|
|
Font Size:
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
STATISTICAL BRIEF #48:
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance Characteristics, by Average Payroll for the Private Sector, 2002
Highlights
- Without exception, the offer, eligibility, and enrollment rates increased across quartiles with increasing average payrolls. Thus, the rates for these items were all lowest for the first payroll quartile and highest for the fourth payroll quartile.
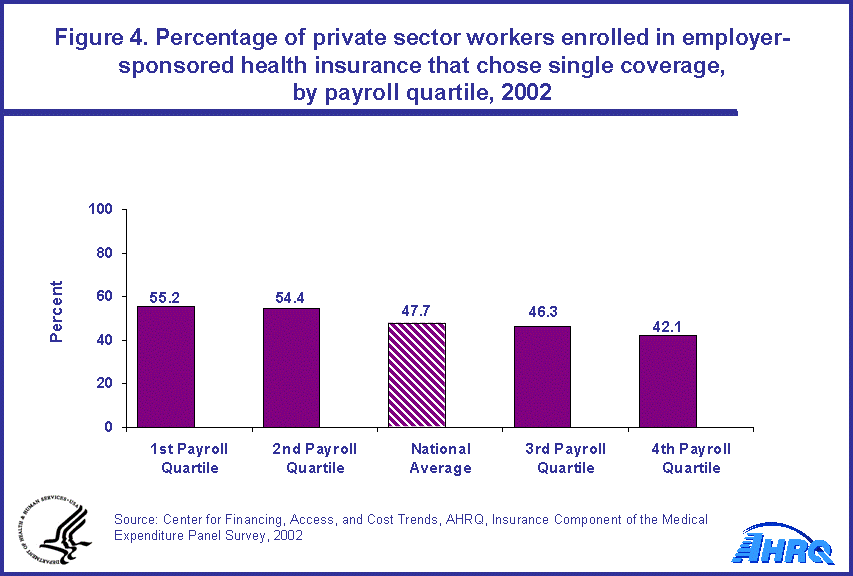
- The percentage of enrollees who selected single coverage rather than family of four coverage in each quartile had the reverse order of the average payroll per employee. The quartile with the least payroll per employee had the highest selection rate of single coverage and that with the highest payroll per employee had the lowest selection rate for single coverage.
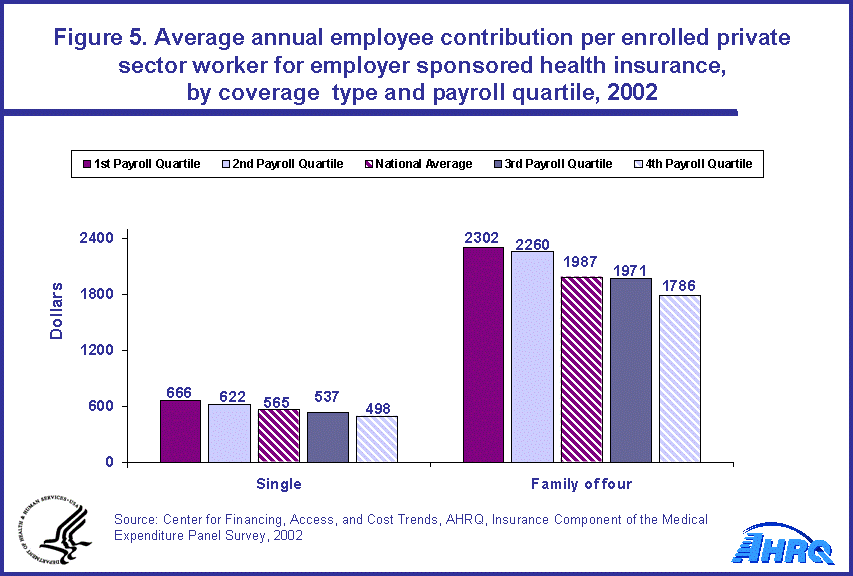
- Average employee contributions, for both single and family of four coverage, declined as payroll rose. The highest average contributions were required of the employees in the lowest payroll quartile and the lowest contributions for the highest payroll quartile.
Introduction
One of the primary sources of health coverage in the United States is coverage provided through employers for their current employees. According to data from the Insurance Component of the 2002 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS-IC), approximately 61.6 million of the 111.5 million employees in the private sector are enrolled in a health insurance plan sponsored by their employer. (Data not shown in figures.)
Many factors are associated with whether an employee has access to a health insurance plan sponsored by his or her employer, whether the employee enrolls, and what the employee contributes towards the cost of coverage. Employer characteristics associated with employer-sponsored health insurance include the size of the employer, the industry, and whether there is a union present.
Employee compensation may also be associated with the provision and cost of employer-sponsored health insurance. In order to analyze the effect of compensation level, private sector establishments from the 2002 MEPS-IC were grouped by compensation level. Average payroll (compensation excluding fringe benefits) per employee was used as an indicator of compensation level.
