Highlights
#1: The Uninsured in America, 1996
Health Insurance Status of the U.S. Civilian Noninstitutionalized
Population By Karen M. Beauregard, Susan K. Drilea,
Jessica P. Vistnes
Introduction
The Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) collects nationally
representative data on health care use, expenditures, source
of payment, and insurance coverage for the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized
population. MEPS is cosponsored by the Agency for Health Care
Research and Quality (AHRQ) and the National Center for Health
Statistics (NCHS). Preliminary data from the MEPS Household Component
of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS HC), collected
in the first several months of 1996, are shown here. Once time-period
and definitional differences are considered, these estimates
are consistent with the findings of other recent surveys.
^top
Briefly
Stated
- Seventeen percent of the U.S. population
were uninsured throughout the first half of 1996, on average.
This represents almost 44.8 million people who were not covered
by insurance, private or public. A revised estimate of the
uninsured derived from MEPS first-round data, which will
incorporate additional data on payment sources, is expected
to be lower than this initial estimate.
- Over 33 percent of Hispanics and 23
percent of blacks were uninsured throughout the first half
of 1996. Less than 14 percent of other race/ethnicity groups
(including whites) were uninsured.
- Nearly 25 percent of all uninsured
Americans were under 18 years of age. Nearly 11 million children—more
than 15 percent of the Nation's noninstitutionalized children—were
uninsured throughout the first half of 1996.
- Among children most likely to be uninsured
throughout the first half of 1996 were Hispanics, children
living outside metropolitan statistical areas, and those
living in families with adults who had less than a high school
education.
^top
Health
Insurance Status
Throughout the first half of 1996, Hispanics
represented almost 11 percent of the U.S. population but
21 percent of the uninsured. Blacks represented almost 13
percent of the U.S. population and 17 percent of the uninsured.
Other race/ethnicity groups (including whites) represented
almost 77 percent of the U.S. population and 62 percent of
the uninsured. For details, select Figure
1.
Lack of insurance throughout
the first half of 1996 was more common in the South (20 percent
of the region's population) and West (19 percent) than in
the Northeast (14 percent) or Midwest (14 percent). Of all
the uninsured in this country, 41 percent lived in the South.
To see the percentages of all uninsured American in the regions,
select Figure 2.
About 28 percent of
Hispanic children under 18 were uninsured throughout the
first half of 1996, compared with 18 percent of black children
and 12 percent of children of other race/ethnicity groups
(including whites). Hispanic children represented almost
15 percent of the Nation's children but 26 percent of the
Nation's uninsured children. For details, select Figure
3.
Over 27 percent of children
living in families where adults had less than a high school
diploma were uninsured throughout the first half of 1996.
In comparison, 19 percent of children living in families
where adults had completed 12 years of education and less
than 11 percent of children living in families where adults
had more than 12 years of education were uninsured. Select Figure
4 for more information.
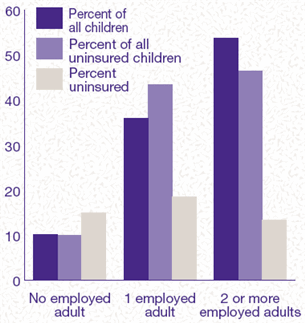
Children living in families
with two or more employed adults were just as likely to be
uninsured throughout the first half of 1996 (13 percent)
as children living in families with no employed adults (15
percent). Of all children uninsured throughout the first
half of 1996, 90 percent lived in families with one or more
employed adults, the same proportion as represented in the
total population; 46 percent lived in families with two or
more employed adults. Select Figure
5 for more information.
MEPS
Sample Design and
Accuracy of Estimates
The sample selected for the 1996 MEPS is
a subsample of the 1995 National Health Interview Survey
(NHIS), designed to produce statistically unbiased national
estimates that are representative of the civilian noninstitutionalized
population of the United States. First-round data were obtained
for approximately 9,400 households in MEPS, resulting in
a survey response rate of 78 percent, which reflects participation
in both
NHIS and MEPS.
The statistics presented here are affected
by both sampling error and sources of nonsampling error,
which include nonresponse bias, respondent reporting errors,
interviewer effects, and data processing misspecifications.
