MEPS HC-126G: 2009 Office-Based Medical Provider Visits (Final)
November 2011
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends
540 Gaither Road
Rockville, MD 20850
(301) 427-1406
Table of Contents
A. Data Use Agreement
B. Background
1.0 Household Component
2.0 Medical Provider Component
3.0 Survey Management and Data Collection
C. Technical and Programming Information
1.0 General Information
2.0 Data File Information
2.1 Codebook Structure
2.2 Reserved Codes
2.3 Codebook Format
2.4 Variable Source and Naming Conventions
2.4.1 General
2.4.2 Expenditure and Source of Payment Variables
2.5 File Contents
2.5.1 Survey Administration Variables
2.5.1.1 Person Identifiers (DUID, PID, DUPERSID)
2.5.1.2 Record Identifiers (EVNTIDX, FFEEIDX)
2.5.1.3 Round Indicator (EVENTRN)
2.5.1.4 Panel Indicator (PANEL)
2.5.2 MPC Indicator (MPCELIG, MPCDATA)
2.5.3 Office-Based Medical Provider Visit Variables
2.5.3.1 Date of Visit (OBDATEYR - OBDATEDD)
2.5.3.2 Visit Details (SEETLKPV-VSTRELCN)
2.5.3.3 Treatments, Procedures, Services, and Prescription Medicines (PHYSTH-MEDPRESC)
2.5.4 Condition and Procedure Codes (OBICD1X-OBICD4X, OBPRO1X – OBPRO3X), and
Clinical Classification Codes (OBCCC1X-OBCCC4X)
2.5.5 Flat Fee Variables (FFEEIDX, FFOBTYPE, FFBEF09, FFTOT10)
2.5.5.1 Definition of Flat Fee Payments
2.5.5.2 Flat Fee Variable Descriptions
2.5.5.2.1 Flat Fee ID (FFEEIDX)
2.5.5.2.2 Flat Fee Type (FFOBTYPE)
2.5.5.2.3 Counts of Flat Fee Events that Cross Years (FFBEF09, FFTOT10)
2.5.5.3 Caveats of Flat Fee Groups
2.5.6 Expenditure Data
2.5.6.1 Definition of Expenditures
2.5.6.2 Data Editing and Imputation Methodologies of Expenditure Variables
2.5.6.2.1 General Data Editing Methodology
2.5.6.2.2 Imputation Procedures
2.5.6.2.3 Office-Based Provider Visit Data Editing and Imputation
2.5.6.3 Capitation Imputation
2.5.6.4 Imputation Flag (IMPFLAG)
2.5.6.5 Flat Fee Expenditures
2.5.6.6 Zero Expenditures
2.5.6.7 Discount Adjustment Factor
2.5.6.8 Sources of Payment
2.5.6.9 Office-Based Expenditure Variables (OBSF09X - OBTC09X)
2.5.7 Rounding
3.0 Sample Weight (PERWT09F)
3.1 Overview
3.2 Details on Person Weight Construction
3.2.1 MEPS Panel 13 Weight
3.2.2 MEPS Panel 14 Weight
3.2.3 The Final Weight for 2009
3.2.4 Coverage
3.3 Using MEPS Data for Trend Analysis
4.0 Strategies for Estimation
4.1 Developing Event-Level Estimates
4.2 Person-Based Estimates for Office-Based Visits
4.3 Variables with Missing Values
4.4 Variance Estimation (VARSTR, VARPSU)
5.0 Merging/Linking MEPS Data Files
5.1 Linking to the Person-Level File
5.2 Linking to the Prescribed Medicines File
5.3 Linking to the Medical Conditions File
_._ References
D. Variable-Source Crosswalk
A. Data Use Agreement
Individual identifiers have been removed from the
micro-data contained in these files. Nevertheless, under sections 308 (d) and
903 (c) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 242m and 42 U.S.C. 299 a-1),
data collected by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) and/or
the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) may not be used for any purpose
other than for the purpose for which they were supplied; any effort to determine
the identity of any reported cases is prohibited by law.
Therefore in accordance with the above referenced
Federal Statute, it is understood that:
- No one is to use the data in this data set in any way except for
statistical reporting and analysis; and
- If the identity of any person or establishment should be discovered
inadvertently, then (a) no use will be made of this knowledge, (b) the
Director Office of Management AHRQ will be advised of this incident, (c) the
information that would identify any individual or establishment will be
safeguarded or destroyed, as requested by AHRQ, and (d) no one else will be
informed of the discovered identity; and
- No one will attempt to link this data set with individually identifiable
records from any data sets other than the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey
or the National Health Interview Survey.
By using these data you signify your agreement to
comply with the above stated statutorily based requirements with the knowledge
that deliberately making a false statement in any matter within the jurisdiction
of any department or agency of the Federal Government violates Title 18 part 1
Chapter 47 Section 1001 and is punishable by a fine of up to $10,000 or up to 5
years in prison.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
requests that users cite AHRQ and the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey as the
data source in any publications or research based upon these data.
Return To Table Of Contents
B. Background
1.0 Household Component
The Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) provides
nationally representative estimates of health care use, expenditures, sources of
payment, and health insurance coverage for the U.S. civilian
non-institutionalized population. The MEPS Household Component (HC) also
provides estimates of respondents’ health status, demographic and socio-economic
characteristics, employment, access to care, and satisfaction with health care.
Estimates can be produced for individuals, families, and selected population
subgroups. The panel design of the survey, which includes 5 Rounds of interviews
covering 2 full calendar years, provides data for examining person level changes
in selected variables such as expenditures, health insurance coverage, and
health status. Using computer assisted personal interviewing (CAPI) technology,
information about each household member is collected, and the survey builds on
this information from interview to interview. All data for a sampled household
are reported by a single household respondent.
The MEPS-HC was initiated in 1996. Each year a new
panel of sample households is selected. Because the data collected are
comparable to those from earlier medical expenditure surveys conducted in 1977
and 1987, it is possible to analyze long-term trends. Each annual MEPS-HC sample
size is about 15,000 households. Data can be analyzed at either the person or
event level. Data must be weighted to produce national
estimates.
The set of households selected for each panel of the
MEPS HC is a subsample of households participating in the previous year’s
National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) conducted by the National Center for
Health Statistics. The NHIS sampling frame provides a nationally representative
sample of the U.S. civilian non-institutionalized population and reflects an
oversample of blacks and Hispanics. In 2006, the NHIS implemented a new sample
design, which included Asian persons in addition to households with black and
Hispanic persons in the oversampling of minority populations. MEPS further
oversamples additional policy relevant sub-groups such as low income households.
The linkage of the MEPS to the previous year’s NHIS provides additional data for
longitudinal analytic purposes.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.0 Medical Provider Component
Upon completion of the household CAPI interview and
obtaining permission from the household survey respondents, a sample of medical
providers are contacted by telephone to obtain information that household
respondents can not accurately provide. This part of the MEPS is called the
Medical Provider Component (MPC) and information is collected on dates of visit,
diagnosis and procedure codes, charges and payments. The Pharmacy Component
(PC), a subcomponent of the MPC, does not collect charges or diagnosis and
procedure codes but does collect drug detail information, including National
Drug Code (NDC) and medicine name, as well as date filled and sources and
amounts of payment. The MPC is not designed to yield national estimates. It is
primarily used as an imputation source to supplement/replace household reported
expenditure information.
Return To Table Of Contents
3.0 Survey Management and Data Collection
MEPS HC and MPC data are collected under the authority
of the Public Health Service Act. Data are collected under contract with Westat,
Inc. (MEPS HC) and Research Triangle Institute (MEPS MPC). Data sets and summary
statistics are edited and published in accordance with the confidentiality
provisions of the Public Health Service Act and the Privacy Act. The National
Center for Health statistics (NCHS) provides consultation and technical
assistance.
As soon as data collection and editing are completed,
the MEPS survey data are released to the public in staged releases of summary
reports, micro data files, and tables via the MEPS Web site: www.meps.ahrq.gov.
Selected data can be analyzed through MEPSnet, an on-line interactive tool
designed to give data users the capability to statistically analyze MEPS data in
a menu-driven environment.
