1 percent) relative to those individuals with no coverage (37.9 percent) for the entire 2001-2004 four-year period.
Individuals who were poor (i.e., persons in families with income equal to the poverty line or less) were disproportionately represented among the long-term uninsured. While poor individuals represented 12.9 percent of the population under age 65, they represented 23.3 percent of those uninsured for the entire 2001-2004 four-year period (figure 5). Alternatively, while individuals with high incomes (i.e., persons in families with income over 400 percent of the poverty line) represented 37.1 percent of the population under age 65, they accounted for only 14.8 percent of those uninsured for the entire 2001-2004 four-year period. Furthermore, for individuals with no coverage for the entire 2003-2004 period, high income individuals were more likely to be represented in the subgroup that had acquired some health insurance coverage in the prior period 2001-2002 (23.6 percent) relative to those individuals with no coverage (14.8 percent) for the entire 2001-2004 four-year period.
Data Source
The estimates shown in this Statistical Brief are drawn from analyses conducted by the MEPS staff from the following public use files: 2003 Full Year Consolidated Data File, HC-079; the 2004 Full Year Population Characteristics File, HC-082; and the MEPS Panel 8 longitudinal weight file. In addition, linkage of the MEPS sample was established with the 2002 National Health Interview Survey.
Definitions
Uninsured
People who were covered only by noncomprehensive State-specific programs (e.g., Maryland Kidney Disease Program) or private single-service plans (e.g., coverage for dental or vision care only, coverage for accidents or specific diseases) were considered to be uninsured. Those sample persons identified as being uninsured on January 1, 2003 in MEPS were asked if they were covered by a health insurance plan or program at any time in 2001 or 2002 in order to determine their health insurance status over the 2001-2004 four-year period. Linkage was established with the 2002 National Health Interview Survey for sample persons uninsured for all of 2003-2004 to further edit their health insurance status prior to 2003.
Age
Age was defined as age at the end of 2003.
Race/ethnicity
Classification by race/ethnicity was based on information reported for each family member. Respondents were asked if each family member's race was best described as American Indian, Alaska Native, Asian or Pacific Islander, black, white, or other. They also were asked if each family member's main national origin or ancestry was Puerto Rican; Cuban; Mexican, Mexicano, Mexican American, or Chicano; other Latin American; or other Spanish. All persons whose main national origin or ancestry was reported in one of these Hispanic groups, regardless of racial background, were classified as Hispanic. Since the Hispanic grouping can include black Hispanic, white Hispanic, Asian and Pacific Islanders Hispanic, and other Hispanic, the race categories of black, white, Asian and Pacific Islanders, and other do not include Hispanic. MEPS respondents who reported other single or multiple races and were non-Hispanic were included in the other category. For this analysis, the following classification by race and ethnicity was used: Hispanic (of any race), non-Hispanic blacks, non-Hispanic whites, non-Hispanic Asian and Pacific Islanders, and non-Hispanic others.
Poverty status
Sample persons were classified according to the total yearly income of their family. Within a household, all people related by blood, marriage, or adoption were considered to be a family. Poverty status categories are defined by the ratio of family income to the Federal income thresholds, which control for family size and age of the head of family. Poverty status was based on annual income in 2003.
Poverty status categories are defined as follows:
- Poor: Persons in families with income less than or equal to the poverty line, including those who had negative income.
- Near poor: Persons in families with income over the poverty line through 125 percent of the poverty line.
- Low income: Persons in families with income over 125 percent through 200 percent of the poverty line.
- Middle income: Persons in families with income over 200 percent through 400 percent of the poverty line.
- High income: Persons in families with income over 400 percent of the poverty line.
In every round, the respondent was asked the following question to rate the health of every member of the family: "In general, compared to other people of (PERSON)'s age, would you say that (PERSON)'s health is excellent, very good, good, fair, or poor?" For this brief, the response categories "fair" and "poor" were collapsed.
About MEPS-HC
MEPS-HC is a nationally representative longitudinal survey that collects detailed information on health care utilization and expenditures, health insurance, and health status, as well as a wide variety of social, demographic, and economic characteristics for the civilian noninstitutionalized population. It is cosponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Center for Health Statistics.
For more information about MEPS, call the MEPS information coordinator at AHRQ (301-427-1406) or visit the MEPS Web site at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/.
References
Cohen, J. Design and Methods of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 1. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0026. Rockville, Md.: Agency for Healthcare Policy and Research, 1997.
Cohen, S. Sample Design of the 1996 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 2. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0027. Rockville, Md.: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997.
Cohen, S. Design Strategies and Innovations in the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. Medical Care, July 2003: 41(7) Supplement: III-5-III-12.
Suggested Citation
Rhoades, J. A., and Cohen, S. B. The Long-Term Uninsured in America, 2001.2004: Estimates for the U.S. Population under Age 65. Statistical Brief #136. August 2006. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st136/stat136.shtml
AHRQ welcomes questions and comments from readers of this publication who are interested in obtaining more information about access, cost, use, financing, and quality of health care in the United States. We also invite you to tell us how you are using this Statistical Brief and other MEPS data and tools and to share suggestions on how MEPS products might be enhanced to further meet your needs. Please e-mail us at mepspd@ahrq.gov or send a letter to the address below:
Steven B. Cohen, PhD, Director
Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
540 Gaither Road
Rockville, MD 20850
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||