|
|
Font Size:
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
STATISTICAL BRIEF #428:
Trends in Health Care Expenditures for Children under Age 18: 2001, 2006, and 2011
Highlights
- A similar proportion (about 85 percent) of children had some expenses for health care in 2001, 2006, and 2011.
- In 2011 the average total annual expense per child with expenses was higher than 2001.
- The proportion of children with expenses for prescribed medicines in 2011 was lower than 2001. Conversely, the proportion with expenses for office-based care and for dental visits was slightly higher in 2011 than 2001.
- The average expense per physician office visit for children was higher in 2011 than in 2006 or 2001.
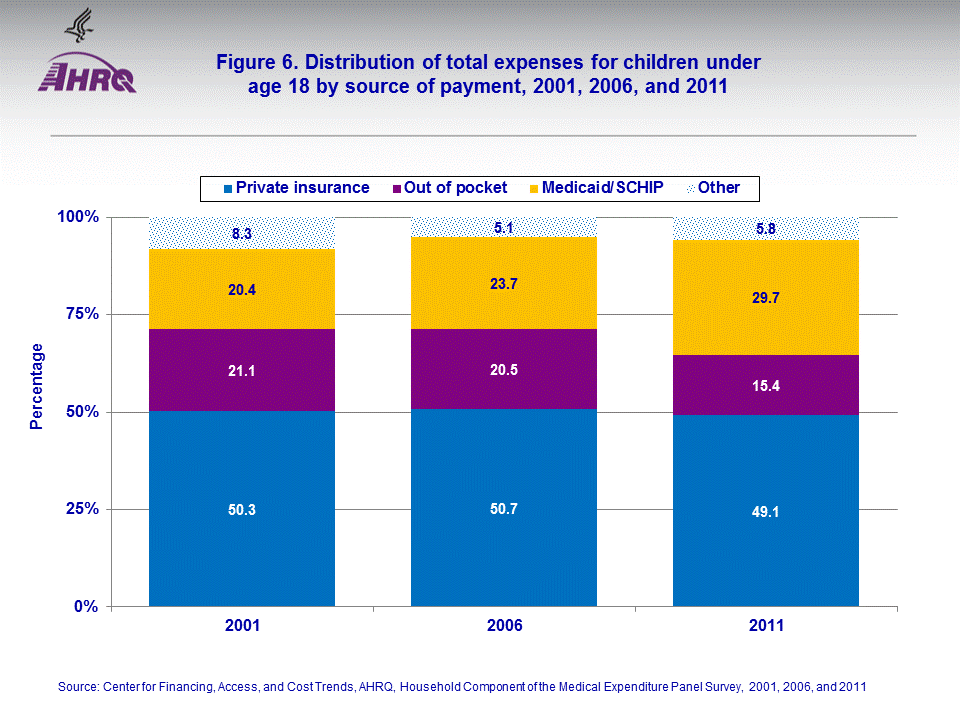
- A notably higher proportion of children's medical expenses was paid by Medicaid/SCHIP in 2011 than in 2001 and the proportion paid out of pocket was significantly lower in 2011 (15.4 percent) than in 2006 or 2001.
