|
|
Font Size:
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
STATISTICAL BRIEF #196:
Prescription Drug Expenditures in the 10 Largest States for Persons under Age 65, 2005
Highlights
- In 2005, prescription drugs represented about 20.8 percent of all medical expenditures for persons under age 65.
- The percentage of persons under age 65 with a prescription drug expenditure in 2005 was lower than the national average in California.
- The average expenditure per person under age 65 with a prescription drug expenditure was lower than the national average in California and Texas.
- The percentage of expenditures for prescription drugs for persons under 65 covered by private insurance was higher than the national average in Michigan.
- The percentage of prescription drug expenditures paid out of pocket by persons under age 65 was lower than the national average in Michigan and higher in Texas.
- The percentage of prescription drug expenditures for persons under age 65 paid by Medicaid in 2005 was 16.0 percent.
Introduction
Prescription drugs are a large portion of health care expenditures. In 2005, expenditures for prescription drugs among the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population accounted for 20.8 percent of total health care expenditures. This compares with a 2004 value of 19.8 percent of total health care expenditures. This increase follows a longer trend. The proportion in 2005 was a significant increase from 1996 when prescription drugs expenditures accounted for only 11.9 percent of total health care expenditures.
As the overall costs of health care continue to rise and prescription drugs become a larger share, more interest is focused on these costs. For persons under age 65, the percentage of total health care expenditures that could be attributed to prescription drugs was 11.5 percent in 1996 and 20.7 percent in the year 2005. Over 95 percent of these costs for persons under age 65 are paid by three sources: private health insurance, individuals out of pocket, and Medicaid. This was also true in 1996. However, the shares of these increasing costs that are paid by the three largest payers have changed. The portion paid by private insurance has remained about the same: 44.9 percent in 1996 versus 44.4 percent in 2005. The out-of-pocket share has dropped from 40.2 percent to 35.2 percent in 2005. Medicaid has taken on a greater share of the total, increasing from 11.0 percent in 1996 to 16.0 percent in 2005.
While the total expenditures for prescription drugs are a significant portion of all health care costs for the nation, the percentage of individuals who have expenditures, the average expenditure, and the percentages paid by the various sources of payments (such as private coverage, Medicaid, and out of pocket) vary considerably across states.
Using data from the Household Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS-HC), this Statistical Brief presents estimates for prescription drug expenditures for persons under age 65 in the 10 largest states for the year 2005 and compares these estimates to the national average. Only those estimates with statistically significant differences from the national average using a multiple comparison procedure at the 0.05 significance level are noted in the text.
Findings
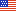
In 2005, 59.1 percent of all persons under 65 years of age had an expenditure for prescription drugs (figure 1). In California, the percentage was 50.2 percent, significantly lower than the national average.
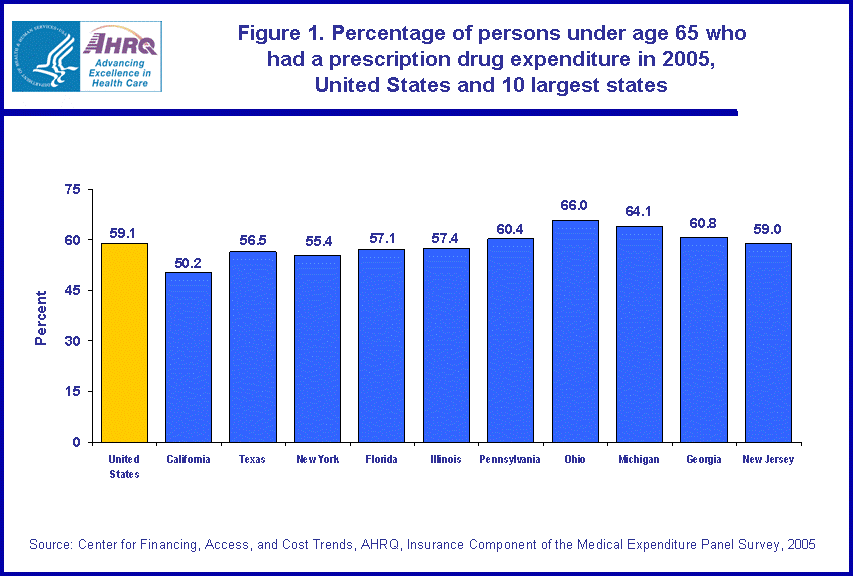
The national average expenditure for prescription drugs in 2005 for persons under 65 years of age who had an expenditure was $933 (figure 2). The average expenditures for those under age 65 in California and Texas were both lower than the national average, at $793 and $773, respectively.