Additional information on MEPS is available from the
MEPS project manager or the MEPS public use data manager at the Center for
Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality,
540 Gaither Road, Rockville, MD 20850 (301-427-1406).
Return To Table Of Contents
C. Technical and Programming Information
1.0 General Information
This documentation describes one in a
series of public use event files from the 2009 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey
(MEPS) Household (HC) and Medical Provider Components (MPC). Released as an
ASCII data file (with related SAS and SPSS programming statements) and a SAS
transport file, the 2009 Office-Based Medical Provider Visits public use event
file provides detailed information on office-based provider visits for a
nationally representative sample of the civilian noninstitutionalized population
of the United States. Data from the office-based provider events file can be
used to make estimates of office-based provider utilization and expenditures for
calendar year 2009. The file contains 75 variables and has a logical record
length of 277 with an additional 2-byte carriage return/line feed at the end of
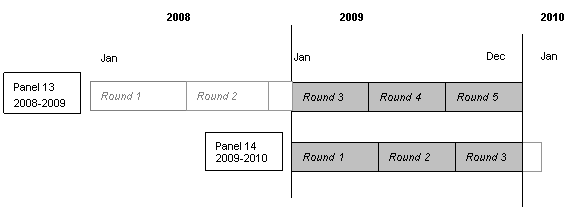
each record. As illustrated below, this file consists of MEPS survey data from
the 2009 portion of Round 3 and Rounds 4 and 5 for Panel 13, as well as Rounds
1, 2 and the 2009 portion of Round 3 for Panel 14 (i.e., the rounds for the MEPS
panels covering calendar year 2009).
Incentive Experiment in Panel 13
With the encouragement of the Office of Management and
Budget (OMB), an experiment was undertaken for MEPS Panel 13 (first fielded in
2008) to evaluate whether and how differential payments to household respondents
might affect survey participation, the level of effort required to obtain
participation, and the quality of the data collected. Each sampled household in
Panel 13 was randomly assigned to one of three different levels of payment--$30,
$50, or $70--with the experiment continuing through the panel’s five rounds
of data collection. Households receiving the $30 payment represent the control
group, since that amount had been offered to all households in the 2007 panel.
To learn more about this experiment, go to the Respondent
Payment Experiment – Results
from Panel 13. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD.
Each record on this event file represents a unique
office-based provider event; that is, an office-based provider event reported by
the household respondent. Office-based events reported in Panel 14 Round 3 and
known to have occurred after December 31, 2009 are not included on this file.
Utilization counts of office-based provider visits are based entirely on
household reports. Information from the MPC is used to supplement expenditure
payment data on the office-based provider file, reported by the household, and
does not affect use estimates.
Data from this event file can be merged with other
2009 MEPS HC data files for purposes of appending person-level data such as
demographic characteristics or health insurance coverage to each office-based
provider visit record on the current file.
This file can also be used to construct summary
variables of expenditures, sources of payment, and related aspects of
office-based provider visits for calendar year 2009. Aggregate annual
person-level information on the use of office-based providers and other health
services is provided on the MEPS 2009 Full Year Consolidated Data File, where
each record represents a MEPS sampled person.
This documentation offers a brief overview of the
types and levels of data provided, and the content and structure of the files
and the codebook. It contains the following sections:
Data File Information
Sample Weights
Strategies for Estimation
Merging/linking MEPS Data Files
References
Variable-Source Crosswalk
For more information on MEPS HC survey design, see T.
Ezzati-Rice, et al. (1998-2007) and S. Cohen, 1996. A copy of the MEPS HC survey
instruments used to collect the information on the office-based provider file is
available on the MEPS Web site at the following address:
www.meps.ahrq.gov.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.0 Data File Information
The 2009 Office-Based Medical Provider public use data
set consists of one event-level data file. The file contains characteristics
associated with the OB event and imputed expenditure data.
The Office-Based Provider public use data set contains
154,599 office-based provider event records; of these records, 150,760 are
associated with persons having a positive person-level weight (PERWT09F). This
file includes office-based provider event records for all household members who
resided in eligible responding households and for whom at least one office-based
provider event was reported.
Each record represents one household-reported
office-based provider event that occurred during calendar year 2009.
Office-based provider visits known to have occurred after December 31, 2009 are
not included on this file. Some household members may have multiple events and
thus will be represented in multiple records on this file. Other household
members may have had no events reported and thus will have no records on this
file. These data were collected during the 2009 portion of Round 3, and Rounds 4
and 5 for Panel 13, as well as Rounds 1, 2, and the 2009 portion of Round 3 for
Panel 14 of the MEPS Household Component. The persons represented on this file
had to meet either (a) or (b):
- Be classified as a key in-scope person who responded for his or her
entire period of 2009 eligibility (i.e., persons with a positive 2009
full-year person-level weight (PERWT09F > 0)), or
- Be an eligible member of a family all of whose key in-scope members have
a positive person-level weight (PERWT09F > 0). (Such a family consists of
all persons with the same value for FAMIDYR.) That is, the person must have
a positive full-year family-level weight (FAMWT09F >0). Note that FAMIDYR
and FAMWT09F are variables on the 2009 Population Characteristics file.
Persons with no office-based medical provider visit
events for 2009 are not included on this event-level OB file but are represented
on the person-level 2009 Full Year Population Characteristics file.
Each office-based medical provider visit event record
includes the following: date of the event; type of provider seen; type of care
received; types of treatments (i.e., physical therapy, occupational therapy,
speech therapy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, etc.) received during the
event; type of services (i.e., lab test, sonogram or ultrasound, x-rays, etc.)
received, medicines prescribed during the event; flat fee information; imputed
sources of payment; total payment and total charge of the office-based event
expenditure; a full-year person-level weight; variance strata; and variance PSU.
To append person-level information such as demographic
or health insurance coverage to each event record, data from this file can be
merged with 2009 MEPS HC person-level data (e.g. Full Year Consolidated or Full
Year Population Characteristics files) using the person identifier, DUPERSID.
The office-based medical provider visit events can also be linked to the MEPS
2009 Medical Conditions File and MEPS 2009 Prescribed Medicines File. Please see
Section 5.0 for details on how to merge MEPS data files.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.1 Codebook Structure
For each variable on the office-based provider file,
both weighted and unweighted frequencies are provided in the accompanying
codebook. The codebook and data file sequence list variables in the following
order:
Unique person identifiers
Unique office-based medical provider visit event identifiers
Office-based medical provider visit characteristic variables
ICD-9-CM condition and procedure codes
Clinical Classification Software (CCS) codes
Imputed expenditure variables
Weight and variance estimation variables
Note that the person identifier is unique within this
data year.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.2 Reserved Codes
The following reserved code values are used:
| Value |
Definition |
| -1 INAPPLICABLE |
Question was not asked due to skip pattern |
| -7 REFUSED |
Question was asked and respondent refused to answer question |
| -8 DK |
Question was asked and respondent did not know answer |
| -9 NOT ASCERTAINED |
Interviewer did not record the data |
Generally, values of -1, -7, -8, and -9 for
non-expenditure variables have not been edited on this file. The values of -1
and -9 can be edited by the data users/analysts by following the skip patterns
in the HC survey questionnaire (located on the MEPS Web site:
www.meps.ahrq.gov/survey_comp/survey_questionnaires.jsp).
Return To Table Of Contents
2.3 Codebook Format
The office-based medical provider visits codebook
describes an ASCII data set (although the data are also being provided in a SAS
transport file). The following codebook items are provided for each variable:
| Identifier |
Description |
| Name |
Variable name (maximum of 8 characters) |
| Description |
Variable descriptor (maximum 40 characters) |
| Format |
Number of bytes |
| Type |
Type of data: numeric (indicated by NUM) or character (indicated by CHAR) |
| Start |
Beginning column position of variable in record |
| End |
Ending column position of variable in record |
Return To Table Of Contents
2.4 Variable Source and Naming Conventions
In general, variable names reflect the content of the
variable, with an 8-character limitation. All imputed/edited variables end with
an "X".
Return To Table Of Contents
2.4.1 General
Variables contained on this file were derived from the
HC survey questionnaire itself, derived from the MPC data collection instrument,
derived from CAPI, or assigned in sampling. The source of each variable is
identified in Section D "Variable - Source Crosswalk" in one of four ways:
- Variables derived from CAPI or assigned in sampling are indicated as
"CAPI derived" or "Assigned in sampling," respectively;
- Variables which come from one or more specific questions have those
questionnaire sections and question numbers indicated in the "Source"
column; questionnaire sections are identified as:
- MV – Office-Based Medical Provider Visits section
- FF – Flat Fee section
- CP – Charge Payment section
- Variables constructed from multiple questions using complex algorithms
are labeled "Constructed" in the "Source" column; and
- Variables which have been edited or imputed are so indicated.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.4.2 Expenditure and Source of Payment Variables
The names of the expenditure and source of payment
variables follow a standard convention, are seven characters in length, and end
in an "X" indicating edited/imputed. Please note that imputed means that a
series of logical edits, as well as an imputation process to account for missing
data, have been performed on the variable.
