|
|
Font Size:
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
STATISTICAL BRIEF #56:
National Health Care Expenses in the
U.S. Community Population, 2001
Highlights
- Health care expenses among the community population were $726.4 billion in 2001, with slightly less than a third (32.3 percent) of the expenses related to hospital inpatient services.
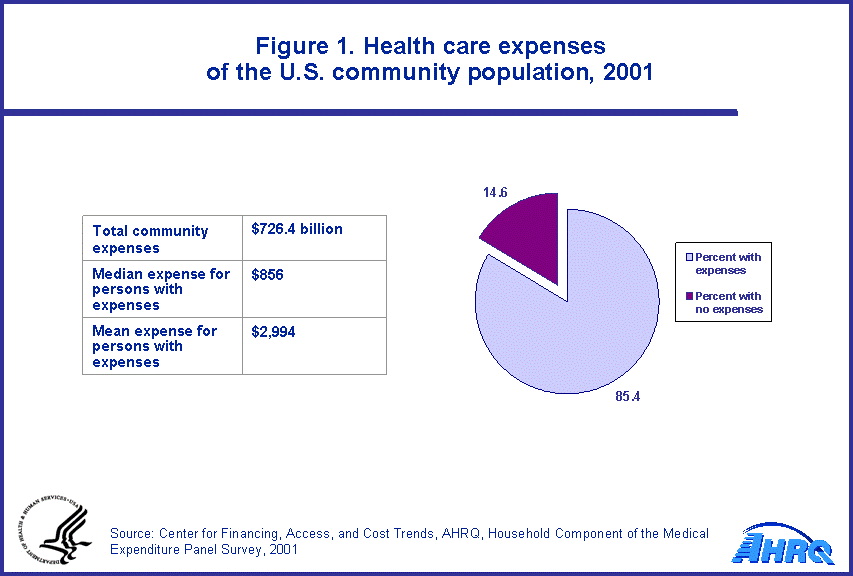
- Overall, the mean and median expenses of persons with any expenses in 2001 (85.4 percent of the community population) were $2,994 and $856, respectively.
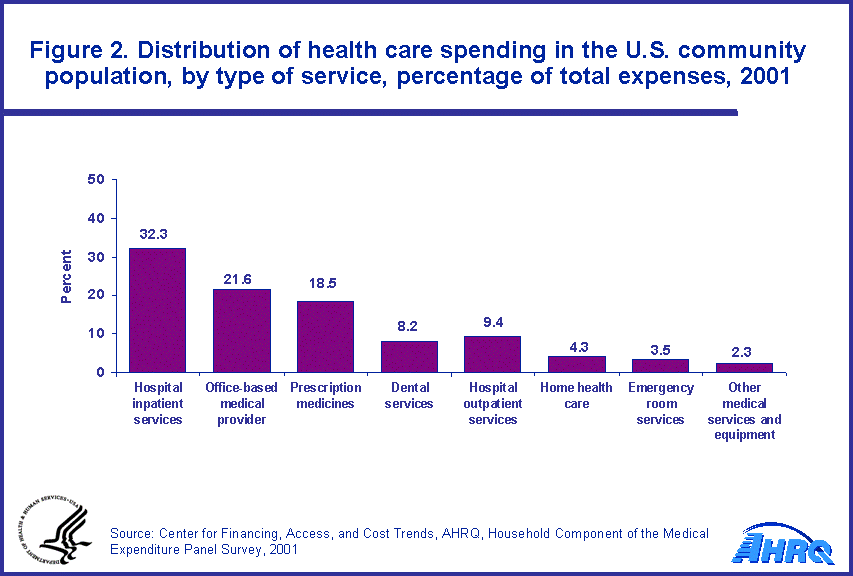
- Total emergency room expenses were $25.5 billion (3.5 percent of total expenses). This is relatively small compared to other ambulatory medical care expenses ($68.0 billion for hospital outpatient services and $156.7 billion for office-based medical provider services).