Introduction
This Statistical Brief compares summary statistics on health care expenditures and expenditure distributions by type of service and sources of payment for children under age 18 in 2001, 2006, and 2011. The estimates are derived from data collected in the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household (MEPS-HC) and Medical Provider Components (MEPS-MPC) on the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population. Health care expenses in MEPS represent payments to physicians, hospitals, and other health care providers for services reported by respondents to the MEPS-HC. Estimates for 2001 and 2006 were adjusted to 2011 dollars based on the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Price Index to remove the impact of medical price inflation on comparisons (http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/about_meps/Price_Index.shtml). All differences between estimates noted in the text are statistically significant at the 0.05 level or better.Findings
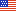
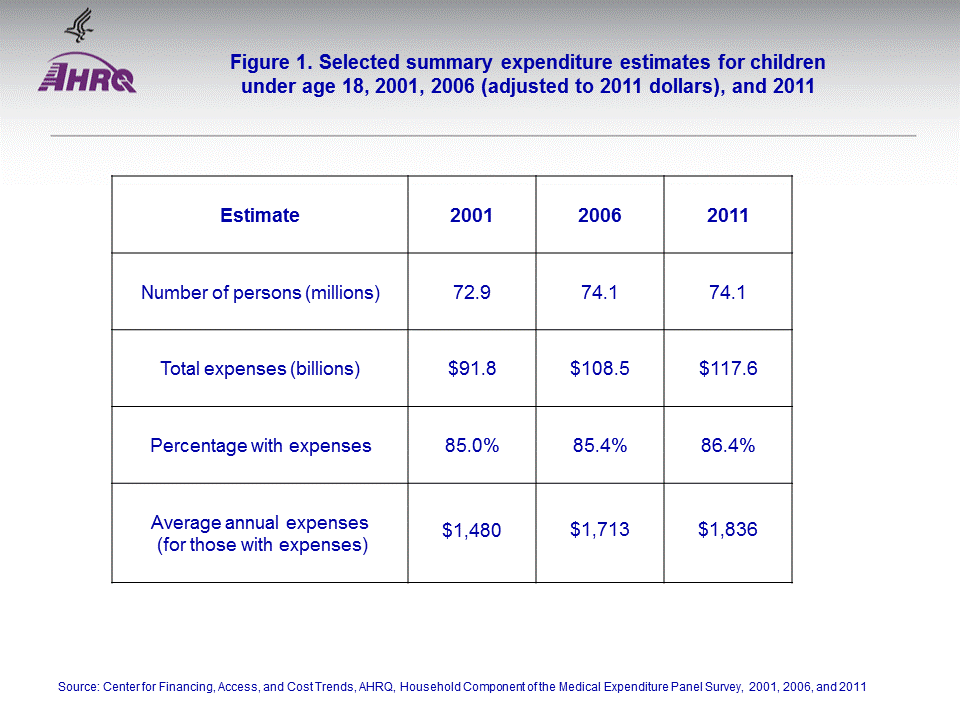