MEPS person-level estimation weights include nonresponse
adjustments and post-stratification adjustments to population
estimates derived from the March 1996 Current Population
Survey (CPS), based on cross-classifications by region, age,
race/ethnicity, and sex.
Tests of statistical significance were
used to determine whether the differences between populations
existed at specified levels of confidence or whether they
occurred by chance. Any comparison made in this Highlights
is based on tests using Z-scores having asymptotic normal
properties, at the .05 level of significance.
Because of methodological differences,
use caution when comparing these data with data from other
sources. For example, CPS measures persons who are uninsured
for a full year; NHIS measures persons who lack insurance
at a given point in time--the month before the interview.
CPS is conducted annually, and NHIS collects insurance data
on a continuous basis each year. In addition, unlike MEPS,
CPS counts military veterans whose source of health care
is the Department of Veterans Affairs as insured. CPS also
counts children of adults covered by Medicaid as being insured.
For these preliminary estimates, MEPS does not consider these
children insured unless their families report them as such.
^top
Figures
Figure 1.
Race/Ethnicity and Health Insurance Status: First Half of 1996
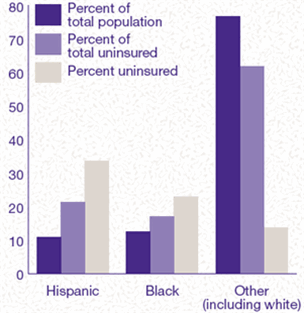
- DATA SOURCE: Medical Expenditure Panel
Survey, Household Component.
^top
Figure 2. Geographic
Region and Health Insurance Status:
First Half of 1996
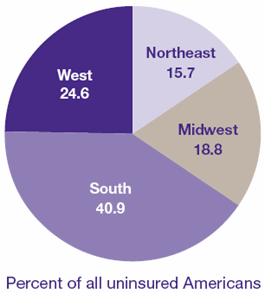
- DATA SOURCE: Medical Expenditure
Panel Survey, Household Component.
^top
Figure 3. Race/Ethnicity
and Health Insurance Status
of Children: First Half of 1996
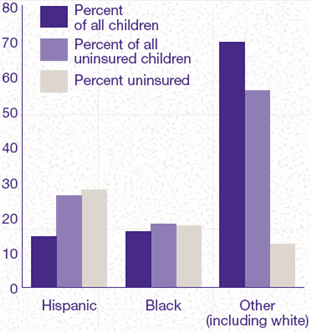
- DATA SOURCE: Medical Expenditure
Panel Survey, Household Component.
^top
Figure 4. Highest
Education of Any Adult Family Member and Health Insurance Status
of Children: First Half of 1996
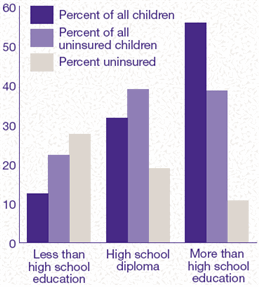
- DATA SOURCE: Medical Expenditure
Panel Survey, Household Component.
^top
Figure 5. Employment
Status of Adult Family Members and Health Insurance Status
of Children: First Half of 1996
- DATA SOURCE: Medical Expenditure
Panel Survey, Household Component.