- Prescription medicine expenses accounted for 18.5 percent of community population spending on health care, and the mean expense for these medicines among those with expenses was $730.
- Private medical insurance--the largest third party payer--covered 41.7 percent of total payments. Medicare and Medicaid--the primary public programs--combined paid 30.2 percent of the total.
- Uninsured people under age 65 with health care expenses had relatively lower expenditures ($1,524), while those age 65 and older on Medicare and other public insurance had relatively higher expenditures ($8,394).
Introduction
This Statistical Brief presents estimates on the health care expenses in the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized (community) population in calendar year 2001. The national estimates are derived from the Household Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS-HC), which provides annual national estimates of health care use and expenditures. Health care expenses, as reported in this brief, represent payments to hospitals, physicians, and other health care providers for services reported by respondents in the MEPS-HC. These expenses are defined as direct payments by individuals, private insurance, Medicare, Medicaid, and other payment sources. All differences between estimates discussed in the text are statistically significant at the 0.05 level.
Findings
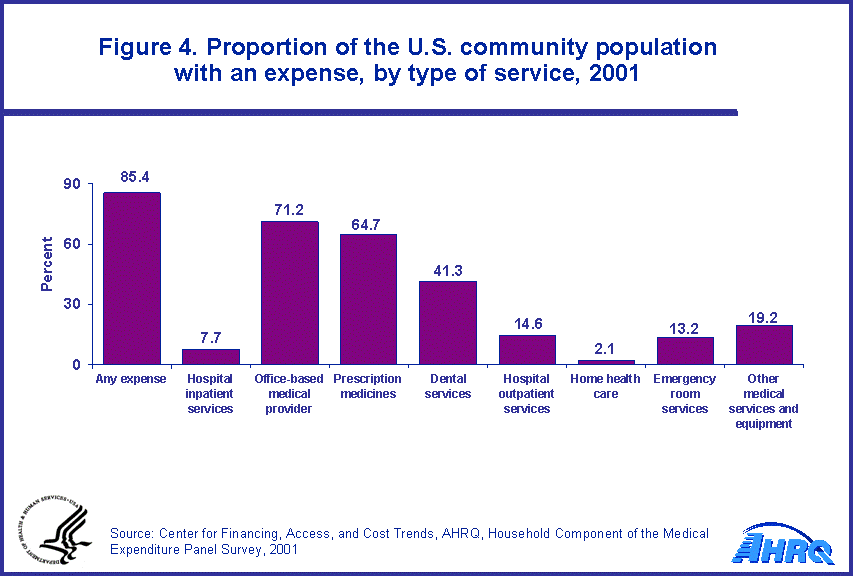
In 2001, the U.S. community population had total expenses of $726.4 billion, consisting of payments for hospital inpatient and outpatient care; emergency room services; office-based medical provider services; dental services; home health care; prescription medicines; and other medical services and equipment (figure 1). Among the 85.4 percent of the population with an expense, the median and mean expenses were $856 and $2,994, respectively. A small proportion of the 14.6 percent of the population who did not have health care expenses during 2001 received health services for which no expenses were incurred.
Hospital inpatient services (facility charges and expenses for physician services incurred during a hospital stay) accounted for 32.3 percent of the total expenses of the community population, while another 21.6 percent of the total was for office-based medical provider services (figure 2). Total emergency room expenses were 3.5 percent of total expenses ($25.5 billion; data not shown), which is relatively small compared to other ambulatory medical care expenses ($68.0 billion for hospital outpatient services and $156.7 billion for office-based medical provider services; data not shown).