This Statistical Brief compares the offer, eligibility, enrollment rates, and the level of employee contributions for private sector establishments (business location), grouped by the average payroll per employee. Each group or quartile contains 25 percent of the total number of employees in the private sector, and each group represents establishments with progressively higher average payrolls. Thus, the first group contains 25 percent of employment in the establishments with the lowest average payrolls per employee while the fourth group contains the highest 25 percent. Only those differences between quartiles that are statistically significant at the 0.05 significance level are discussed. Additional details on the grouping methodology are contained in the Definitions section of this report.
Findings
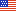
In 2002, the percentage of employees in the private sector who worked where health insurance was offered increased with average payroll. Thus, 72.4 percent of all employees in the first payroll quartile, 88.1 percent of those in the second quartile, 95.9 percent of those in the third payroll quartile, and 97.4 percent of those in the fourth payroll quartile worked where health insurance was offered (figure 1).
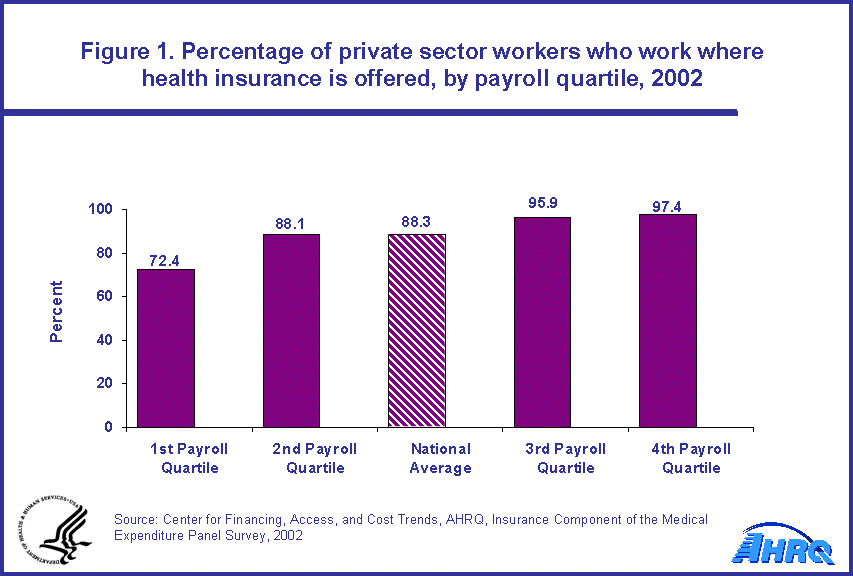
The percentage eligible for health insurance where health insurance was offered followed this same pattern for all employees. Thus, among the employees at establishments that offered health insurance, in the first quartile of establishments only 55.5 percent of these employees were eligible for health insurance while 89.9 percent were eligible in the fourth quartile, which had the highest average payrolls (figure 2).
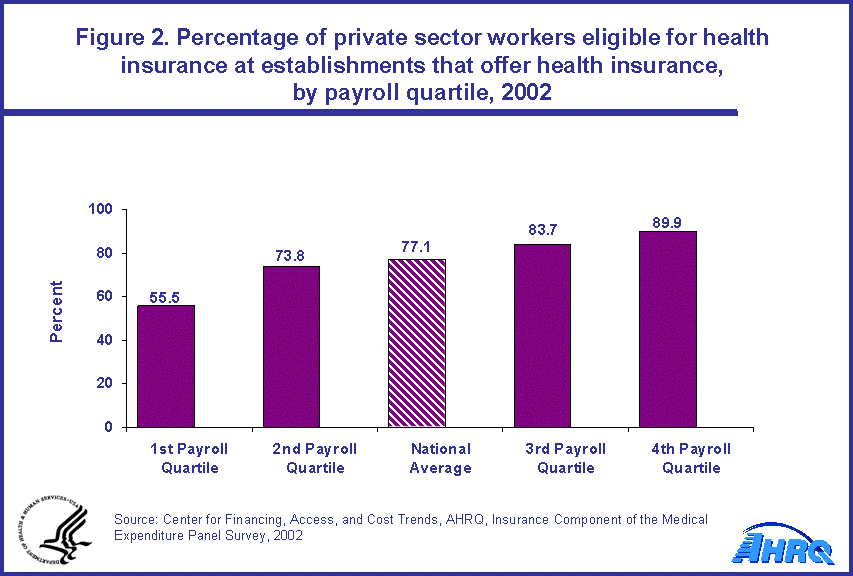
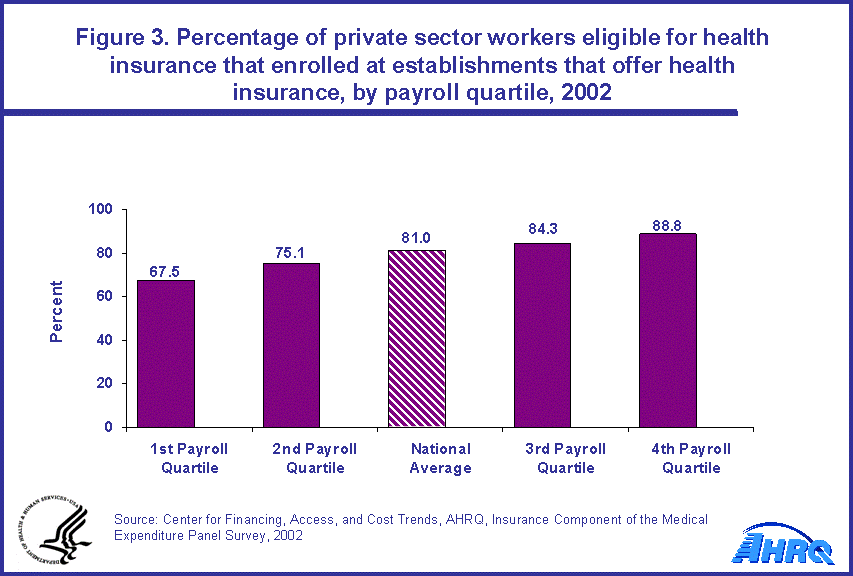
Employers control whether health insurance is offered and who is eligible. Employees choose who enrolls. When the employees could choose whether or not to enroll in employer-sponsored health insurance, the same increasing pattern held as payroll rose. Among all eligible employees in the establishments in the first quartile of average payroll, only 67.5 percent enrolled in health insurance compared to 75.1 percent in the second quartile, 84.3 percent in the third quartile, and 88.8 percent in the fourth quartile (figure 3).
