|
|
Font Size:
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
STATISTICAL BRIEF #209:
Co-pays, Deductibles, and Coinsurance Percentages for Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance in the Private Sector, by Firm Size Classification, 2006
Highlights
- In 2006, 66.4 percent of private sector employees enrolled in employer-sponsored health insurance were required to pay a deductible by their health insurance plan.
- In 2006, private employees enrolled in employer-sponsored health insurance who were required to pay a deductible had an average single deductible of $714 and an average family deductible of $1,351. Both of these values varied significantly by the size of the employee's firm.
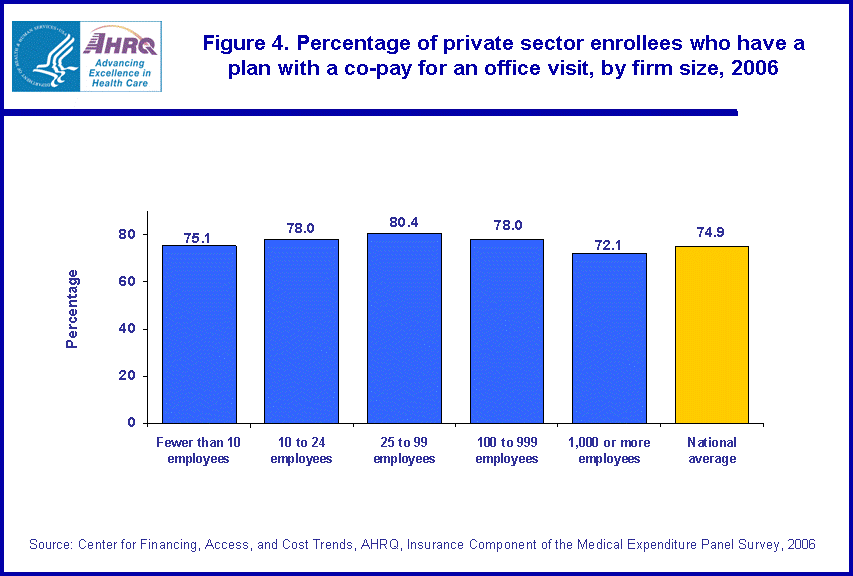
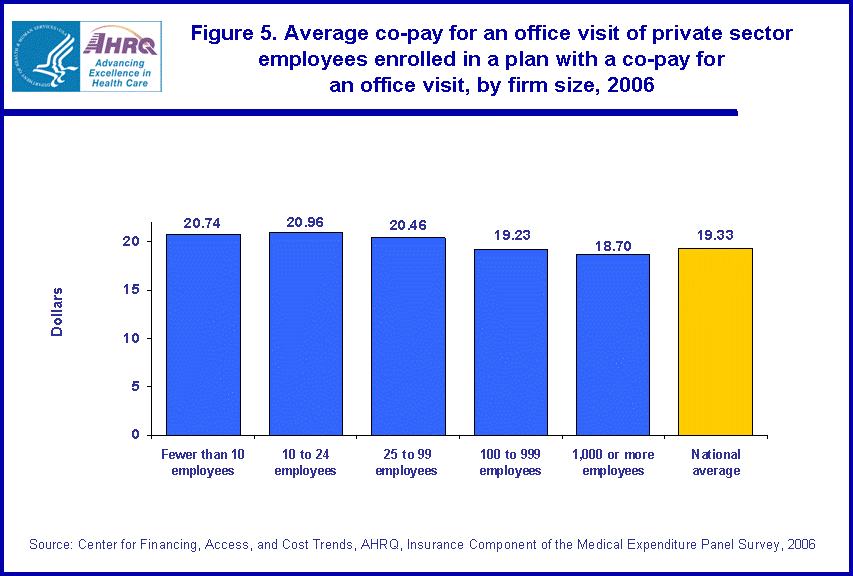
- In 2006, 74.9 percent of private sector employees enrolled in employer-sponsored health insurance paid a dollar co-pay for each doctor visit. The average dollar co-pay among these enrollees was $19.33. Both of these values varied significantly by size of firm.