Summary expenditure statisticsTotal health care expenses for children in 2011 ($117.6 billion) did not differ significantly from 2006 but was slightly higher than in 2001 ($91.8 billion adjusted to 2011 dollars) (figure 1). A similar proportion of children had some expenses for health care in each year, about 85 percent. The average annual expense per child with expenses was higher in 2011 ($1,836) than in 2001 ($1,480 in 2011 dollars). However, differences in average expenses between 2006 and 2001 or 2011 were not significant. In 2011, the median annual health care expenditure for children was $415 (figure 2), with about one-quarter of children having expenses under $116 (25th percentile) and one-quarter having expenses over $1,243 (75th percentile). These quartiles in 2011 were higher than in 2001 (after adjusting for inflation).
Expenditures by type of service
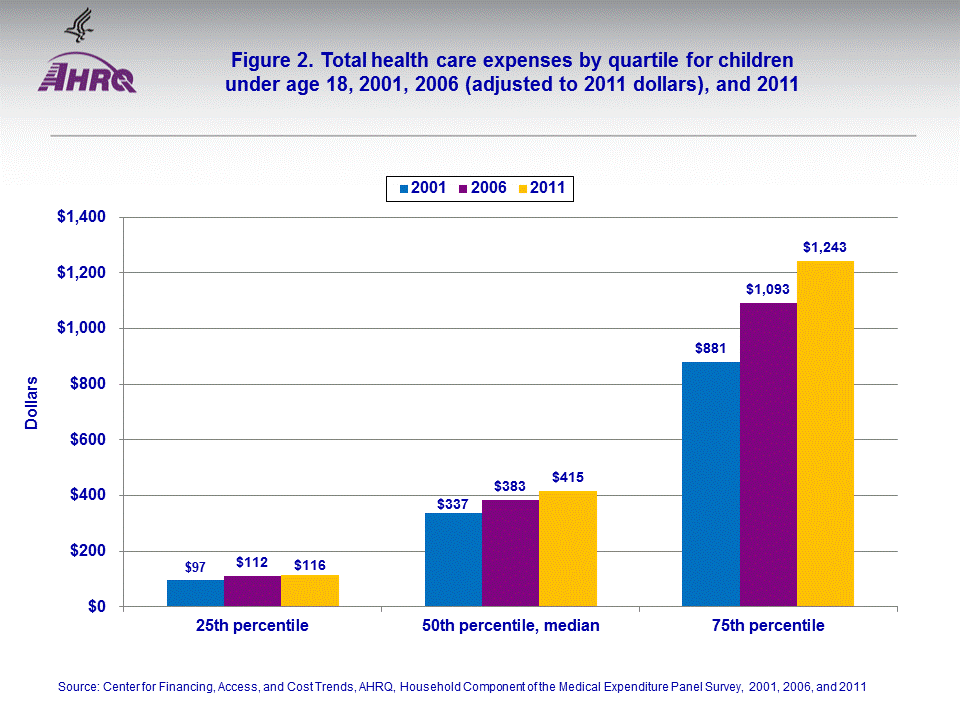
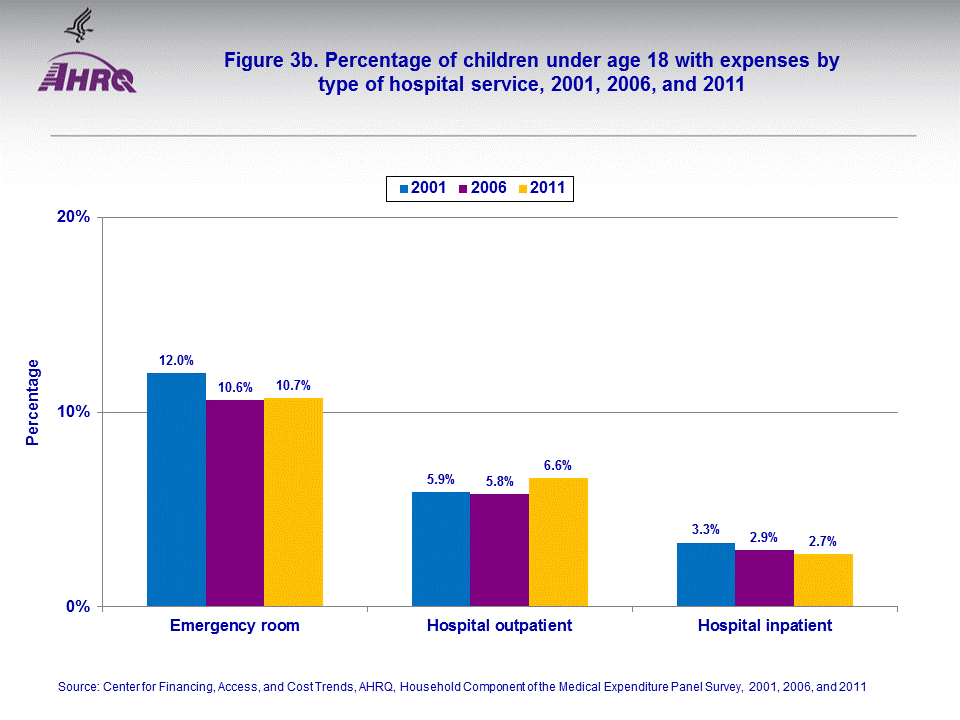
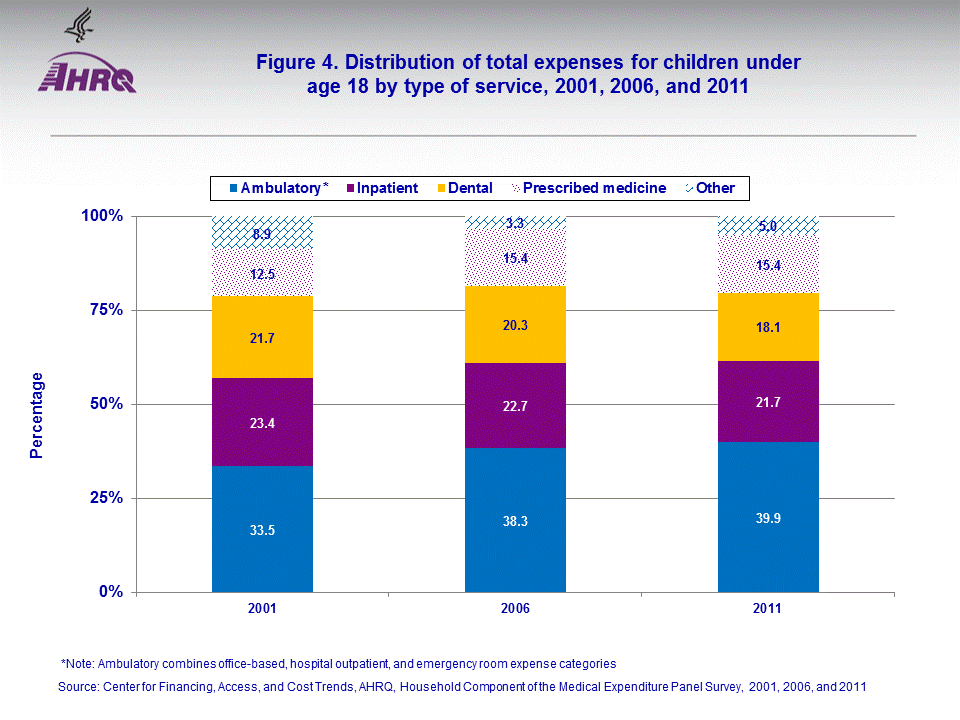
The proportion of children with expenses for prescribed medicines in 2011 was lower than in 2001 (46.7 versus 52.0 percent). Conversely, the proportions with expenses for office-based care and for dental visits were slightly higher in 2011 than 2001 (figure 3a). The percentages of children with expenses for hospital services were fairly similar across the three years (figure 3b).