The total sum of payments and the 12 sources of
payment are named in the following way:
The first two characters indicate the type of event:
IP - inpatient stay
ER - emergency room visit
HH - home health visit
OM - other medical equipment
OB - office-based visit
OP - outpatient visit
DV - dental visit
RX - prescribed medicine
In the case of source of payment variables, the third
and fourth characters indicate:
SF - self or family
MR - Medicare
MD - Medicaid
PV - private insurance
VA - Veterans Administration/CHAMPVA
TR - TRICARE
OF - other Federal Government
SL - State/local government
WC - Workers’ Compensation
OT - other insurance
OR - other private
OU - other public
XP - sum of payments
In addition, the total charge variable is indicated by
TC in the variable name.
The fifth and sixth characters indicate the year (09).
The seventh character, "X", indicates whether the variable is edited/imputed.
For example, OBSF09X is the edited/imputed amount paid
by self or family for an office-based medical provider visit expenditure
incurred in 2009.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5 File Contents
2.5.1 Survey Administration Variables
2.5.1.1 Person Identifiers (DUID, PID, DUPERSID)
The dwelling unit ID (DUID) is a five-digit random
number assigned after the case was sampled for MEPS. The three-digit person
number (PID) uniquely identifies each person within the dwelling unit. The
eight-character variable DUPERSID uniquely identifies each person represented on
the file and is the combination of the variables DUID and PID. For detailed
information on dwelling units and families, please refer to the documentation
for the 2009 Full Year Population Characteristics.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.1.2 Record Identifiers (EVNTIDX, FFEEIDX)
EVNTIDX uniquely identifies each office-based medical
provider visit event (i.e., each record on the office-based medical provider
visits file) and is the variable required for linking office-based medical
provider visit events to data files containing details on conditions and/or
prescribed medicines (MEPS 2009 Medical Condition file and MEPS 2009 Prescribed
Medicine file, respectively). For details on linking see Section 5.0 or the MEPS
2009 Appendix File, HC-126I.
FFEEIDX is a constructed variable that uniquely
identifies a flat fee group, that is, all events that were part of a flat fee
payment. For example, pregnancy is typically covered in a flat fee arrangement
where the prenatal visits, the delivery, and the postpartum visits are all
covered under one flat fee dollar amount. These events (the prenatal visit, the
delivery, and the postpartum visits) would have the same value for FFEEIDX.
FFEEIDX identifies a flat fee payment that was identified using information from
the Household Component. A "mixed" flat fee group could contain both outpatient
and office-based visits. Only outpatient and office-based events are allowed in
a mixed bundle. Please note that FFEEIDX should be used to link up the
outpatient and office-based events in order to determine the full set of events
that are part of a flat fee group.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.1.3 Round Indicator (EVENTRN)
EVENTRN indicates the round in which the office-based
event was reported. Please note that Rounds 3, 4, and 5 are associated with MEPS
survey data collected from Panel 13. Likewise, Rounds 1, 2, and 3 are associated
with data collected from Panel 14.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.1.4 Panel Indicator (PANEL)
PANEL is a constructed variable used to specify the
panel number for the person. PANEL will indicate either Panel 13 or Panel 14 for
each person on the file. Panel 13 is the panel that started in 2008, and Panel
14 is the panel that started in 2009.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.2 MPC Indicator (MPCELIG, MPCDATA)
MPCELIG is a constructed variable that indicates
whether the office-based provider visit was eligible for MPC data collection.
MPCDATA is a constructed variable that indicates whether or not MPC data was
collected for the office-based provider.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.3 Office-Based Medical Provider Visit Variables
The file contains variables describing office-based
medical provider visit events reported by respondents in the Medical Provider
Visits section of the MEPS HC survey questionnaire.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.3.1 Date of Visit (OBDATEYR - OBDATEDD)
There are three variables that, together, indicate the
day, month, and year an office-based provider visit occurred (OBDATEDD,
OBDATEMM, and OBDATEYR, respectively). These variables have not been edited or
imputed.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.3.2 Visit Details (SEETLKPV-VSTRELCN)
The questionnaire determines if, during the
office-based medical provider visit, the person actually saw the provider or
talked to the provider on the telephone (SEETLKPV). Also, the questionnaire
establishes the kind of place the person saw the medical provider (MVPLACE). One
of the answer categories for the variable MVPLACE is "Laboratory/X-Ray
Facility". The importance of laboratory and x-ray events in relation to the
creation of office-based medical provider events is discussed above in Section
2.0. The categories "Birthing Center" and "Indian Health Service" were added to
MVPLACE starting in Panel 12. The questionnaire also establishes whether the
person saw or spoke to a medical doctor (SEEDOC). If during the medical visit
the patient did not see a specialty doctor (DRSPLTY), or, if the person did not
see a physician (i.e., a medical doctor), the respondent was asked to identify
the type of medical person seen (MEDPTYPE). Whether or not any medical doctors
worked at the visit location (DOCATLOC), the type of care the person received
(VSTCTGRY), and whether or not the visit or telephone call was related to a
specific condition (VSTRELCN) were also determined.
Note that, in 2002, four new categories were added to
the imputation process (13 categories in total) as opposed to nine categories in
2001. These new categories are for alternative care ("Acupuncture", "Massage
Therapist", "Homeopathic/Naturopathic/Herbalist", and "Other
Alternative/Complementary Care Pro"). In 2001, these alternative care
categories, as indicated by the variable MEDPTYPE, were not available for all
rounds; therefore, records that indicated the medical provider type was
"Acupuncture", "Massage Therapist", "Homeopathic/Naturopathic/Herbalist", or
"Other Alternative/Complementary Care Pro" were included in the "Other" category
in the 2001 imputation process.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.3.3 Treatments, Procedures, Services,
and Prescription Medicines (PHYSTH-MEDPRESC)
Types of treatments received during the office-based
medical provider visit include physical therapy (PHYSTH), occupational therapy
(OCCUPTH), speech therapy (SPEECHTH), chemotherapy (CHEMOTH), radiation therapy
(RADIATTH), kidney dialysis (KIDNEYD), IV therapy (IVTHER), drug or alcohol
treatment (DRUGTRT), allergy shots (RCVSHOT), psychotherapy/counseling
(PSYCHOTH), and shots other than allergy (OTHSHOT).
Services received during the visit included whether or
not the person received lab tests (LABTEST), a sonogram or ultrasound
(SONOGRAM), x-rays (XRAYS), a mammogram (MAMMOG), an MRI or a CAT scan (MRI), an
electrocardiogram (EKG), an electroencephalogram (EEG), a vaccination (RCVVAC),
anesthesia (ANESTH), throat swab (THRTSWAB), or other diagnostic tests or exams
(OTHSVCE). Minimal editing was done across treatment, services, and procedures
to ensure consistency across "inapplicable," "not ascertained," "don’t know,"
"refused," and "no services received" values. THRTSWAB was introduced in the
2008 version of this file.
Whether or not a surgical procedure was performed
during the visit was asked (SURGPROC).
Finally, the questionnaire determined if a medicine
was prescribed for the person during the visit (MEDPRESC). For a repeat visit
event group, if a prescribed medicine is linked to the stem event (MEDPRESC=1),
then the value of MEDPRESC is copied to the leaf events without linking the leaf
events to the prescribed medicine. Beginning in 2009, MEDPRESC=1 was recoded to
-9 for all leaf events.
VAPLACE, a constructed variable that indicates whether
the service was provided at a VA facility, was dropped from this file for
confidentiality purposes beginning in 2008.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.4 Condition and Procedure Codes
(OBICD1X-OBICD4X, OBPRO1X – OBPRO3X), and Clinical Classification Codes (OBCCC1X-OBCCC4X)
Information on household-reported medical conditions
and procedures associated with each office-based medical provider visit is
provided on this file. There are up to four condition and CCS codes
(OBICD1X-OBICD4X, OBCCC1X-OBCCC4X) and up to three procedure codes (OBPRO1X –
OBPRO3X) listed for each office-based medical provider visit. In order to obtain
complete condition information associated with an event, the analyst must link
to the Medical Conditions File. Details on how to link to the MEPS Medical
Conditions File are provided in Section 5.0. The user should note that due to
confidentiality restrictions, provider-reported condition information is not
publicly available.