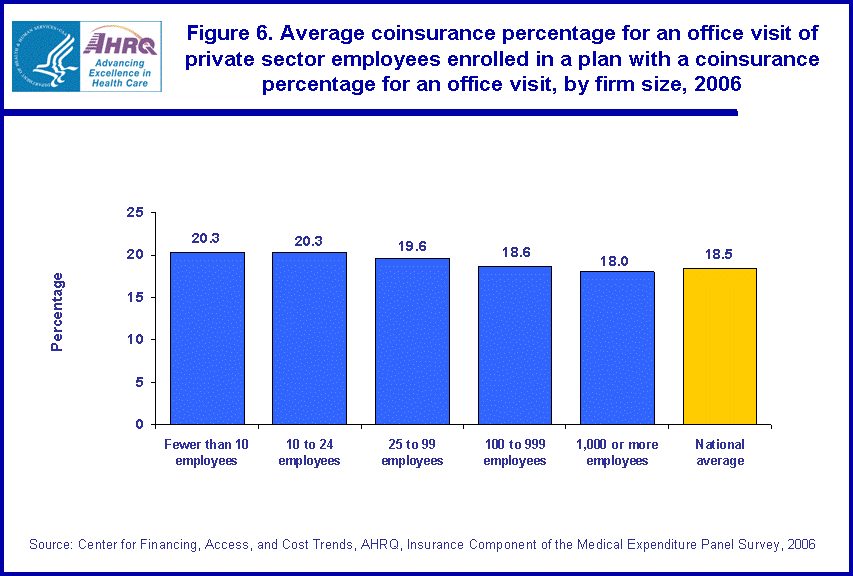
- The average coinsurance percentage for a doctor visit for employees enrolled in employer-sponsored health insurance with a coinsurance percentage to pay was 18.5 percent.
Introduction
Employer-sponsored health insurance for current workers is one of the primary sources of health insurance coverage in the United States. According to data from the 2006 Insurance Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS-IC), approximately 99.7 million of the 114.7 million employees from the private sector worked in firms where the employer offered health insurance. Of those employees who worked where health insurance was offered, approximately 60.6 million were enrolled.
In recent years, premiums for employer-sponsored health insurance have risen dramatically. However, premium costs are only one of several factors that determine costs of health care for enrollees. Other factors, such as whether an employee has a deductible, the size of deductibles, and the size of co-pays, also contribute to differences in cost of care.
This Statistical Brief examines what percentage of enrollees paid a deductible and the size of deductibles, what percentage paid co-pays and the size of the co-pays, and the average coinsurance percentage paid. These values are compared for firms of different employment size. Only those estimates that had a statistically significant difference from the national average at the 0.05 percent significance level are noted in the text.
Findings
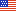
Among the 60.6 million private sector employees enrolled in employer-sponsored health insurance in 2006 (estimate not shown in figures), 66.4 percent were enrolled in a plan that required they meet an annual deductible (figure 1).
