|
|
Font Size:
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
STATISTICAL BRIEF #53:
Employee Copays and Deductibles for Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance in 1999 and 2002
Highlights
- From 1999 to 2002, the average single deductible per single enrollee with a deductible increased from $335 to $409. Although there was significant variation in the average single deductible by size of employer and economic sector (public, private), the average single deductible increased for employees in all these employer groups.
- The average family deductible per family enrollee with a deductible increased from $772 to $920 during the period 1999 to 2002. There were significant differences in the level of this deductible by size of employer and economic sector (public, private), family deductibles increased for employees in all these employer groups.
- From 1999 to 2002, the percentage of enrollees in employer-sponsored health insurance who had no dollar or percentage copay for a physician office visit fell from 7.9 percent to 5.1 percent. There were significant reductions across economic sectors (public, private) and small and large employers.
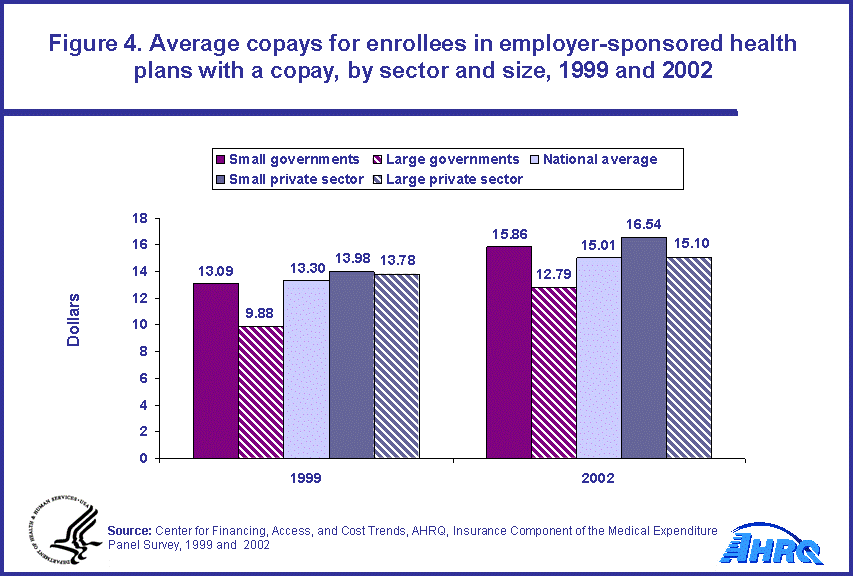
- The average dollar copay for a physician office visit increased from $13.30 to $15.01 over the period 1999 to 2002. This copay varied significantly by type of employer but increased for each economic sector (public, private) and size of employer.
Introduction
While the percentage of workers covered by employer-sponsored health insurance has declined in recent years, such insurance continues to be one of the primary sources of health coverage in the United States. According to data from the Insurance Component of the 2002 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS-IC), 55.1 percent of private sector employees were enrolled in health insurance sponsored by their employer.
Using data from the 1999 and 2002 MEPS-IC, this Statistical Brief examines the values of copays and deductibles for employer-sponsored health insurance. Private sector and public sector (state and local government) employers are examined separately and within each sector by size of employer. Small employers are defined as those having fewer than 50 employees; large employers are those with 50 or more employees. Only those differences that are statistically significant at the 0.05 significance level are discussed in the text.