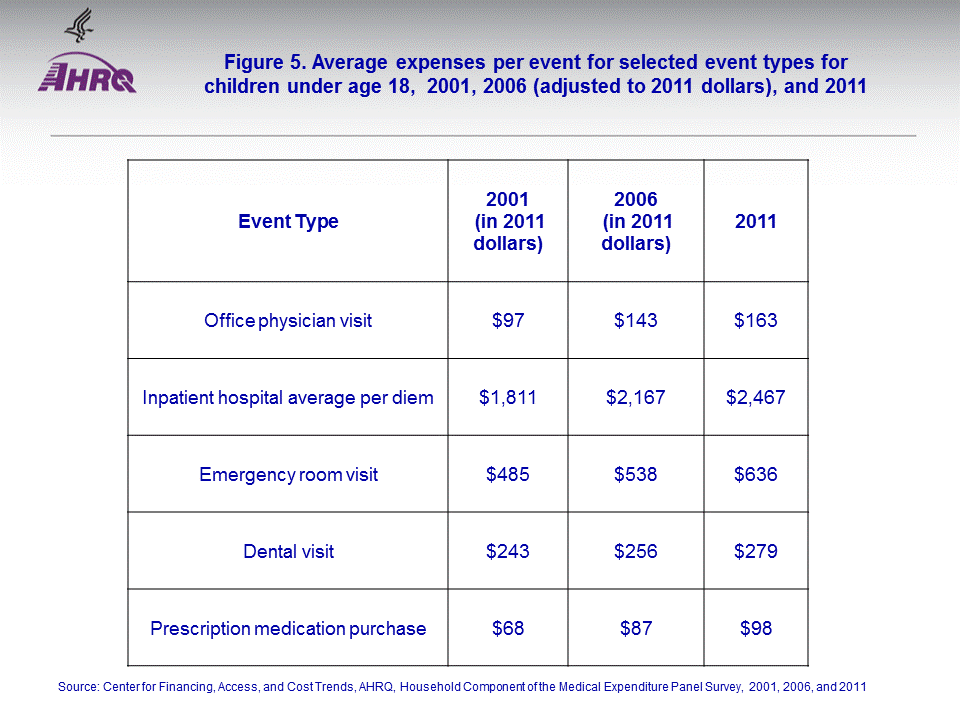
The average expense per physician office visit was higher in 2011 ($163) than in 2006 ($143 adjusted to 2011 dollars) or 2001 ($97 adjusted to 2011 dollars) (figure 5). For emergency room visits, dental visits, and per diem inpatient hospital stays the average expenses per event were higher in 2011 than in 2001. However, the average expense per prescription medication purchase was not significantly different across the three years.
Expenditures by source of payment
About half of all expenses for children were paid by private insurance in all three years (figure 6). However, a notably higher proportion of expenses were paid by Medicaid/SCHIP in 2011 (29.7 percent) than in 2001 (20.4 percent), and the proportion paid out of pocket was significantly lower in 2011 (15.4 percent) than earlier years (about 21 percent).
Data Source
The estimates in this Statistical Brief are based upon data from the 2011, 2006, and 2001 Full Year Consolidated (HC-147, HC-105, and HC-60, respectively) and Event Level Data Files (HC-144, HC-102, and HC-59 A, B, D, E, and G).Definitions
Expenditures (expenses)Expenditures include the total direct payments from all sources to hospitals, physicians, other health care providers (including dental care), and pharmacies for services reported by respondents in the MEPS-HC. Expenditures for hospital-based services include those for both facility and separately billed physician services. Estimates for 2001 and 2006 were adjusted to 2011 dollars based on the GDP Price Index (http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/about_meps/Price_Index.shtml). Health insurance premiums are not included as expenses.