The medical conditions and procedures reported by the
Household Component respondent were recorded by the interviewer as verbatim
text, which were then coded to fully-specified 2009 ICD-9-CM codes, including
medical condition and V codes (see Health Care Financing Administration, 1980),
by professional coders. Although codes were verified and error rates did not
exceed 2.5 percent for any coder, data users/analysts should not presume this
level of precision in the data; the ability of household respondents to report
condition data that can be coded accurately should not be assumed (see Cox and
Cohen, 1985; Cox and Iachan, 1987; Edwards, et al, 1994; and Johnson and
Sanchez, 1993). For detailed information on how conditions and procedures were
coded, please refer to the documentation on the MEPS 2009 Medical Conditions
File. For frequencies of conditions by event type, please see the MEPS 2009
Appendix File, HC-126I.
The ICD-9-CM conditions were aggregated into
clinically meaningful categories. These categories, included on the file as
OBCCC1X-OBCCC4X, were generated using Clinical Classification Software [formerly
known as Clinical Classifications for Health Care Policy Research (CCHPR),
(Elixhauser, et al., 1998)], which aggregates conditions and V-codes into
mutually exclusive categories, most of which are clinically homogeneous.
In order to preserve household member confidentiality,
nearly all of the condition codes provided on this file have been collapsed from
fully-specified codes to three-digit code categories. The reported ICD-9-CM code
values were mapped to the appropriate clinical classification category prior to
being collapsed to the 3-digit categories. Similarly, the procedure codes have
been collapsed from fully-specified codes to two-digit code categories.
Because of this collapsing, it
is possible for there to be duplicate ICD-9-CM condition or procedure codes
linked to a single medical event when different fully-specified codes are
collapsed into the same code. For more information on ICD-9-CM codes, see the
HC-128 documentation.
The condition codes (and clinical classification
codes) and procedure codes linked to each office-based medical provider visit
event are sequenced in the order in which the conditions were reported by the
household respondent, which was in order of input into the database and not in
order of importance or severity. Data users/analysts who use the Medical
Conditions file in conjunction with this office-based medical provider visits
file should note that the order of conditions on this file is not identical to
that on the 2009 Medical Conditions file.
Analysts should use the clinical classification codes
listed in the Conditions PUF document (HC-128) and the Appendix to the Event
Files (HC-126I) document when analyzing MEPS conditions data. Although there is
a list of clinical classification codes and labels on the Healthcare Cost and
Utilization Project (HCUP) Web site, if updates to these codes and/or labels are
made on the HCUP Web site after the release of the 2009 MEPS PUFs, these updates
will not be reflected in the 2009 MEPS data.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.5 Flat Fee Variables (FFEEIDX, FFOBTYPE, FFBEF09, FFTOT10)
2.5.5.1 Definition of Flat Fee Payments
A flat fee is the fixed dollar amount a person is
charged for a package of services provided during a defined period of time. An
example would be an obstetrician’s fee covering a normal delivery, and the
associated pre- and post-natal care. A flat fee group is the set of medical
services (i.e., events) that are covered under the same flat fee payment. The
flat fee groups represented on the office-based provider file include flat fee
groups where at least one of the health care events, as reported by the HC
respondent, occurred during 2009. By definition, a flat fee group can span
multiple years and/or event types (only outpatient department visits and
physician office visits). Furthermore, a single person can have multiple flat
fee groups.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.5.2 Flat Fee Variable Descriptions
2.5.5.2.1 Flat Fee ID (FFEEIDX)
As noted earlier in Section 2.5.1.2 "Record
Identifiers," the variable FFEEIDX uniquely identifies all events that are part
of the same flat fee group for a person. On any 2009 MEPS event file, every
event that is part of a specific flat fee group will have the same value for
FFEEIDX. Note that prescribed medicine and home health events are never included
in a flat fee group and FFEEIDX is not a variable on those event files.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.5.2.2 Flat Fee Type (FFOBTYPE)
FFOBTYPE indicates whether the 2009 office-based
medical provider visit event is the "stem" or "leaf" of a flat fee group. A stem
(records with FFOBTYPE = 1) is the initial medical service (event) which is
followed by other medical events that are covered under the same flat fee
payment. The leaves of the flat fee group (records with FFOBTYPE = 2) are those
medical events that are tied back to the initial medical event (the stem) in the
flat fee group. These "leaf" records have their expenditure variables set to
zero. For the office-based visits that are not part of a flat fee payment, the
FFOBTYPE is set to -1, "INAPPLICABLE."
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.5.2.3 Counts of Flat Fee Events that
Cross Years (FFBEF09, FFTOT10)
As described in Section 2.5.5.1, a flat fee payment
covers multiple events and the multiple events could span multiple years. For
situations where the office-based medical provider visit occurred in 2009 as a
part of a group of events, and some of the events occurred before 2009, counts
of the known events are provided on the office-based medical provider visit
event file record. Variables that indicate events occurred before or after 2009
are as follows:
FFBEF09 - total number of pre-2009 events in
the same flat fee group as the 2009 office-based medical provider visit.
This count would not include the 2009 office-based medical visit(s).
FFTOT10 - the number of 2010 office-based
events expected to be in the same flat fee group as the office-based
medical provider visit event(s) that occurred in 2009.
If there are no 2008 events on the file, FFBEF09 will
be omitted. Likewise, if there are no 2010 events on the file, FFTOT10 will be
omitted. If there are no flat fee data related to the records in this file,
FFEEIDX and FFOBTYPE will be omitted as well. Please note that the crosswalk in
this document lists all possible flat fee variables.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.5.3 Caveats of Flat Fee Groups
Data users/analysts should note that flat fee payments
are common on the office-based medical provider visits file. There are 3,403
office-based medical provider visit events that are identified as being part of
a flat fee payment group. In order to correctly identify all events that are
part of a flat fee group, the user should link all MEPS events, except those in
the prescribed medicine file, using the variable FFEEIDX. In general, every flat
fee group should have an initial visit (stem) and at least one subsequent visit
(leaf). There are some situations where this is not true. For some of these flat
fee groups, the initial visit reported occurred in 2009, but the remaining
visits that were part of this flat fee group occurred in 2010. In this case, the
2009 flat fee group represented on this file would consist of one event (the
stem). The 2010 leaf events that are part of this flat fee group are not
represented on this file. Similarly, the household respondent may have reported
a flat fee group where the initial visit began in 2008 but subsequent visits
occurred during 2009. In this case, the initial visit would not be represented
on the file. This 2009 flat fee group would then consist only of one or more
leaf records and no stem. Another reason for which a flat fee group would not
have a stem and at least one leaf record is that the stem or leaves could have
been reported as different event types. Outpatient and Office-based medical
provider visits are the only two event types allowed in a single flat fee group.
The stem may have been reported as an outpatient department visit and the leaves
may have been reported as office-based medical provider visits.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.6 Expenditure Data
2.5.6.1 Definition of Expenditures
Expenditures on this file refer to what is paid for
health care services. More specifically, expenditures in MEPS are defined as the
sum of payments for care received, including out-of-pocket payments and payments
made by private insurance, Medicaid, Medicare, and other sources. The definition
of expenditures used in MEPS differs slightly from its predecessors: the 1987
NMES and 1977 NMCES surveys where "charges" rather than sum of payments were
used to measure expenditures. This change was adopted because charges became a
less appropriate proxy for medical expenditures during the 1990s due to the
increasingly common practice of discounting. Although measuring expenditures as
the sum of payments incorporates discounts in the MEPS expenditure estimates,
the estimates do not incorporate any payment not directly tied to specific
medical care visits, such as bonuses or retrospective payment adjustments paid
by third party payers. Another general change from the two prior surveys is that
charges associated with uncollected liability, bad debt, and charitable care
(unless provided by a public clinic or hospital) are not counted as expenditures
because there are no payments associated with those classifications. While
charge data are provided on this file, data users/analysts should use caution
when working with this data because a charge does not typically represent actual
dollars exchanged for services or the resource costs of those services, nor is
it directly comparable to the resource costs of those services or the
expenditures defined in the 1987 NMES (for details on expenditure definitions,
see Monheit et al., 1999). AHRQ has developed factors to apply to the 1987 NMES
expenditure data to facilitate longitudinal analysis. These factors can be
accessed via the CFACT data center. For more information, see the Data Center
section of the MEPS Web site
www.meps.ahrq.gov/data_stats/onsite_datacenter.jsp.
If examining trends in MEPS expenditures or performing longitudinal analysis on
MEPS expenditures please refer to Section C, sub-Section 3.3 for more
information.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.6.2 Data Editing and Imputation Methodologies of Expenditure Variables
The expenditure data included on this file were
derived from both the MEPS household (HC) and medical provider (MPC) components.