Findings
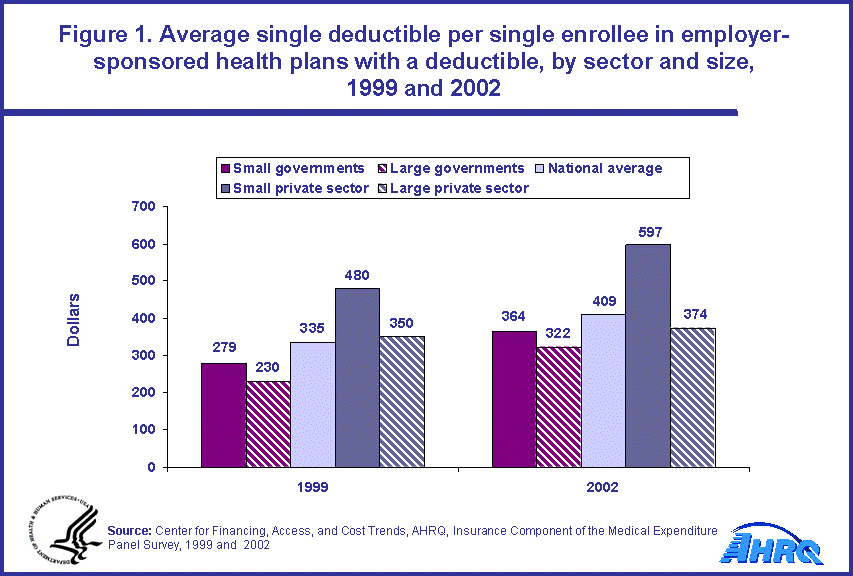
From 1999 to 2002, the percentage of all enrollees in employer-sponsored health insurance who had a plan with a deductible increased from 43.91 percent to 46.63 percent (data not shown). The average single deductible per single enrollee with a deductible increased from $335 to $409 per enrollee over this time period (figure 1). Single deductibles in 2002 were highest within each economic sector (public, private) for small employers. In 2002, in the private sector for single enrollees with a deductible, the average single deductible was $597 in small firms versus $374 in large firms. For the comparably sized employer in the public sector, the single deductible for single enrollees with a deductible was lower: $364 for small governments and $322 for large governments.
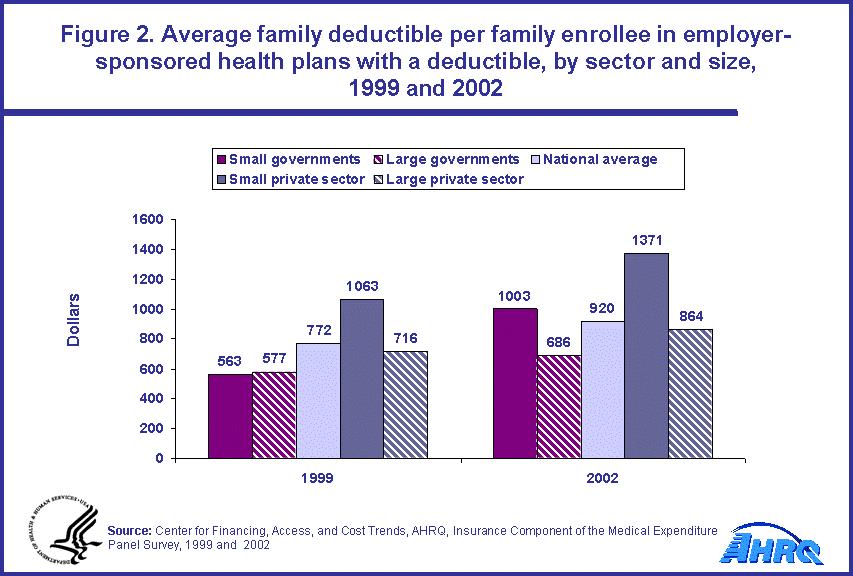
During the 1999 to 2002 time period, the average family deductible per family enrollee in employer-sponsored health insurance increased from $772 to $920 (figure 2). A significant increase in family-level deductibles was experienced by enrollees in all the employer groups. As in the case for single deductibles, the average family deductibles were lower in 2002 for family enrollees in the public sector than the private sector and, within these sectors, large employers required lower family deductibles. The average family deductibles were $1,371 and $864 for small and large employers, respectively, in the private sector versus $1,003 and $686 for small and large employers, respectively, in the public sector.
