|
|
Font Size:
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
STATISTICAL BRIEF #32:
Reasons for Lacking a Usual Source of Care: 2001 Estimates for the U. S. Civilian Noninstitutionalized Population
Highlights
- Approximately 51.9 million people (18.4 percent of the total population) reported having no usual source of care in 2001.
- Hispanics were the most likely to report having no usual source of care.
- Men were more likely than women to report having no usual source of care.
- People between the ages of 19 and 24 were the most likely to report having no usual source of care, while children under 6 and the elderly were the least likely to report having no usual source of care.
- The reason most respondents gave for not having a usual source of care was that they were seldom sick.
Introduction
Adequate access to care, including equal access among all segments of the population, is an important dimension of a quality health care system. Having a usual source of care is one indicator of access to care. People with a usual source of care have been shown to receive more preventive health care services than those without a usual source of care. Having a usual source of health care, however, can vary among groups with different demographic and health-related characteristics, including age, race/ethnicity, sex, perceived health status, health insurance coverage, and place of residence.
In this Statistical Brief, data from the Access to Care Supplement of the 2001 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Household Component (MEPS-HC) were used to estimate 1) the proportion of people who lack a usual source of care, by race/ethnicity, sex, and age; and 2) the proportions by race/ethnicity with regard to the reasons for not having a usual source of care.
Findings
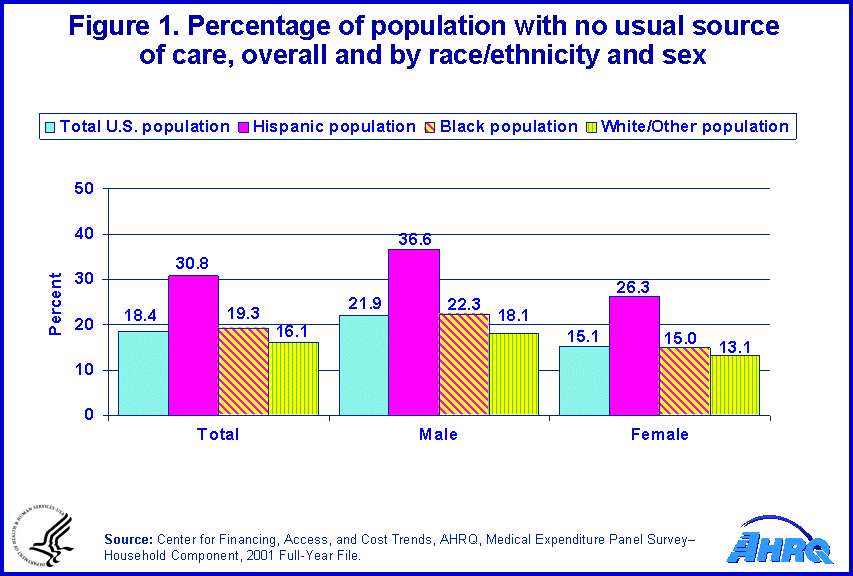
In 2001, approximately 18.4 percent of the total population reported having no usual source of care (figure 1). This means that more than 51 million Americans could not name a doctor, clinic, health center, or other place that they would usually visit when sick. Consistent with previous findings, lacking a usual source of care was associated with gender, race/ethnicity, and age. Hispanics were more likely to report having no usual source of care (30.8 percent) than blacks (19.3 percent) and whites (16.1 percent). Men were more likely to report having no usual source of care than women (21.9 percent and 15.1 percent, respectively).