The MPC contacted medical providers identified by household respondents. The
charge and payment data from medical providers were used in the expenditure
imputation process to supplement missing household data. For all office-based
medical provider visits, MPC data were used if available; otherwise HC data were
used. Missing data for office-based medical provider visits where HC data were
not complete and MPC data were not collected, or MPC data were not complete,
were derived through the imputation process.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.6.2.1 General Data Editing Methodology
Logical edits were used to resolve internal
inconsistencies and other problems in the HC and MPC survey-reported data. The
edits were designed to preserve partial payment data from households and
providers, and to identify actual and potential sources of payment for each
household-reported event. In general, these edits accounted for outliers,
co-payments or charges reported as total payments, and reimbursed amounts that
were reported as out-of-pocket payments. In addition, edits were implemented to
correct for misclassifications between Medicare and Medicaid and between
Medicare HMOs and private HMOs as payment sources. These edits produced a
complete vector of expenditures for some events, and provided the starting point
for imputing missing expenditures in the remaining events.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.6.2.2 Imputation Procedures
For events in this file that were eligible for the
MEPS-MPC (i.e. physician office visits where MPCELIG=1), a predictive mean
matching imputation method was used to impute missing expenditures. This
procedure uses regression models (based on events with completely reported
expenditure data) to predict total expenses for each event. Then, for each event
with missing payment information, a donor event with the closest predicted
payment to that for the event with missing payment was used to impute the
missing payment value. For events in this file that were not eligible for the
MEPS-MPC (i.e. non-physician visits where MPCELIG=2), a weighted sequential
hot-deck procedure was used to impute missing expenditures. This procedure uses
survey data from respondents to replace missing data while taking into account
the persons’ weighted distribution in the imputation process. Classification
variables vary by type of provider in the hot-deck imputations, but total
charge (when available) and insurance coverage are key variables in all of the
imputations. Separate imputations were performed for flat fee and simple events.
After the imputations were completed, visits to physician and non-physician
providers were combined into this office-based medical provider visits file.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.6.2.3 Office-Based Provider Visit Data Editing and Imputation
Expenditures for office-based provider visits were
developed in a sequence of logical edits and imputations. "Household" edits were
applied to sources and amounts of payment for all events reported by HC
respondents. "MPC" edits were applied to provider-reported sources and amounts
of payment for records matched to household-reported events. Both sets of edits
were used to correct obvious errors (as described above) in the reporting of
expenditures. After the data from each source were edited, a decision was made
as to whether household- or MPC-reported information would be used in the final
editing and hot-deck imputations for missing expenditures. The general rule was
that MPC data would be used for events where a household-reported event
corresponded to an MPC-reported event (i.e., a matched event), since providers
usually have more complete and accurate data on sources and amounts of payment
than households.
One of the more important edits separated flat fee
events from simple events. This edit was necessary because groups of events
covered by a flat fee (i.e., a flat fee bundle) were edited and imputed
separately from individual events covered by a single charge (i.e., simple
events). (See Section 2.5.5 for more details on flat fee groups).
Logical edits also were used to sort each event into a
specific category for the imputations. Events with complete expenditures were
flagged as potential donors for the hot-deck imputations, while events with
missing expenditure data were assigned to various recipient categories. Each
event with missing expenditure data was assigned to a recipient category based
on the extent of its missing charge and expenditure data. For example, an event
with a known total charge but no expenditure information was assigned to one
category, while an event with a known total charge and partial expenditure
information was assigned to a different category. Similarly, events without a
known total charge and no or partial expenditure information were assigned to
various recipient categories.
The logical edits produced eight recipient categories
in which all events had a common extent of missing data. Separate hot-deck
imputations were performed on events in each recipient category. For hospital
inpatient and emergency room events, the donor pool was restricted to
events with complete expenditures from the MPC. Due to the low ratio of donors
to recipients for hospital outpatient and office based events there were no
donor pool restrictions.
The donor pool included "free events" because, in some
instances, providers are not paid for their services. These events represent
charity care, bad debt, provider failure to bill, and third party payer
restrictions on reimbursement in certain circumstances. If free events were
excluded from the donor pool, total expenditures would be over-counted because
the distribution of free events among complete events (donors) would not be
represented among incomplete events (recipients).
For office-based and outpatient events, the donor pool
also included events originally reported by providers as paid on a capitated
basis. To obtain the fee-for-service (FFS) equivalent payments for these
capitated events, a "capitation imputation" was implemented (see the next
section). Once imputed with the FFS equivalent payments, these events became
donors for all other incomplete events, particularly for events reported by the
household as services covered under managed care plans.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.6.3 Capitation Imputation
The imputation process was also used to estimate
expenditures at the event level for events that were paid on a per month per
person (capitated) basis. The capitation imputation procedure was designed as a
reasonable approach to complete event-level expenditures for persons in non-fee
for service managed care plans. HMO events reported in the MPC as covered by
capitation arrangements were imputed using similar completed HMO events paid on
a fee-for-service, with total charge as a key variable. Then this fully
completed set of MPC events was used in the donor pool for the main imputation
process for cases in HMOs. By using this strategy, capitated HMO events
were imputed as if the provider were reimbursed from the HMO on a discounted
fee-for-service basis.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.6.4 Imputation Flag (IMPFLAG)
IMPFLAG is a six-category variable that indicates if
the event contains complete Household Component (HC) or Medical Provider
Component (MPC) data, was fully or partially imputed, or was imputed in the
capitated imputation process (for OP and MV events only). The following list
identifies how the imputation flag is coded; the categories are mutually
exclusive.
IMPFLAG = 0 not eligible for imputation (includes zeroed out and flat fee leaf events)
IMPFLAG = 1 complete HC data
IMPFLAG = 2 complete MPC data
IMPFLAG = 3 fully imputed
IMPFLAG = 4 partially imputed
IMPFLAG = 5 complete MPC data through capitation imputation
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.6.5 Flat Fee Expenditures
The approach used to count expenditures for flat fees
was to place the expenditure on the first visit of the flat fee group. The
remaining visits have zero payments. Thus, if the first visit in the flat fee
group occurred prior to 2009, all of the events that occurred in 2009 will have
zero payments. Conversely, if the first event in the flat fee group occurred at
the end of 2009, the total expenditure for the entire flat fee group will be on
that event, regardless of the number of events it covered after 2009. See
Section 2.5.5 for details on the flat fee variables.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.6.6 Zero Expenditures
There are some medical events reported by respondents
where the payments were zero. Zero payment events can occur in MEPS for the
following reasons: (1) the visit was covered under a flat fee arrangement (flat
fee payments are included only on the first event covered by the arrangement),
(2) there was no charge for a follow-up visit, (3) the provider was never paid
directly for services provided by an individual, insurance plan, or other
source, (4) charges were included in another bill, or (5) event was paid through
government or privately funded research or clinical trials.
The file also contains a small number of events
involving a telephone call rather than a visit to the medical provider (SEETLKPV
= 2). The expenditure variables for telephone calls have a value of -1
"INAPPLICABLE".
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.6.7 Discount Adjustment Factor
An adjustment was also applied to some HC-reported
expenditure data because an evaluation of matched HC/MPC data showed that
respondents who reported that charges and payments were equal were often unaware
that insurance payments for the care had been based on a discounted charge. To
compensate for this systematic reporting error, a weighted sequential hot-deck
imputation procedure was implemented to determine an adjustment factor for
HC-reported insurance payments when charges and payments were reported to be
equal. As for the other imputations, selected predictor variables were used to
form groups of donor and recipient events for the imputation process.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.6.8 Sources of Payment
In addition to total expenditures, variables are
provided which itemize expenditures according to major source of payment
categories. These categories are:
- Out-of-pocket by user (self) or family,
- Medicare,
- Medicaid,
- Private Insurance,
- Veterans /CHAMPVA,
- TRICARE,
- Other Federal sources - includes Indian Health Service, Military
Treatment Facilities, and other care by the Federal government,
- Other State and Local Sources - includes community and neighborhood
clinics, State and local health departments, and State programs other than
Medicaid,
- Workers’ Compensation, and
- Other Unclassified Sources - includes sources such as automobile,
homeowner’s, and liability insurance, and other miscellaneous or unknown
sources.
Two additional source of payment variables were
created to classify payments for events with apparent inconsistencies
between insurance coverage and sources of payment based on data collected in
the survey. These variables include:
- Other Private - any type of private insurance payments reported for
persons not reported to have any private health insurance coverage during
the year as defined in MEPS, and
- Other Public – Medicare/Medicaid payments reported for persons who were
not reported to be enrolled in the Medicare/Medicaid program at any time
during the year.
