|
|
Font Size:
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
STATISTICAL BRIEF #205:
Trends in Statins Utilization and Expenditures for the U.S. Civilian Noninstitutionalized Population, 2000 and 2005
Highlights
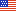
- From 2000 to 2005, total expenditures for statins in an outpatient setting more than doubled, rising from $7.7 billion to $19.7 billion.
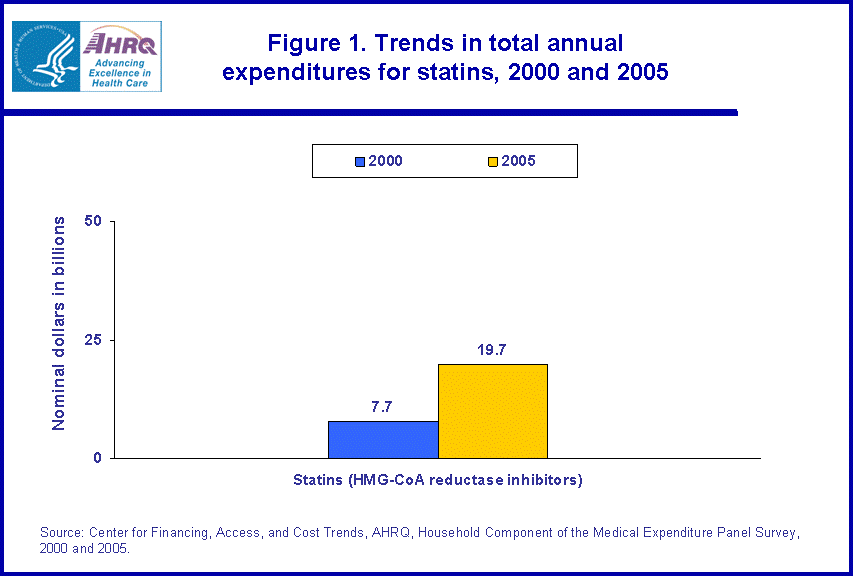
- The average expenditure for persons with a prescription medicine purchase of at least one statin increased about 37 percent, rising from $484 to $661, when comparing 2000 to 2005.
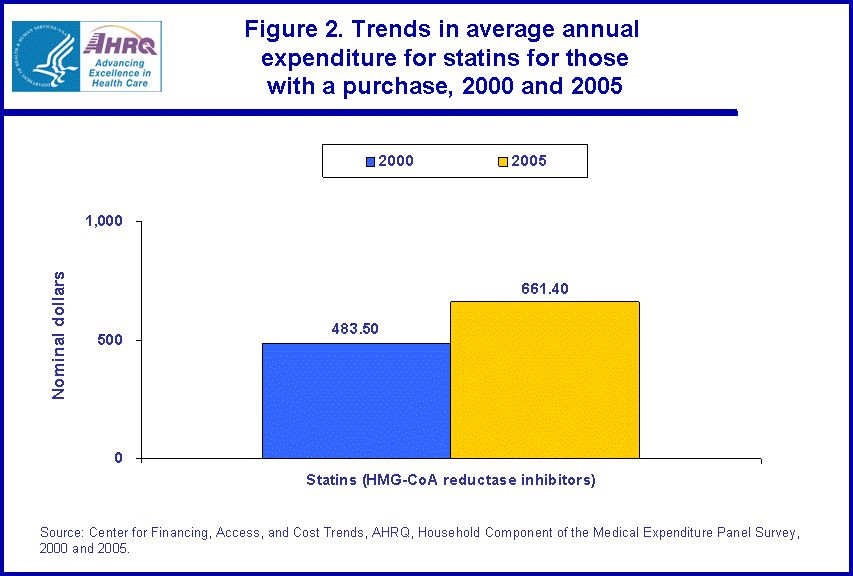
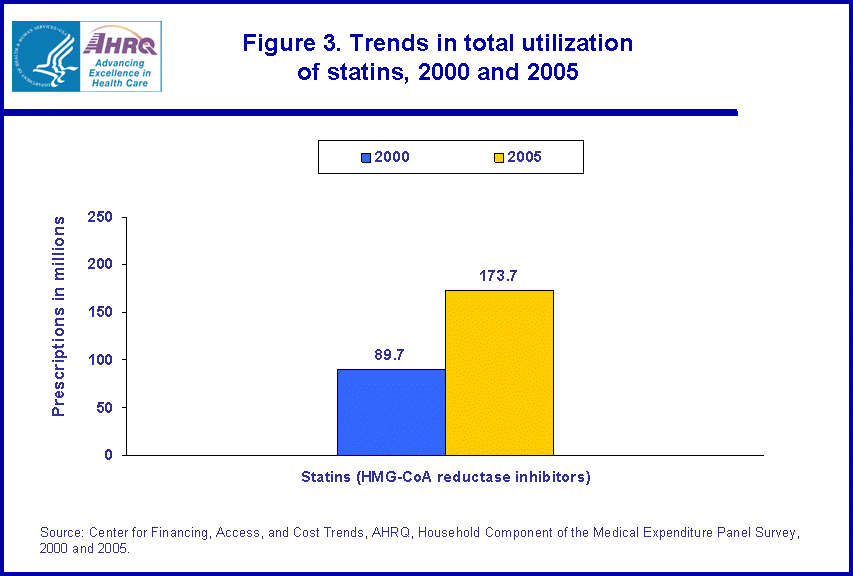
- When comparing 2000 and 2005, total number of outpatient prescription purchases of statins nearly doubled, increasing from 89.7 million prescription purchases in 2000 to 173.7 million prescription purchases.