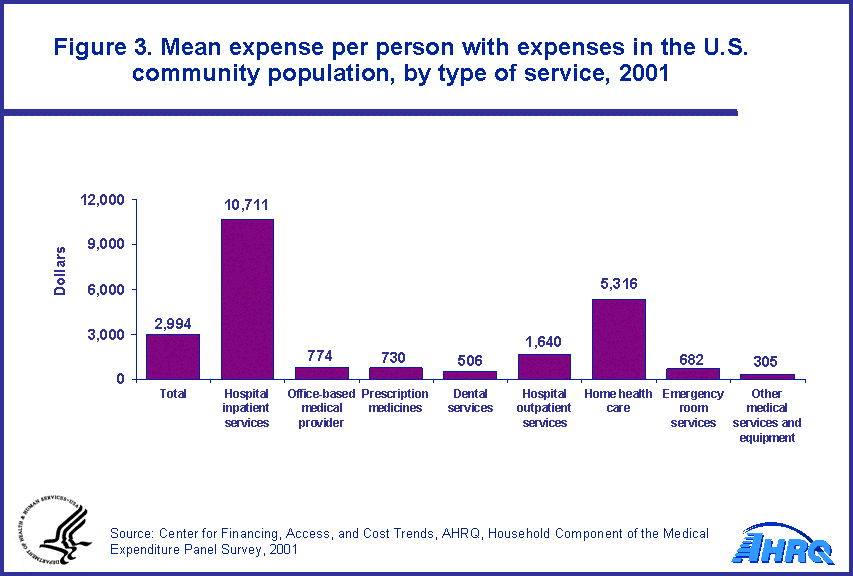
Prescription medicine expenses accounted for 18.5 percent of spending on health care, and the mean expense for these $10,711 for hospital inpatient services to a low of $305 for other medical equipment and services, but the proportion of people with expenses varied widely (ranging from 2.1 percent to 71.2 percent) by type of service (figure 4).
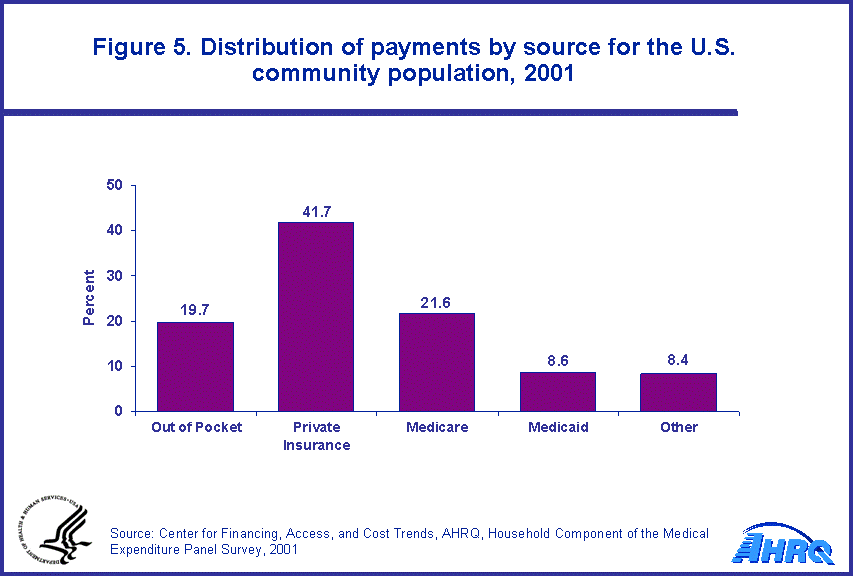
Health care expenses are paid by individuals and third party payers, such as private insurance and public programs. In 2001, private insurance covered 41.7 percent of the total expenses; individuals and family members paid out of pocket 19.7 percent; and Medicare and Medicaid combined paid 30.3 percent (figure 5).