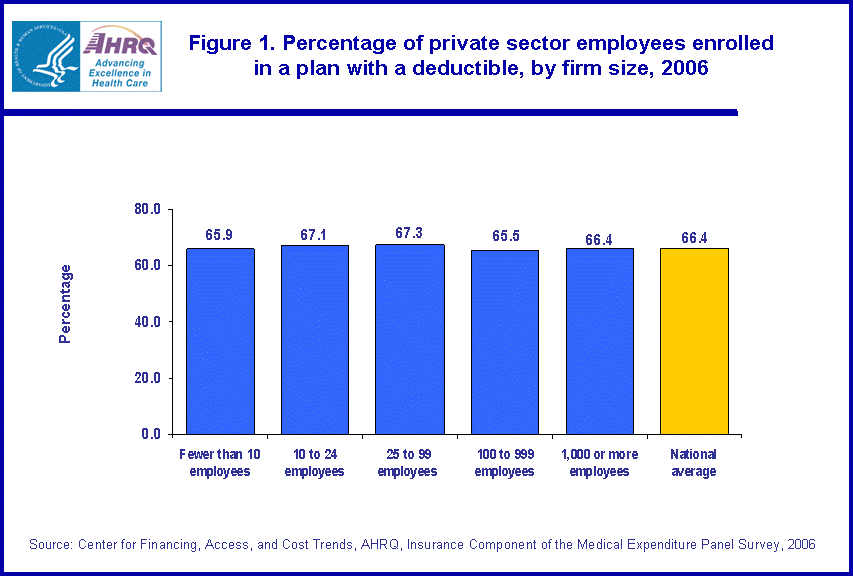
Among enrollees who paid a deductible, the size of both single and family deductibles varied by firm size in 2006. Enrollees who paid deductibles from firms with fewer than 10 employees, firms with 10 to 24 employees, and firms with 25 to 99 employees paid single deductibles higher than the national average. Single enrollees from these firms paid average single deductibles of $1,006, $981, and $944, respectively (figure 2). All these values were higher than the national private sector average deductible of $714. Single enrollees who paid deductibles and worked for firms with 1,000 or more employees, paid an average single deductible of $537, lower than the national average.
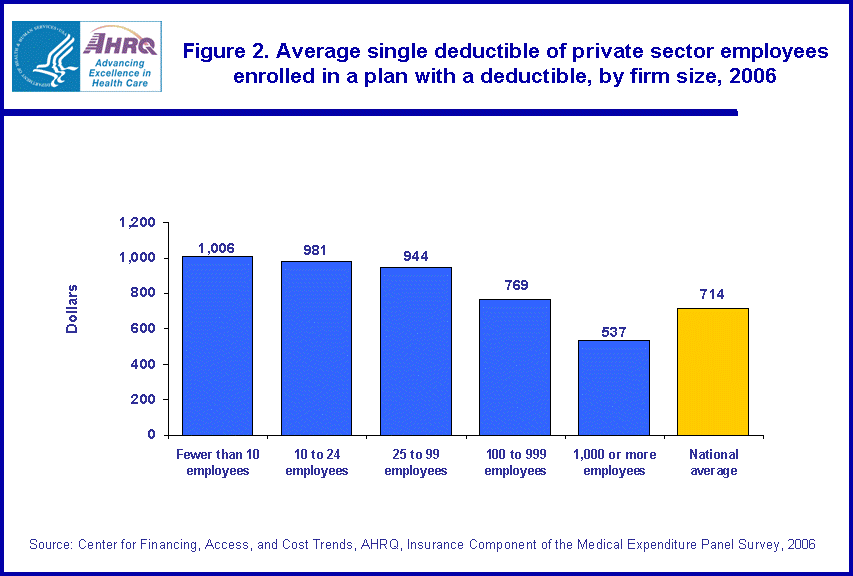
A similar pattern also held for family deductibles in 2006. Those family enrollees with deductibles in firms with fewer than 10 employees, firms with 10 to 24 employees and firms with 25 to 99 paid family deductibles higher than the national private sector average of $1,351 (figure 3). These enrollees paid average family deductibles of $1,940, $1,957 and $1,762, respectively. Family enrollees with deductibles in firms with 1,000 or more employees paid an average family deductible of $1,206, significantly less than the national private sector average.
In 2006, 74.9 percent of private sector enrollees in employer-sponsored health insurance paid a co-pay for an office visit (figure 4). Higher percentages of enrollees who worked at firms with 10 to 24 employees, 25 to 99 employees and 100 to 999 employees had plans with co-pays. For enrollees in these three sizes of firms, the percentages who had co-pays were 78.0, 80.4, and 78.0, respectively.
On average, the co-pay for enrollees with co-pays was $19.33 in 2006 (figure 5). Enrollees with co-pays in firms with fewer than 10 employees, firms with 10 to 24 employees, and firms with 25 to 99 employees paid higher than average amounts of $20.74, $20.96, and $20.46, respectively. Enrollees in firms with 1,000 or more employees paid a lower average co-pay of $18.70.