Considering the offer (72.4 percent, figure 1), eligibility (55.5 percent, figure 2), and enrollment (67.5 percent, figure 3) rates, the percentage of all employees in quartile one who were enrolled in health insurance in employer-sponsored health insurance in 2002 was 27.1 percent (.724 x .555 x .675 = .271). The same estimates for quartiles two, three, and four (obtained using the products of results from figures 1, 2, and 3) were 48.8, 67.7, and 77.8 percent, respectively.
The type of coverage that employees from each of the payroll quartiles tended to select also differed. The enrollment rate for single coverage for the first two quartiles, 55.2 percent for the first quartile and 54.4 percent for the second, were higher than the national average of 47.7 percent. The rate for the third quartile was 46.3 percent, about the national average. For the fourth quartile, the value was 42.1 percent, which was lower than the national average (figure 4).
Employee contributions towards the premium for both single and family of four coverage decreased as average payroll rose. The higher the average payroll per employee, the lower the average employee contribution per employee for employer-sponsored health insurance. Single contributions fell from $666 per enrollee for the first quartile to $498 for the fourth quartile. Similarly, the employee contributions for family of four coverage fell across the groups from $2,302 to $1,786 (figure 5).
Data Source
This Statistical Brief summarizes data from the 2002 MEPS-IC. The data are available on the MEPS Web site (http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/) or have been produced using special computation runs using the confidential MEPS-IC data available at the U.S. Bureau of the Census.
Definitions
In this Statistical Brief, an establishment is defined as a single business location. Multiple establishments can be controlled by a single entity denoted as a firm. Establishments from the same firm can be in different payroll quartiles defined in the Introduction.
This analysis includes only establishments from the private sector.
Quartiles are groups of establishments, each of which contains 25 percent of the total employment. To determine the establishments within each of these employment quarters or quartiles, the following process was used:
- The list of establishments were placed in order from lowest to highest average payroll per employee.
- Starting with the establishment with the lowest average payroll, the employment was summed until the cumulative employment of the establishments on the list was 25 percent of the total employment of all establishments. The set of establishments on the list to that point are in the first quartile.
- The second quartile begins with the next establishment on the list and includes all establishments from that point on the list until the cumulative employment reaches 50 percent.
- The third quartile includes all establishments after the second quartile and ends with the establishment that brings the cumulative employment to 75 percent of the total.
- The fourth quartile includes all establishments above the third quartile.
Payroll includes all forms of compensation, such as salaries, wages, commissions, dismissal pay, bonuses, and employee contributions to pension plans, but excludes fringe benefits. This definition is the same as that used by the Internal Revenue Service on Form 941.
About MEPS-IC
MEPS-IC is a survey of business establishments and governments that collects information on employer-sponsored health insurance, such as whether insurance is offered, enrollments, types of plans, and premiums. The survey is conducted annually by the U.S. Bureau of the Census under the sponsorship of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The yearly response rate has averaged 78 percent for in-scope sample units. Approximately 4 percent of the original sample has been out-of-scope in a typical year. A total sample of 42,000 establishments was selected for the 2002 survey, prior to accounting for losses due to non-response and out-of-scope cases.
For more information on MEPS-IC, see MEPS Methodology Reports 6, 8, and 10 under MEPS publications at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_stats/publications.jsp and the MEPS-IC Technical Appendix at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/survey_comp/ic_technical_notes.shtml.
Suggested Citation
Sommers, J. Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance Characteristics, by Average Payroll for the Private Sector, 2002. Statistical Brief #48. July 2004. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st48/stat48.shtml
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||