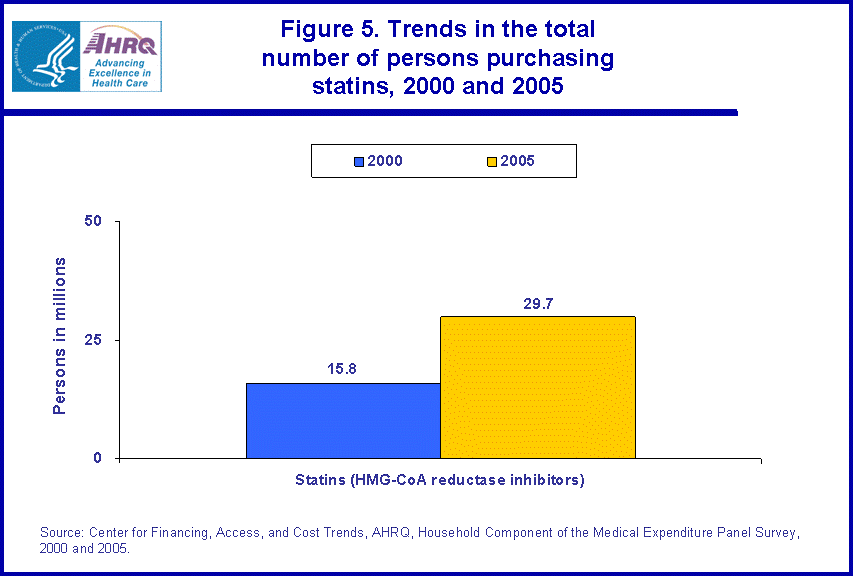
- The number of persons purchasing a statin increased 88 percent from 2000 to 2005, rising from 15.8 million people to 29.7 million people.
Introduction
This Statistical Brief examines trends for 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors, commonly know as statins, for the years 2000 and 2005. The data included in this brief are derived from 2000 and 2005 data for the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population from the Household Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS-HC). The brief compares 2000 and 2005 total expenditures, total number of purchases, and total number of persons purchasing, as well as average total expenditure and average number of purchases of statins for those with one or more statin purchases.
Only prescribed medicine purchases in an outpatient setting are included in the estimates presented in this brief. Prescription medicines administered in an inpatient setting or in a clinic or physician's office are excluded from these estimates. Expenditures are in nominal dollars. All differences discussed in the text are statistically significant at the 0.05 level.
Findings
When comparing 2000 and 2005, MEPS estimates showed an increase of 156 percent from $7.7 billion in 2000 to $19.7 billion in 2005 for total outpatient prescription expenditures for HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor prescribed drugs, which are more commonly known as statins (figure 1).
When comparing 2000 and 2005, for those with a drug purchase (173.3 million persons in 2000, and 187.0 million persons in 2005), the average annual expenditure for statins increased about 37 percent from 2000 to 2005 ($484 and $661, respectively) (figure 2).
Total prescribed medicine purchases of statins nearly doubled from 2000 to 2005 rising from 89.7 million prescriptions to 173.7 million prescription purchases (figure 3).