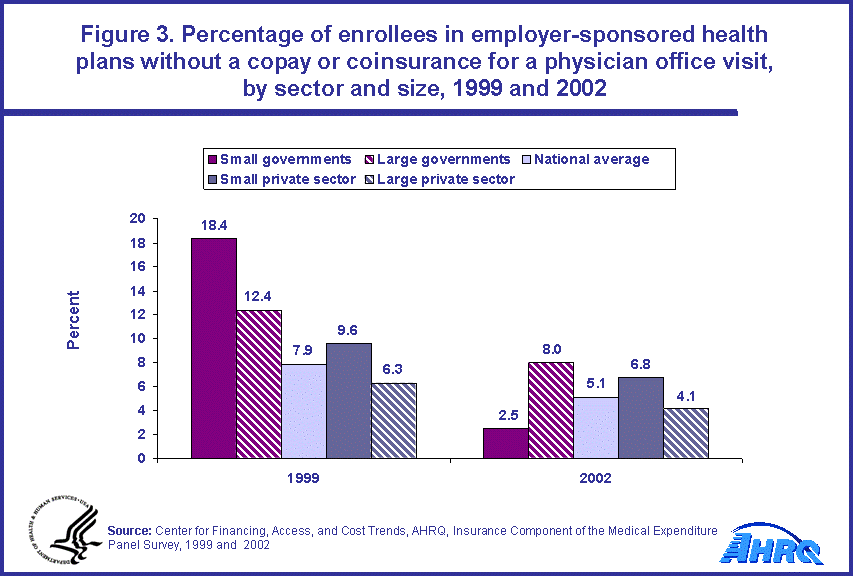
The percentage of enrollees who had neither a copay nor coinsurance for a physician office visit dropped from 7.9 percent to 5.1 percent during the period 1999 to 2002. These percentages dropped for all four groups of employers studied (figure 3). In 2002, the values ranged from 2.5 percent for small governments to 8.0 percent for large governments.
From 1999 to 2002, for those enrollees with a copay for a physician office visit, the average copay per enrollee per visit rose from $13.30 to $15.01 (figure 4). These copays rose for all four groups of employers. Within economic sectors, these copays were lower in 2002 for enrollees in large employer plans than for enrollees in small employer plans. In the private sector, average copays for large employers in 2002 were $15.10 versus $16.54 for small employers. In the public sector, the copays were $12.79 for large employers versus $15.86 for small employers.
Data Source
This Statistical Brief summarizes data from the 1999 and 2002 MEPS-IC. The data are available on the MEPS Web site (http://www.meps.ahrq.gov) or have been produced using special computation runs on the confidential MEPS-IC data available at the U.S. Bureau of the Census.
Definitions
Employer
An employer is defined as a private sector firm or a state or local government. The Federal government is not included. A private sector firm is defined as a business entity that controls one or more business establishments or locations. Thus, an employer can have multiple work locations. For example, a large multi-location auto maker is an employer and a single production plant is not.
Copay
A copay is a fixed dollar amount that an enrollee pays when medical service is received, regardless of the total charge for the service.
Coinsurance
Coinsurance is a fixed percentage that an enrollee pays for medical expenses after the deductible amount, if any, is paid.
Deductible
A deductible is a fixed dollar amount during the benefit period (usually a year) that an insured person pays before the insurer starts to make payments for covered medical services.
About MEPS-IC
MEPS-IC is a survey of business establishments and governments that collects information on employer-sponsored health insurance, such as whether insurance is offered, enrollments, types of plans, and premiums. The survey is conducted annually by the U.S. Bureau of the Census under the sponsorship of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The yearly response rate has averaged 78 percent for in-scope sample units. Approximately 4 percent of the original sample has been out-of-scope in a typical year. A total sample of 42,000 establishments was selected for the 2002 survey, prior to accounting for losses due to non-response and out-of-scope cases.
For more information on MEPS-IC, see MEPS Methodology Reports 6, 8, and 10 under MEPS publications at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_stats/publications.jsp and the MEPS-IC Technical Appendix at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/survey_comp/ic_technical_notes.shtml.
Suggested Citation
Sommers, J. Employee Copays and Deductibles for Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance in 1999 and 2002. Statistical Brief #53. September 2004. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/publications/st53/stat53.shtml
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||