Persons who do not have co-pays have a coinsurance percentage to pay. For enrollees in the private sector in 2006, the average coinsurance for an office visit for those enrollees who paid a coinsurance was 18.5 percent (figure 6). Enrollees in firms with fewer than 10 employees and those in firms with 10 to 24 employees both paid a higher than average rate of 20.3 percent. Enrollees in firms with 25 to 99 employees also had an above average coinsurance rate of 19.6 percent.
Data Source
This Statistical Brief summarizes data from the 2006 MEPS-IC. The data are available on the MEPS Web site at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/survey_comp/Insurance.jsp or have been produced using special computation runs on the confidential MEPS-IC data available at the U.S. Census Bureau.
Definitions
Employer
In this Statistical Brief, an employer is defined as a private sector firm. A firm is defined as a business entity that controls one or more business establishments or locations. Consequently, an employer can have multiple work locations.
Firm size
Firm size is the count of employees across all locations controlled by an individual firm.
Deductible
A deductible is a fixed dollar amount during the benefit period, usually a year, that an insured person pays before the insurer starts to make payments for covered medical services. Plans may have both per individual and family deductibles. Some plans may have separate deductibles for specific services. For example, a plan may have a hospitalization deductible per admission. Deductibles may differ if services are received from an approved provider or if received from providers not on the approved list.
Co-pay
A co-pay is a form of medical cost sharing in a health insurance plan that requires an insured person to pay a fixed dollar amount when a medical service is received, regardless of the total charge for service. The insurer is responsible for the rest of the reimbursement. There may be separate co-pay for different services. For example, an enrollee may pay a $10 co-pay for each doctor's office visit, $75 for each day in the hospital, and $5 for each prescription. Some plans require that a deductible first be met for some specific services before a co-pay applies.
Coinsurance
Coinsurance is a form of medical cost sharing in a health insurance plan that requires an insured person to pay a stated percentage of medical expenses after the deductible amount, if any, was paid. Once any deductible amount and coinsurance are paid, the insurer is responsible for the rest of the reimbursement for covered benefits up to allowed charges; the individual could also be responsible for any charges in excess of what the insurer determines to be "usual, customary and reasonable." Coinsurance rates may differ if services are received from an approved provider (i.e., a provider with whom the insurer has a contract or an agreement specifying payment levels and other contract requirements) or if received by providers not on the approved list. In addition to overall coinsurance rates, rates may also differ for different types of services.
About MEPS-IC
MEPS-IC is a survey of business establishments and governments that collects information on employer-sponsored health insurance, such as whether insurance is offered, enrollments, types of plans, and premiums. The survey is conducted annually by the U.S. Bureau of the Census under the sponsorship of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The yearly response rate has averaged 78 percent for in-scope sample units. Approximately 4 percent of the original sample has been out-of-scope in a typical year. A total sample of 42,000 establishments was selected for the 2006 survey, prior to accounting for losses due to nonresponse and out-of-scope cases.
For more information on this survey, see MEPS Methodology Reports 6, 8, 10, 14, 17, and 18 on the MEPS Web site at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_stats/publications.jsp and Insurance Component Survey Basics at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/survey_comp/Insurance.jsp.
Suggested Citation
Sommers, J. P., Crimmel, B.L., Co-pays, Deductibles, and Coinsurance Percentages for Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance in the Private Sector, by Firm Size Classification, 2006. Statistical Brief #209. July 2008. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD, http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st209/stat209.pdf
AHRQ welcomes questions and comments from readers of this publication who are interested in obtaining more information about access, cost, use, financing, and quality of health care in the United States. We also invite you to tell us how you are using this Statistical Brief and other MEPS data and tools and to share suggestions on how MEPS products might be enhanced to further meet your needs. Please e-mail us at mepsprojectdirector@ahrq.hhs.gov or send a letter to the address below:
Steven B. Cohen, PhD, Director
Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
540 Gaither Road
Rockville, MD 20850
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||