Type of service
- Office-based: Includes expenses for visits to both physician and non-physician medical providers seen in office settings.
- Hospital inpatient: Includes room and board and all hospital diagnostic and laboratory expenses associated with the basic facility charge, payments for separately billed physician inpatient services, and some emergency room expenses incurred immediately prior to inpatient stays.
- Hospital outpatient: Includes expenses for visits to both physicians and other medical providers seen in hospital outpatient departments, including payments for services covered under the basic facility charge and those for separately billed physician services.
- Emergency room: Includes payments for services covered under the basic facility charge and those for separately billed physician services, but excludes expenses for emergency room services that are included in a hospital inpatient admission.
- Prescribed medicines: Includes expenses for all prescribed medications that were initially purchased or refilled during the year, as well as expenses for diabetic supplies.
- Dental: Includes payments for services to any type of dental care provider, including general dentists, dental hygienists, dental technicians, dental surgeons, orthodontists, endodontists, and periodontists.
- Ambulatory: Combines office-based, hospital outpatient, and emergency room expense categories described above.
- Other: Includes expenses for care in all categories not specified as a separate category, including those for home care and for miscellaneous medical equipment and supplies.
- Private insurance: This category includes payments made by insurance plans covering hospital and medical care (excluding payments from Medicare, Medicaid, and other public sources), Medigap plans, or TRICARE (Armed Forces-related coverage). Payments from plans that provide coverage for a single service only, such as dental or vision coverage, are not included.
- Medicaid/SCHIP: Medicaid and SCHIP are means-tested government programs jointly financed by Federal and state funds that provide health care to those who are eligible. Medicaid is designed to provide health coverage to families and individuals who are unable to afford necessary medical care while SCHIP provides coverage to additional low income children not eligible for Medicaid. Eligibility criteria for both programs vary significantly by state.
- Out of pocket: This category includes expenses paid by the user or other family member.
- Other sources: This category includes payments from Medicare, other miscellaneous Federal sources (Indian Health Service, military treatment facilities, and other care provided by the Federal government); various state and local sources (community and neighborhood clinics, state and local health departments, and state programs other than Medicaid/SCHIP); various unclassified sources (e.g., automobile, homeowner's, or other liability insurance, and other miscellaneous or unknown sources); Medicaid/SCHIP payments reported for persons who were not reported as enrolled in the Medicaid or SCHIP programs at any time during the year; and private insurance payments reported for persons without any reported private health insurance coverage during the year.
About MEPS-HC
MEPS-HC is a nationally representative longitudinal survey that collects detailed information on health care utilization and expenditures, health insurance, and health status, as well as a wide variety of social, demographic, and economic characteristics for the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population. It is cosponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Center for Health Statistics.For more information about MEPS, call the MEPS information coordinator at AHRQ (301) 427-1406 or visit the MEPS Web site at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/.
References
For a detailed description of the MEPS survey design, sample design, and methods used to minimize sources of nonsampling error, see the following publications:Cohen, J., Cohen S., and Banthin, J. “The Medical Expenditure Panel Survey: A National Information Resource to Support Healthcare Cost Research and Inform Policy and Practice.” Medical Care 2009, 47(7), Supplement, pp S44–S50.
Cohen, J. Design and Methods of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 1. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0026. Rockville, MD: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/mr1/mr1.shtml
Ezzati-Rice, T.M., Rohde, F., Greenblatt, J. Sample Design of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component, 1998–2007. Methodology Report No. 22. March 2008. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/mr22/mr22.shtml
Suggested Citation
Mirel, L.B., and Carper, K. Trends in Health Care Expenditures for Children under Age 18: 2001, 2006, and 2011. Statistical Brief #428. January 2014. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st428/stat428.shtmlAHRQ welcomes questions and comments from readers of this publication who are interested in obtaining more information about access, cost, use, financing, and quality of health care in the United States. We also invite you to tell us how you are using this Statistical Brief and other MEPS data and tools and to share suggestions on how MEPS products might be enhanced to further meet your needs. Please email us at MEPSProjectDirector@ahrq.hhs.gov or send a letter to the address below:
Steven B. Cohen, PhD, Director
Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
540 Gaither Road
Rockville, MD 20850
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||