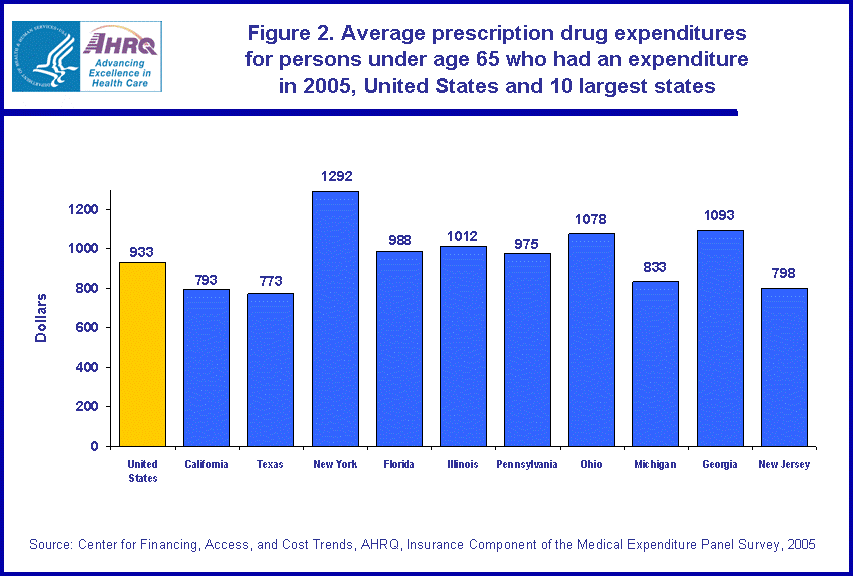
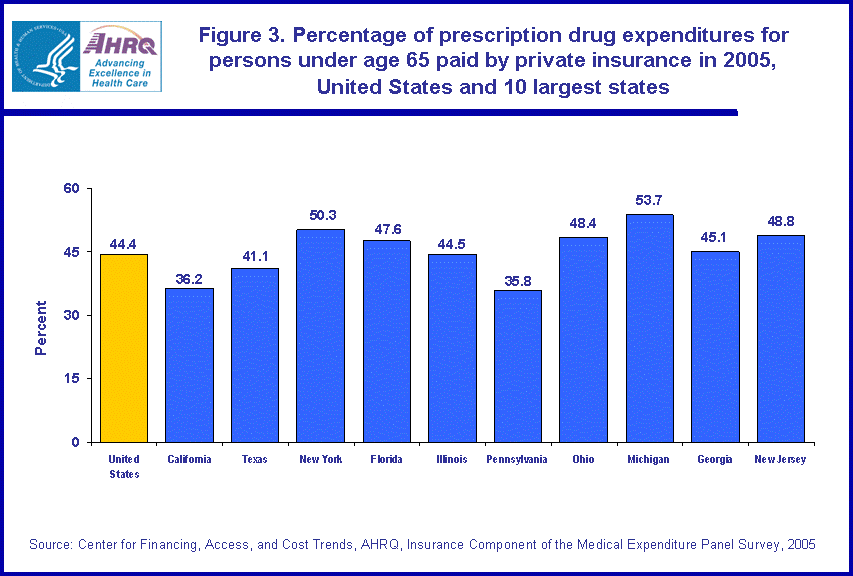
Nationwide in 2005, private insurance paid for 44.4 percent of the expenditures for prescription drugs for persons under 65 years of age (figure 3). In Michigan, private insurance paid for a higher proportion of these expenditures, 53.7 percent.
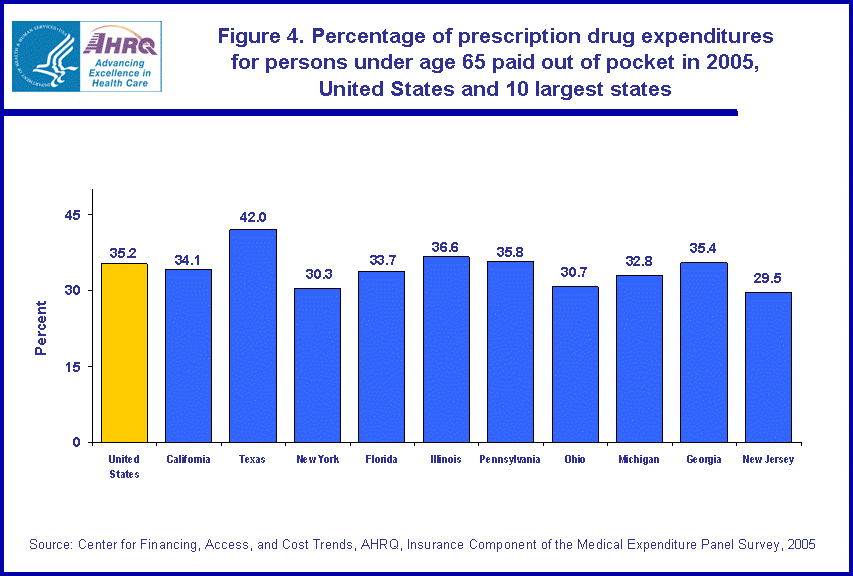
Out-of-pocket payments by persons under age 65 in 2005 accounted for 35.2 percent of the expenditures for their prescription drugs (figure 4). Persons under age 65 in Ohio contributed a smaller share of prescription drug expenditures with their out-of-pocket payments, 30.7 percent. Persons under age 65 in Texas paid a higher than average share in 2005, 42.0 percent.