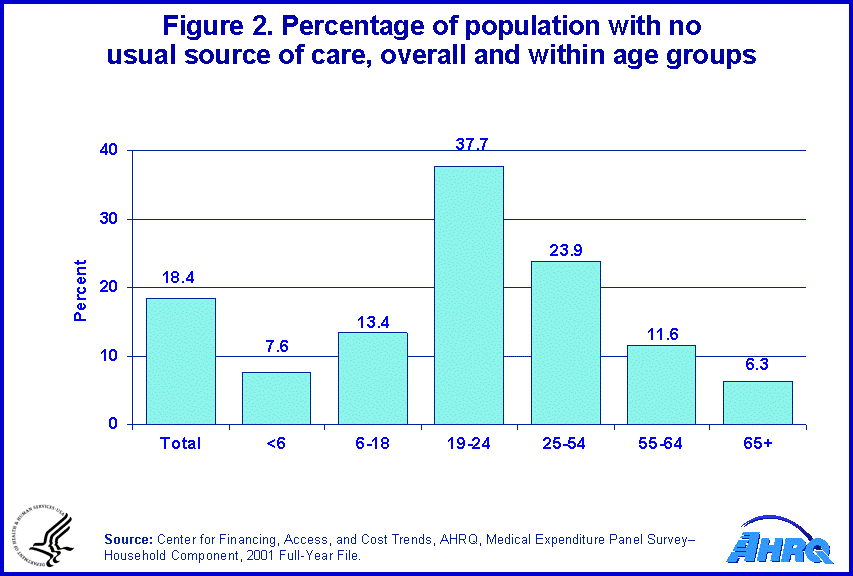
Not having a usual source of care also varied by age (figure 2). Approximately 13.4 percent of children, ages 6 to 18, were reported to have had no usual source of care. Adults between the ages of 19 and 24 were the most likely to report having no usual source of care (37.7 percent). Of those between the ages of 25 and 54, 23.9 percent reported having no usual source of care, while 11.6 percent of those between the ages of 55 and 64 reported having no usual source of care. In comparison, persons under 6 years of age and persons 65 and over were the least likely to report having no usual source of care (7.6 percent and 6.3 percent, respectively).
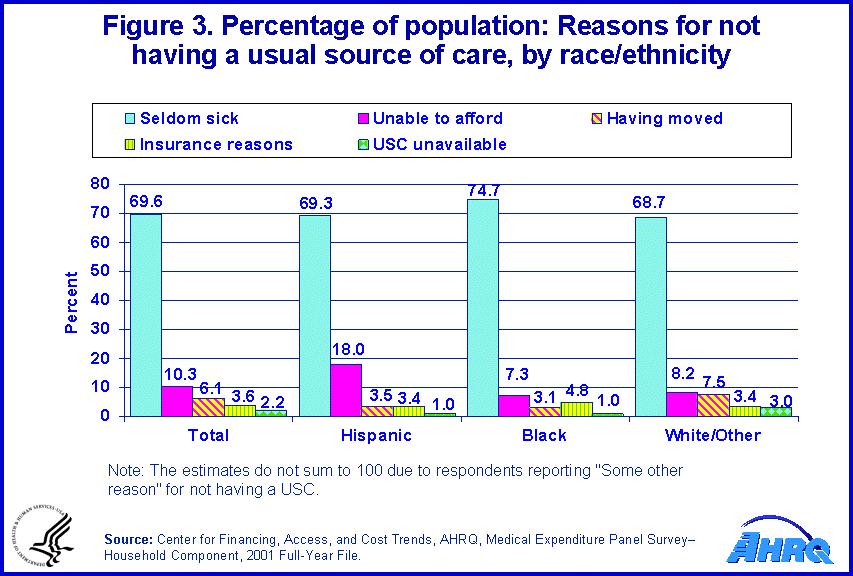
When asked to report the reason for lacking a usual source of care, 69.6 percent of the population reported that they were seldom sick (figure 3). Approximately 10.3 percent reported that they were unable to afford medical care, and 6.1 percent reported that they had recently relocated to the area. Nearly 3.6 percent of the population cited that insurance-related problems prevented them from having a usual source of care. Hispanics were more likely to report that they could not afford a usual source of care (18.0 percent) than blacks or whites (7.3 percent and 8.2 percent, respectively).
Data Source
The data from the Access to Care Supplement of the 2001 MEPS-HC data were collected using computer-assisted personal interviews. One household respondent reported information for all members of the household. The survey had a sample size of 33,556 respondents and a response rate of 71.4 percent.
Definitions
Usual source of care is defined as a particular doctor's office, clinic, health center, or other place where a person usually goes if he or she is sick or needs advice about personal health matters.
Race/ethnicity is coded hierarchically into the following codes: Hispanic, black, and white/other.
About MEPS-HC
MEPS-HC is a nationally representative longitudinal survey that collects detailed information on health care utilization and expenditures, health insurance, and health status, as well as a wide variety of social, demographic, and economic characteristics for the civilian noninstitutionalized population. It is cosponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) and the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS).
References
For a detailed description of the MEPS-HC survey design, sample design, and methods used to minimize sources on nonsampling error, see the following publications:
Cohen, J. Design and Methods of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 1. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0026. Rockville, Md.: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997.
Cohen, S. Sample Design of the 1996 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 2. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0027. Rockville, Md.: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997.
These publications and more information about MEPS are available on the MEPS Web site: http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/.
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||