Though these two sources are relatively small
in magnitude, data users/analysts should exercise caution when interpreting the
expenditures associated with these two additional sources of payment. While
these payments stem from apparent inconsistent responses to health insurance and
source of payment questions in the survey, some of these inconsistencies may
have logical explanations. For example, private insurance coverage in MEPS is
defined as having a major medical plan covering hospital and physician services.
If a MEPS sampled person did not have such coverage but had a single service
type insurance plan (e.g., dental insurance) that paid for a particular episode
of care, those payments may be classified as "other private". Some of the "other
public" payments may stem from confusion between Medicaid and other state and
local programs or may be persons who were not enrolled in Medicaid, but were
presumed eligible by a provider who ultimately received payments from the public
payer.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.6.9 Office-Based Expenditure Variables (OBSF09X - OBTC09X)
OBSF09X - OBOT09X are the 12 sources of payment. The
12 sources of payment are: self/family (OBSF09X), Medicare (OBMR09X), Medicaid
(OBMD09X), private insurance (OBPV09X), Veterans /CHAMPVA (OBVA09X), TRICARE
(OBTR09X), other Federal sources (OBOF09X), State and Local (non-federal)
government sources (OBSL09X), Workers’ Compensation (OBWC09X), other private
insurance (OBOR09X), other public insurance (OBOU09X), and other insurance
(OBOT09X). OBXP09X is the sum of the 12 sources of payment for the Office Based
expenditures, and OBTC09X is the total charge.
Return To Table Of Contents
2.5.7 Rounding
Expenditure variables have been rounded to the nearest
penny. Person-level expenditure information released on the MEPS 2009
Person-Level Expenditure File will be rounded to the nearest dollar. It should
be noted that using the MEPS 2009 event files to create person-level
totals will yield slightly different totals than that those found on the
person-level expenditure file. These differences are due to rounding only.
Moreover, in some instances, the number of persons having expenditures on the
event files for a particular source of payment may differ from the number of
persons with expenditures on the person-level expenditure file for that source
of payment. This difference is also an artifact of rounding only. Please see the
MEPS 2009 Appendix File, HC-126I, for details on such rounding differences.
Return To Table Of Contents
3.0 Sample Weight (PERWT09F)
3.1 Overview
There is a single full year person-level weight
(PERWT09F) assigned to each record for each key, in-scope person who responded
to MEPS for the full period of time that he or she was in-scope during 2009. A
key person either was a member of an NHIS household at the time of the NHIS
interview, or became a member of a family associated with such a household after
being out-of-scope at the time of the NHIS (the latter circumstance includes
newborns as well as persons returning from military service, an institution, or
living outside the United States). A person is in-scope whenever he or she is a
member of the civilian noninstitutionalized portion of the U.S. population.
Return To Table Of Contents
3.2 Details on Person Weight Construction
The person-level weight PERWT09F was developed in
several stages. Person-level weights for Panel 13 and Panel 14 were created
separately. The weighting process for each panel included an adjustment for
nonresponse over time and calibration to independent population figures. The
calibration was initially accomplished separately for each panel by raking the
corresponding sample weights to Current Population Survey (CPS) population
estimates based on five variables. The five variables used in the establishment
of the initial person-level control figures were: census region (Northeast,
Midwest, South, West); MSA status (MSA, non-MSA); race/ethnicity (Hispanic,
non-Hispanic with black as sole reported race, non-Hispanic with Asian as sole
reported race, and other); sex; and age. A 2009
composite weight was then formed by multiplying each weight from Panel 13 by the
factor .52 and each weight from Panel 14 by the factor .48. The choice of
factors reflected the relative sample sizes of the two panels, helping to limit
the variance of estimates obtained from pooling the two samples. The composite
weight was again raked to the same set of CPS-based control totals. When poverty
status information derived from income variables became available, a final
raking was undertaken on the previously established weight variable. Control
totals were established using poverty status (five categories: below poverty,
from 100 to 125 percent of poverty, from 125 to 200 percent of poverty, from 200
to 400 percent of poverty, at least 400 percent of poverty) as well as the
original five variables used in the previous calibrations.
Return To Table Of Contents
3.2.1 MEPS Panel 13 Weight
The person-level weight for MEPS Panel 13 was
developed using the 2008 full year weight for an individual as a "base" weight
for survey participants present in 2008. For key, in-scope RU members who joined
an RU some time in 2009 after being out-of-scope in 2008, the 2008 family weight
associated with the family the person joined served as a "base" weight. The
weighting process included an adjustment for nonresponse over Rounds 4 and 5 as
well as raking to population control figures for December 2009. These control
figures were derived by scaling back the population totals obtained from the
March 2010 CPS to correspond to a national estimate for the civilian
noninstitutionalized population provided by the Census Bureau for December 2009.
Variables used in the establishment of person-level control figures included:
census region (Northeast, Midwest, South, West); MSA status (MSA, non-MSA);
race/ethnicity (Hispanic, black but non-Hispanic, Asian but non-Hispanic,
and other); sex; and age. Key, responding persons not in-scope on
December 31, 2009 but in-scope earlier in the year retained, as their final
Panel 13 weight, the weight after the nonresponse adjustment.
Return To Table Of Contents
3.2.2 MEPS Panel 14 Weight
The person-level weight for MEPS Panel 14 was
developed using the MEPS Round 1 person-level weight as a "base" weight. For
key, in-scope RU members who joined an RU after Round 1, the Round 1 family
weight served as a "base" weight. The weighting process included an adjustment
for nonresponse over Round 2 and the 2009 portion of Round 3 as well as raking
to the same population control figures for December 2009 used for the MEPS Panel
13 weights. The same five variables employed for Panel 13 raking (census region,
MSA status, race/ethnicity, sex, and age) were used for Panel 14 raking.
Similarly, for Panel 14, key, responding persons not in-scope on December 31,
2009 but in-scope earlier in the year retained, as their final Panel 14 weight,
the weight after the nonresponse adjustment.
Note that the MEPS Round 1 weights incorporated the
following components: the original household probability of selection for the
NHIS; ratio-adjustment to NHIS-based national population estimates at the
household (occupied dwelling unit) level; adjustment for nonresponse at the
dwelling unit level for Round 1; and poststratification to figures at the family
and person level obtained from the March CPS data base of the corresponding year
(i.e., 2008 for Panel 13 and 2009 for Panel 14).
Return To Table Of Contents
3.2.3 The Final Weight for 2009
The composite weights of two groups of persons who
were out-of-scope on December 31, 2009 were poststratified. Specifically, the
weights of those who were in-scope some time during the year, out-of-scope on
December 31, and entered a nursing home during the year were poststratified to a
corresponding control total obtained from the 1996 MEPS Nursing Home Component.
Those who died while in-scope during 2009 were poststratified to corresponding
estimates derived using data obtained from the Medicare Current Beneficiary
Survey (MCBS) and Vital Statistics information provided by the National Center
for Health Statistics (NCHS). Separate decedent control totals were developed
for the "65 and older" and "under 65" civilian noninstitutionalized populations.
Overall, the weighted population estimate for the
civilian noninstitutionalized population for December 31, 2009 is 302,964,200
(PERWT09F>0 and INSC1231=1). The sum of the person-level weights across all
persons assigned a positive person-level weight is 306,660,588.
Return To Table Of Contents
3.2.4 Coverage
The target population for MEPS in this file is the
2009 U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population. However, the MEPS sampled
households are a subsample of the NHIS households interviewed in 2007 (Panel 13)
and 2008 (Panel 14). New households created after the NHIS interviews for the
respective Panels and consisting exclusively of persons who entered the target
population after 2007 (Panel 13) or after 2008 (Panel 14) are not covered by
MEPS. Neither are previously out-of-scope persons who join an existing household
but are unrelated to the current household residents. Persons not covered by a
given MEPS panel thus include some members of the following groups: immigrants;
persons leaving the military; U.S. citizens returning from residence in another
country; and persons leaving institutions. The set of uncovered persons
constitutes only a small segment of the MEPS target population.
Return To Table Of Contents
3.3 Using MEPS Data for Trend Analysis
MEPS began in 1996, and the utility of the survey for
analyzing health care trends expands with each additional year of data. However,
it is important to consider a variety of factors when examining trends over time
using MEPS. Statistical significance tests should be conducted to assess the
likelihood that observed trends may be attributable to sampling variation. The
length of time being analyzed should also be considered. In particular, large
shifts in survey estimates over short periods of time (e.g. from one year to the
next) that are statistically significant should be interpreted with caution,
unless they are attributable to known factors such as changes in public policy,
economic conditions, or MEPS survey methodology. Looking at changes over longer
periods of time can provide a more complete picture of underlying trends.