Tables
Table 1. Health insurance
status: U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population, by selected
characteristics, first half of 1996
| Percent
Characteristic |
Population |
Percent
distribution of population |
Percent
uninsured |
Distribution of
uninsured population |
|
Percent (standard error) |
| Total |
263,515,813 |
100.0 |
17.0
(0.5) |
100.0 |
|
Age in Years |
| Under 18 |
71,420,710 |
27.1 (0.4) |
15.4 (0.8) |
24.5 (1.0) |
| 18-64 |
160,255,618 |
60.8 (0.4) |
20.9 (0.5) |
74.9 (1.0) |
| 65 or over |
31,839,485 |
12.1 (0.4) |
0.9 (0.2) |
0.6 (0.2) |
|
Race/Ethnicity |
| Hispanic |
28,384,339 |
10.8 (0.5) |
33.5 (1.6) |
21.2 (1.4) |
| Black |
32,974,563 |
12.5 (0.7) |
23.0 (1.3) |
16.9 (1.3) |
| Other |
202,156,911 |
76.7 (0.8) |
13.7 (0.5) |
61.9 (1.7) |
|
Sex |
| Male |
128,383,237 |
48.7 (0.3) |
18.7 (0.6) |
53.5 (0.8) |
| Female |
135,132,576 |
51.3 (0.3) |
15.4 (0.5) |
46.5 (0.8) |
|
Perceived Physical Health Status (1) |
| Excellent |
95,602,424 |
36.3 (0.5) |
16.4 (0.7) |
35.1 (1.1) |
| Very good |
78,524,536 |
29.8 (0.4) |
15.2 (0.6) |
25.4 (0.9) |
| Fair |
21,320,848 |
8.1 (0.3) |
18.3 (1.0) |
8.7 (0.5) |
| Poor |
8,225,956 |
3.1 (0.2) |
14.7 (1.6) |
2.7 (0.3) |
| Unknown(2) |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
|
Census Region |
| Northeast |
51,464,265 |
19.5 (0.8) |
13.7 (0.9) |
5.7 (1.0) |
| Midwest |
61,827,772 |
23.5 (0.9) |
13.6 (1.0) |
18.8 (1.4) |
| South |
91,854,957 |
34.9 (1.2) |
19.9 (0.8) |
40.9 (1.8) |
| West |
58,368,819 |
22.2 (0.8) |
18.9 (1.0) |
24.6 (1.2) |
(1) Physical
health status as perceived by respondent.
(2) Cell size too small for reliable estimates.
Note: Percent distributions may not sum to 100 percent due to rounding.
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, Agency for Health Care
Policy and Research: Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, Household Component, 1996
(Round 1).
Table 2. Health insurance
status of children: U.S. children under 18 years of age, by
selected characteristics,
first half of 1996
| Percent
Characteristic |
Population |
Percent
distribution of children in population |
Percent
uninsured |
Distribution of
uninsured children |
|
Percent (standard error) |
| Total Status (1) |
71,420,710 |
100.0 |
15.4
(0.8) |
100.0 |
|
Age
in Years |
| Under 6 |
24,099,593 |
33.7 (0.8) |
13.2 (1.0) |
28.9 (1.8) |
| 6-12 |
28,285,339 |
39.6 (0.7) |
15.5 (1.0) |
40.0 (1.6) |
| 13-17 |
19,035,778 |
26.7 (0.7) |
17.9 (1.1) |
31.1 (1.5) |
|
Race/Ethnicity |
| Hispanic |
10,373,234 |
14.5 (0.9) |
27.6 (1.9) |
26.1 (2.2) |
| Black |
11,285,178 |
15.8 (1.0) |
17.5 (2.0) |
18.0 (2.2) |
| Other |
49,762,299 |
69.7 (1.2) |
12.3 (0.8) |
55.8 (2.7) |
|
Metropolitan Statistical Area |
| MSA |
56,641,290 |
79.3 (1.3) |
14.0 (0.8) |
72.1 (2.9) |
| Non-MSA |
14,779,420 |
20.7 (1.3) |
20.7 (2.2) |
27.9 (2.9) |
|
Perceived Physical Health Status (2,3) |
| Excellent |
37,063,155 |
51.9 (0.9) |
14.8 (0.9) |
49.9 (2.1) |
| Very good |
20,124,942 |
28.2 (0.8) |
14.1 (1.1) |
25.9 (1.5) |
| Good |
11,325,060 |
15.9 (0.6) |
18.6 (1.7) |
19.2 (1.6) |
| Fair/Poor |
2,770,053 |
3.9 (0.3) |
15.4 (2.5) |
3.9 (0.7) |
|
Family size (3) |
| 2 persons |
4,312,903 |
6.0 (0.4) |
18.0 (2.6) |
7.1 (1.1) |
| 3 persons |
12,978,814 |
18.2 (0.7) |
13.7 (1.2) |
16.2 (1.5) |
| 4 or more persons |
53,979,583 |
75.6 (0.8) |
15.5 (0.9) |
76.4 (1.8) |
|
Census Region |
| Northeast |
13,286,659 |
18.6 (0.9) |
10.9 (1.4) |
13.2 (1.6) |
| Midwest |
16,919,711 |
23.7 (1.2) |