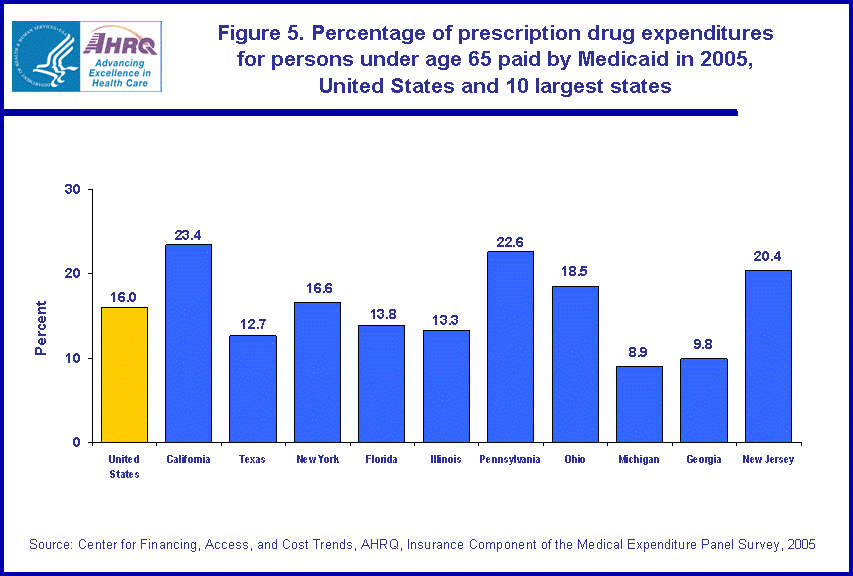
Nationally, Medicaid paid for 16.0 percent of the expenditures for prescription drugs for persons under age 65 years in 2005 (figure 5).
Data Source
The estimates shown in this Statistical Brief are drawn from analyses conducted by the MEPS staff from the following public use files: 2005 Full-Year Consolidated Data Files, HC-097, November 2007.
Definitions
Expenditures
Expenses include total payments from all sources to hospitals, physicians, other health care providers (including dental care and home health), pharmacies, and providers of other medical equipment for services reported by respondents in the MEPS-HC. Sources include direct payments from individuals, private insurance (including TRICARE), Medicare, Medicaid, and various other sources (including the Veterans Administration, Workers' Compensation, and miscellaneous public sources).
Prescribed medicine expenditures
This subcategory of expenditures includes those for all prescribed medications initially purchased or otherwise obtained during the year, as well as any refills.
About MEPS-HC
MEPS-HC is a nationally representative longitudinal survey that collects detailed information on health care utilization and expenditures, health insurance, and health status, as well as a wide variety of social, demographic, and economic characteristics for the civilian noninstitutionalized population. It is cosponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Center for Health Statistics.
For more information about MEPS, call the MEPS information coordinator at AHRQ (301-427-1406) or visit the MEPS Web site at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/.
References
For a detailed description of the MEPS-HC survey design, sample design, and methods used to minimize sources of nonsampling error, see the following publications:
Cohen, J. Design and Methods of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 1. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0026. Rockville, MD: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997.
Cohen, S. Sample Design of the 1996 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 2. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0027. Rockville, MD: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997.
Cohen, S. Design Strategies and Innovations in the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. Medical Care, July 2005: 41(7) Supplement: III-5-III-12.
Sommers, J. P. Producing State Estimates with the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey--Household Component. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Working Paper No. 05011, March 2005.
Suggested Citation
Sommers, J. P. Prescription Drug Expenditures in the 10 Largest States for Persons under Age 65, 2005. Statistical Brief #196. January 2008. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st196/stat196.shtml
AHRQ welcomes questions and comments from readers of this publication who are interested in obtaining more information about access, cost, use, financing, and quality of health care in the United States. We also invite you to tell us how you are using this Statistical Brief and other MEPS data and tools and to share suggestions on how MEPS products might be enhanced to further meet your needs. Please e-mail us at mepspd@ahrq.gov or send a letter to the address below:
Steven B. Cohen, PhD, Director
Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
540 Gaither Road
Rockville, MD 20850
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||