Analysts may wish to consider using techniques to smooth or stabilize analyses
of trends using MEPS data such as comparing pooled time periods (e.g. 1996-97
versus 2004-05), working with moving averages, or using modeling techniques with
several consecutive years of MEPS data to test the fit of specified patterns
over time. Finally, researchers should be aware of the impact of multiple
comparisons on Type I error. Without making appropriate allowance for multiple
comparisons, undertaking numerous statistical significance tests of trends
increases the likelihood of concluding that a change has taken place when one
has not.
Return To Table Of Contents
4.0 Strategies for Estimation
4.1 Developing Event-Level Estimates
The data in this file can be used to develop national
2009 event level estimates for the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population
on office-based medical provider visits as well as expenditures, and sources of
payment for these visits. Estimates of total visits are the sum of the weight
variable (PERWT09F) across relevant event records while estimates of other
variables must be weighted by PERWT09F to be nationally representative. The
tables below contain event-level estimates for selected variables.
Selected Event Level Estimates
Office-Based Visits
| Estimate of Interest |
Variable
Name |
Estimate (SE) |
Estimate
Excluding Zero
Payment Events
(SE)** |
Total number of office-based
medical provider visits
(including phone call events*,
in millions) |
PERWT09F |
1,555.8 (42.65) |
1,485.1 (40.99) |
Total number of office-based
medical provider visits in
person and not by telephone
(SEETLKPV=1, in millions) |
PERWT09F |
1,545.8 (42.45) |
1,484.9 (40.98) |
Total number of in-person
visits to doctor (SEETLKPV=1
& SEEDOC=1, in millions) |
PERWT09F |
987.5 (24.76) |
956.2 (24.15) |
Proportion of office-based
medical provider visits with
expenditures > 0** |
OBXP09X |
0.955 (0.0024) |
------------- |
Office-Based Expenditures (SEETLKPV = 1)
| Estimate of Interest |
Variable
Name |
Estimate (SE) |
Estimate
Excluding Zero
Payment Events
(SE)** |
Mean total payments per visit
(all sources) |
OBXP09X |
$197 ($4.1) |
$205 ($4.2) |
Mean out-of-pocket payment
per visit |
OBSF09X |
$28 ($0.6) |
$29 ($0.7) |
Mean proportion of total
expenditures paid by private
insurance per visit |
OBPV09X/
OBXP09X |
------------- |
0.390 (0.0069) |
Office-Based Expenditures: Physician Visits (SEEDOC = 1 & SEETLKPV = 1)
| Estimate of Interest |
Variable
Name |
Estimate (SE) |
Estimate
Excluding Zero
Payment Events
(SE)** |
Mean total payments per visit
where person saw medical
doctor |
OBXP09X |
$218 ($5.1) |
$225 ($5.2) |
|
Mean out-of-pocket payment
per visit where person saw
medical doctor |
OBSF09X |
$28 ($0.7) |
$29 ($0.7) |
|
Mean proportion of total
expenditures per visit paid
by private insurance where
person saw medical doctor |
OBPV09X/
OBXP09X |
------------- |
0.396 (0.0064) |
*OBXP09X=-1 (inapplicable) for all phone call events
(SEETLKPV=2).
** Zero payment events can occur in MEPS for the
following reasons: (1) the visit was covered under a flat fee arrangement (flat
fee payments are included only on the first event covered by the arrangement),
(2) there was no charge for a follow-up visit, (3) the provider was never paid
directly for services provided by an individual, insurance plan, or other
source, (4) charges were included in another bill, or (5) event was paid through
government or privately funded research or clinical trials.
Return To Table Of Contents
4.2 Person-Based Estimates for Office-Based Visits
To enhance analyses of office-based visits, analysts
may link information about office-based visits by sample persons in this file to
the annual full year consolidated file (which has data for all MEPS sample
persons), or conversely, link person-level information from the full year
consolidated file to this event level file (see Section 5.0 below for more
details). Both this file and the full year consolidated file may be used to
derive estimates for persons with office-based care and annual estimates of
total expenditures. However, if the estimate relates to the entire population,
this file cannot be used to calculate the denominator, as only those persons
with at least one office-based event are represented on this data file.
Therefore, the full year consolidated file must be used for person-level
analyses that include both persons with and without office-based care.
Return To Table Of Contents
4.3 Variables with Missing Values
It is essential that the analyst examine all variables
for the presence of negative values used to represent missing values. For
continuous or discrete variables, where means or totals may be taken, it may be
necessary to set minus values to values appropriate to the analytic needs. That
is, the analyst should either impute a value or set the value to one that will
be interpreted as missing by the computing language used. For categorical and
dichotomous variables, the analyst may want to consider whether to recode or
impute a value for cases with negative values or whether to exclude or include
such cases in the numerator and/or denominator when calculating proportions.
Methodologies used for the editing/imputation of
expenditure variables (e.g., sources of payment, flat fee, and zero
expenditures) are described in Section 2.5.6.
Return To Table Of Contents
4.4 Variance Estimation (VARSTR, VARPSU)
MEPS has a complex sample design. To obtain estimates
of variability (such as the standard error of sample estimates or corresponding
confidence intervals) for MEPS estimates, analysts need to take into account the
complex sample design of MEPS for both person-level and family-level analyses.
Several methodologies have been developed for estimating standard errors for
surveys with a complex sample design, including the Taylor-series linearization
method, balanced repeated replication, and jackknife replication. Various
software packages provide analysts with the capability of implementing these
methodologies. Replicate weights have not been developed for the MEPS data.
Instead, the variables needed to calculate appropriate standard errors based on
the Taylor-series linearization method are included on this file as well as all
other MEPS public use files. Software packages that permit the use of the
Taylor-series linearization method include SUDAAN, Stata, SAS (version 8.2 and
higher), and SPSS (version 12.0 and higher). For complete information on the
capabilities of each package, analysts should refer to the corresponding
software user documentation.
Using the Taylor-series linearization method, variance
estimation strata and the variance estimation PSUs within these strata must be
specified. The variance strata variable is named VARSTR, while the variance PSU
variable is named VARPSU. Specifying a "with replacement" design in a computer
software package, such as SUDAAN, provides standard errors appropriate for
assessing the variability of MEPS survey estimates. It should be noted that the
number of degrees of freedom associated with estimates of variability indicated
by such a package may not appropriately reflect the actual number available. For
MEPS sample estimates for characteristics generally distributed throughout the
country (and thus the sample PSUs), one can expect at least 100 degrees of
freedom for the 2009 full year data associated with the corresponding estimates
of variance.
Prior to 2002, MEPS variance strata and PSUs were
developed independently from year to year, and the last two characters of the
strata and PSU variable names denoted the year. However, beginning with the 2002
Point-in-Time PUF, the variance strata and PSUs were developed to be compatible
with MEPS data associated with the NHIS sample design used through 2005. Such
data can be pooled and the variance strata and PSU variables provided can be
used without modification for variance estimation purposes for estimates
covering multiple years of data.
As a result of the change in the NHIS sample design in
2006, a new set of variance strata and PSUs have been established for variance
estimation purposes for use with MEPS Panel 12 and subsequent MEPS panels. There
were 165 variance strata associated with both MEPS Panel 13 and Panel 14,
providing a substantial number of degrees of freedom for subgroups as well as
the nation as a whole. Each variance stratum contains either two or three
variance estimation PSUs.
Return To Table Of Contents
5.0 Merging/Linking MEPS Data Files
Data from this file can be used alone or in
conjunction with other files for different analytic purposes. This section
summarizes various scenarios for merging/linking MEPS event files. The set of
households selected for MEPS is a subsample of those participating in the
National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), thus, each MEPS panel can also be
linked back to the previous year’s NHIS public use data files. For information
on obtaining MEPS/NHIS link files please see
www.meps.ahrq.gov/data_stats/more_info_download_data_files.jsp.
Return To Table Of Contents
5.1 Linking to the Person-Level File
Merging characteristics of interest from person-level
file (e.g., MEPS 2009 Full Year Consolidated File) expands the scope of
potential estimates. For example, to estimate the total number of office-based
medical provider visits of persons with specific demographic characteristics
(such as age, race, sex, and education), population characteristics from a
person-level file need to be merged onto the office-based medical provider
visits file. This procedure is illustrated below. The MEPS 2009 Appendix File,
HC-126I, provides additional detail on how to merge MEPS data files.