13.2 (1.6) |
20.4 (2.2) |
| South |
24,446,161 |
34.2 (1.5) |
18.7 (1.4) |
41.7 (2.9) |
| West |
16,768,178 |
23.5 (1.2) |
16.2 (1.6) |
24.7 (2.2) |
|
Highest education of persons
18 or over in family (3) |
| Less than 12 years |
8,827,971 |
12.4 (0.8) |
27.6 (2.5) |
22.2 (2.1) |
| 12
years |
22,582,319 |
31.6 (1.0) |
18.9 (1.2) |
38.9 (2.2) |
| More than 12 years |
39,823,174 |
55.8 (1.2) |
10.6 (0.9) |
38.6 (2.7) |
|
Number of persons 18 or over
in family (3) |
| 1 |
12,502,839 |
17.5 (0.9) |
16.5 (1.8) |
18.8 (2.1) |
| 2 or more |
58,730,625 |
82.2 (0.9) |
15.1 (0.8) |
80.8 (2.1) |
|
Number of employed persons 18
or over in family (3,4) |
| 0 |
7,211,407 |
10.1 (0.7) |
15.0 (2.0) |
9.9 (1.3) |
| 1 |
25,688,027 |
36.0 (1.0) |
18.5 (1.4) |
43.4 (2.5) |
| 2 or more |
38,334,029 |
53.7 (1.1) |
13.3 (1.0) |
46.4 (2.6) |
|
Age of oldest person in family (3) |
| 18-24 |
2,558,956 |
3.6 (0.3) |
19.2 (3.8) |
4.5 (0.9) |
| 25-34 |
17,955,536 |
25.1 (1.0) |
14.7 (1.4) |
24.0 (2.0) |
| 35-44 |
33,253,478 |
46.6 (1.0) |
14.6 (1.1) |
44.2 (2.3) |
| 45 and over |
17,465,493 |
24.5 (0.9) |
16.9 (1.3) |
26.9 (2.0) |
(1) Includes
persons with unknown perceived physical health status and persons
living alone or in families with either no adult members or whose
adult members have missing information on education. In a reporting
unit, families consist
of all persons related by blood or marriage.
(2) Physical health status as perceived by
respondent.
(3) Percent distributions may not sum to 100 percent. See
footnote 1 for details.
(4) Individuals are counted as employed if they are employed
at
the Round 1 interview date.
Note: Percent distributions may not sum to 100 percent due to
rounding.
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, Agency for Health Care
Policy and Research: Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, Household Component, 1996
( Round 1).
References
For more information
on MEPS, call the MEPS information coordinator at AHRQ
(301/594-1406) or select "Data: Public Use
Data File
Index".
For a detailed description of the MEPS survey
design, sample design, and methods used to minimize sources of
nonsampling error, see:
Cohen S. Sample design of the 1996 Medical
Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. Rockville (MD):
Agency for Health Care Policy and Research; 1997.
AHRQ Pub. No. 97-0027.
Cohen J. Design and methods of the Medical
Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. Rockville (MD):
Agency for Health Care Policy and Research; 1997.
AHRQ Pub. No. 97-0026.
For detailed data on which the 1996 numbers
in this Highlights were based, a set of two tables ("Medical
Expenditure Panel Survey Insurance Status Tables: First Half
of 1996") can be accessed (Table
1 & 2). Print versions of the tables (AHRQ Pub No. 97-R052)
are available from the AHRQ
Clearinghouse(800/358-9295) from AHRQ
InstantFAX(301/594-2800).
More detailed information on the uninsured
population will be published in:
Vistnes JP, Monheit AC. Health insurance status
of the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population. Rockville
(MD): Agency for Health Care Policy and Research; 1997. MEPS
Research Findings No. 1. AHRQ Pub. No. 97-0030.
MEPS Highlights No.
1, AHRQ Pub.
No. 97-0025, May 1997.
^top
Suggested Citation:
Beauregard, K. M., Drilea, S. K., and Vistnes, J. P. Highlights #1: The Uninsured in America, 1996. May 1997. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov
/data_files/publications/hl1/hl1.shtml |
|