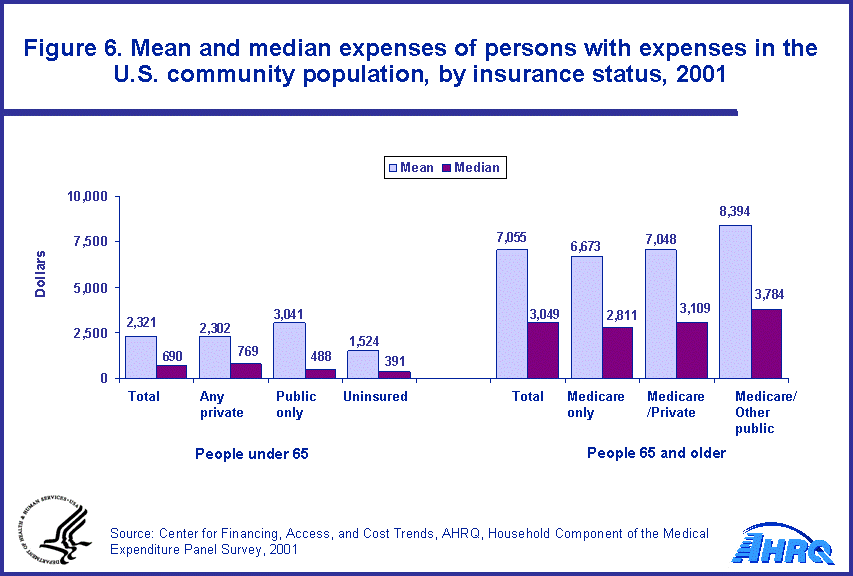
As shown in figure 6, health care expenses were not uniformly distributed across the community population. Uninsured people under age 65 with expenses were characterized by relatively lower expenditures; those with expenses had a mean expense of $1,524. Alternatively, persons age 65 and older on Medicare and other public insurance were characterized by relatively higher expenditures; those with expenses had a mean expense of $8,394.
Data Source
The estimates in this Statistical Brief are derived from the 2001 MEPS Compendium of Tables, which is based on data from the Household Component of the 2001 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey.
Definitions
Expenditures
Expenditures included the total payments from all sources to hospitals, physicians, other health care providers (including dental care), and pharmacies for services reported by respondents in the MEPS-HC. Sources included direct payments from individuals, private insurance, Medicare, Medicaid, and miscellaneous other sources.
Uninsured
People who did not have insurance coverage at any time during the survey year were classified as uninsured for the full year. People who did not have coverage during the period from January of the survey year through the time of their first interview in that year were classified as uninsured throughout the first half of the year. (Interviews were typically conducted from February to June.) People who lacked coverage for at least one month during the year were classified as uninsured at any time during the survey year. People who were covered only by noncomprehensive State-specific programs (e.g., Maryland Kidney Disease Program) or private single service plans (e.g., coverage for dental or vision care only, coverage for accidents or specific diseases) were considered to be uninsured.
Public only coverage
People were considered to have public only health insurance coverage if they were not covered by private insurance, and they were covered by Medicare, Medicaid, TRICARE, or other public hospital and physician coverage.
Private coverage
Private health insurance coverage was defined as non-public insurance that provided coverage for hospital and physician care (including Medigap coverage).
About MEPS-HC
MEPS-HC is a nationally representative longitudinal survey that collects detailed information on health care utilization and expenditures, health insurance, and health status, as well as a wide variety of social, demographic, and economic characteristics for the civilian noninstitutionalized population. It is cosponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Center for Health Statistics.
For more information about MEPS, call the MEPS information coordinator at AHRQ (301-427-1406) or visit the MEPS Web site at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/.
References
Cohen, J. Design and Methods of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 1. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0026. Rockville, Md.: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997.
Cohen, S. Sample Design of the 1996 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. MEPS Methodology Report No. 2. AHCPR Pub. No. 97-0027. Rockville, Md.: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1997.
Suggested Citation
Kashihara, D. and Carper, K. National Health Care Expenses in the U.S. Community Population, 2001. Statistical Brief #56. October 2004. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/data_files/publications/st56/stat56.shtml
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ, Household Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, 2001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ, Household Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, 2001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ, Household Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, 2001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ, Household Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, 2001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ, Household Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, 2001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ, Household Component of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, 2001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|