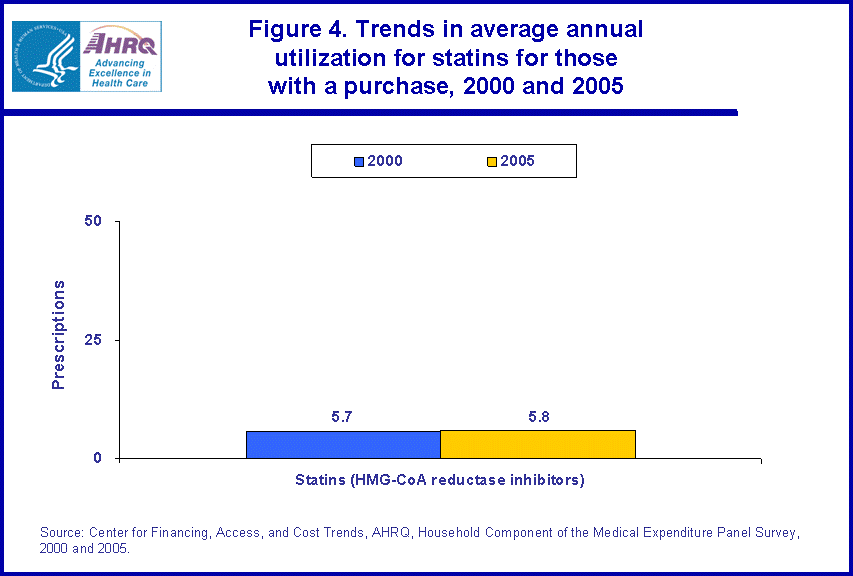
There were no significant differences in average annual utilization for those persons with one or more statin purchases when comparing the years 2000 and 2005 (figure 4).
The number of people purchasing statins nearly doubled when comparing 2000 and 2005, rising from 15.8 million people to 29.7 million people (figure 5).
Data Source
The estimates presented in this Statistical Brief are based on data from the HC-094A 2005 Prescribed Medicines File and HC-051A 2000 Prescribed Medicines File.
Definitions/Methodology
Utilization and expenditures
Utilization was defined as one or more purchases of a prescribed medicine of interest. Refills as well as original prescriptions are included in expenditure and utilization estimates. Individuals were classified as using a prescribed medicine of interest if they had one or more purchases of the drug of interest during the year. Expenditures are in nominal dollars.
Therapeutic classifications
Therapeutic class and subclass were assigned to MEPS prescribed medicines using Multum Lexicon variables from Cerner Multum, Inc. MEPS prescribed medicines files were linked to the Multum Lexicon database to obtain therapeutic class and subclass variables. For additional information on these and other Multum Lexicon variables, as well as the Multum Lexicon database itself, please refer to the following Web site: http://www.multum.com/Lexicon.htm.
About MEPS-HC
MEPS-HC is a nationally representative longitudinal survey that collects detailed information on health care utilization and expenditures, health insurance, and health status, as well as a wide variety of social, demographic, and economic characteristics for the civilian noninstitutionalized population. It is cosponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Center for Health Statistics.
For more information about MEPS, call the MEPS information coordinator at AHRQ (301-427-1656) or visit the MEPS Web site at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/.
References
For a detailed description of the MEPS-HC survey design, sample design, and methods used to minimize sources of nonsampling error, see the following publications:
Cohen, J. Design and Methods of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 1. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0026. Rockville, MD: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/mr1/mr1.shtml
Cohen, S. Sample Design of the 1996 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 2. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0027. Rockville, MD: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/mr2/mr2.shtml
Cohen, S. Design Strategies and Innovations in the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. Medical Care, July 2003: 41(7) Supplement: III-5-III-12.
Ezzati-Rice, TM, Rohde, F, Greenblatt, J, Sample Design of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component, 1998-2007. Methodology Report No. 22. March 2008. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/mr22/mr22.pdf
Suggested Citation
Stagnitti, M. N. Trends in Statins Utilization and Expenditures for the U.S. Civilian Noninstitutionalized Population, 2000 and 2005. Statistical Brief #205. May 2008. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st205/stat205.pdf
AHRQ welcomes questions and comments from readers of this publication who are interested in obtaining more information about access, cost, use, financing, and quality of health care in the United States. We also invite you to tell us how you are using this Statistical Brief and other MEPS data and tools and to share suggestions on how MEPS products might be enhanced to further meet your needs. Please e-mail us at mepspd@ahrq.gov or send a letter to the address below:
Steven B. Cohen, PhD, Director
Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
540 Gaither Road
Rockville, MD 20850
 |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||