- Create data set PERSX by sorting the 2009 Full Year Consolidated File by
the person identifier, DUPERSID. Keep only variables to be merged onto the
office-based medical provider visits file and DUPERSID.
- Create data set OBMP by sorting the office-based medical provider visits
file by person identifier, DUPERSID.
- Create final data set NEWOBMP by merging these two files by DUPERSID,
keeping only records on the office-based medical provider visits file.
The following is an example of SAS code, which
completes these steps:
PROC SORT DATA=HCXXX (KEEP=DUPERSID AGE31X AGE42X
AGE53X SEX RACEX EDUCYR)
OUT=PERSX;
BY DUPERSID;
RUN;
PROC SORT DATA=OBMP;
BY DUPERSID;
RUN;
DATA NEWOBMP;
MERGE OBMP (IN=A) PERSX(IN=B);
BY DUPERSID;
IF A;
RUN;
Return To Table Of Contents
5.2 Linking to the Prescribed Medicines File
The RXLK file provides a link from the MEPS event
files to the Prescribed Medicine Event File. When using RXLK, data
users/analysts should keep in mind that one office-based visit can link to more
than one prescribed medicine record. Conversely, a prescribed medicine event may
link to more than one office-based visit or different types of events. When this
occurs, it is up to the data user/analyst to determine how the prescribed
medicine expenditures should be allocated among those medical events. For
detailed linking examples, including SAS code, data users/analysts should refer
to the MEPS 2009 Appendix File, HC-126I.
Return To Table Of Contents
5.3 Linking to the Medical Conditions File
The CLNK provides a link from MEPS event files to the
2009 Medical Conditions File. When using the CLNK, data users/analysts should
keep in mind that (1) conditions are household-reported, (2) there may be
multiple conditions associated with an office-based medical provider visit, and
(3) a condition may link to more than one office-based medical provider visit or
any other type of visit. Users should also note that not all office-based
medical provider visits link to the condition file.
Return To Table Of Contents
References
Cohen, S.B. (1996). The Redesign of the Medical
Expenditure Panel Survey: A Component of the DHHS Survey Integration Plan.
Proceedings of the COPAFS Seminar on Statistical Methodology in the Public
Service.
Cox, B.G. and Cohen, S.B. (1985). Chapter 6: A
Comparison of Household and Provider Reports of Medical Conditions. In
Methodological Issues for Health Care Surveys. Marcel Dekker, New York.
Cox, B. and Iachan, R. (1987). A Comparison of
Household and Provider Reports of Medical Conditions. Journal of the American
Statistical Association 82(400):1013-18.
Edwards, W.S., Winn, D.M., Kurlantzick V., et al.
(1994). Evaluation of National Health Interview Survey Diagnostic Reporting.
National Center for Health Statistics, Vital Health 2(120).
Elixhauser A., Steiner C.A., Whittington C.A., and
McCarthy E. Clinical Classifications for Health Policy Research: Hospital
Inpatient Statistics, 1995. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, HCUP-3
Research Note. Rockville, MD: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research; 1998. AHCPR Pub. No. 98-0049.
Ezzati-Rice, T.M., Rohde, F., Greenblatt, J., Sample
Design of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component, 1998–2007.
Methodology Report No. 22. March 2008. Agency for Healthcare Research and
Quality, Rockville, MD.
Health Care Financing Administration (1980).
International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical
Modification (ICD-CM). Vol. 1. (DHHS Pub. No. (PHS) 80-1260). DHHS: U.S. Public
Health Services.
Johnson, A.E. and Sanchez, M.E. (1993). Household and
Medical Provider Reports on Medical Conditions: National Medical Expenditure
Survey, 1987. Journal of Economic and Social Measurement. Vol. 19,
199-233.
Monheit, A.C., Wilson, R., and Arnett, III, R.H.
(Editors). Informing American Health Care Policy. (1999). Jossey-Bass Inc, San
Francisco.
Shah, B.V., Barnwell, B.G., Bieler, G.S., Boyle, K.E.,
Folsom, R.E., Lavange, L., Wheeless, S.C., and Williams, R. (1996). Technical
Manual: Statistical Methods and Algorithms Used in SUDAAN Release 7.0,
Research Triangle Park, NC: Research Triangle Institute.
Return To Table Of Contents
D. Variable-Source Crosswalk
VARIABLE-SOURCE CROSSWALK
FOR MEPS HC-126G: 2009 OFFICE-BASED MEDICAL PROVIDER
VISITS
Survey Administration Variables
| Variable |
Description |
Source |
| DUID |
Dwelling unit ID |
Assigned in sampling |
| PID |
Person number |
Assigned in sampling |
| DUPERSID |
Person ID (DUID + PID) |
Assigned in sampling |
| EVNTIDX |
Event ID |
Assigned in sampling |
| EVENTRN |
Event round number |
CAPI derived |
| PANEL |
Panel number |
Constructed |
| FFEEIDX |
Flat fee ID |
CAPI derived |
| MPCELIG |
MPC eligibility flag |
Constructed |
| MPCDATA |
MPC data flag |
Constructed |
Return To Table Of Contents
Medical Provider Visits Variables
| Variable |
Description |
Source |
| OBDATEYR |
Event date – year |
CAPI derived |
| OBDATEMM |
Event date – month |
CAPI derived |
| OBDATEDD |
Event date – day |
CAPI derived |
| SEETLKPV |
Did P visit prov in person or telephone |
MV01 |
| MVPLACE |
Kind of place patient saw MV provider |
MV02A |
| SEEDOC |
Did P talk to MD this visit/phone call |
MV03 |
| DRSPLTY |
MVIS doctor’s specialty |
MV03A |
| MEDPTYPE |
Type of med person P talked to on vst dt |
MV04 |
| DOCATLOC |
Any MD work at location where P saw prov |
MV06 |
| VSTCTGRY |
Best category for care P recv on vst dt |
MV07 |
| VSTRELCN |
This vst/phone call related to spec cond |
MV08 |
| PHYSTH |
This visit did P have physical therapy |
MV10 |
| OCCUPTH |
This vis did P have occupational therapy |
MV10 |
| SPEECHTH |
This visit did P have speech therapy |
MV10 |
| CHEMOTH |
This visit did P have chemotherapy |
MV10 |
| RADIATTH |
This visit did P have radiation therapy |
MV10 |
| KIDNEYD |
This visit did P have kidney dialysis |
MV10 |
| IVTHER |
This visit did P have IV therapy |
MV10 |
| DRUGTRT |
This vis did P have trt for drug/alcohol |
MV10 |
| RCVSHOT |
This visit did P receive an allergy shot |
MV10 |
| PSYCHOTH |
Did P have psychotherapy/counseling |
MV10 |
| OTHSHOT |
This visit did P have other shot |
MV10 |
| LABTEST |
This visit did P have lab tests |
MV11 |
| SONOGRAM |
This visit did P have sonogram or ultrsd |
MV11 |
| XRAYS |
This visit did P have x-rays |
MV11 |
| MAMMOG |
This visit did P have a mammogram |
MV11 |
| MRI |
This visit did P have an MRI/Catscan |
MV11 |
| EKG |
This visit did P have an EKG or ECG |
MV11 |
| EEG |
This visit did P have an EEG |
MV11 |
| RCVVAC |
This visit did P receive a vaccination |
MV11 |
| ANESTH |
This visit did P receive anesthesia |
MV11 |
| OTHSVCE |
This visit did P have oth diag test/exam |
MV11 |
| THRTSWAB |
This visit did P have throat swab |
MV11 |
| SURGPROC |
Was surg proc performed on P this visit |
MV12 |
| MEDPRESC |
Any medicines prescribed for P this visit |
MV14 |
| OBICD1X |
3-digit ICD-9-CM condition code |
Edited |
| OBICD2X |
3-digit ICD-9-CM condition code |
Edited |
| OBICD3X |
3-digit ICD-9-CM condition code |
Edited |
| OBICD4X |
3-digit ICD-9-CM condition code |
Edited |
| OBPRO1X |
2-digit ICD-9-CM procedure code |
Edited |
| OBPRO2X |
2-digit ICD-9-CM procedure code |
Edited |
| OBPRO3X |
2-digit ICD-9-CM procedure code |
Edited |
| OBCCC1X |
Modified Clinical Classification Code |
Constructed/Edited |
| OBCCC2X |
Modified Clinical Classification Code |
Constructed/Edited |
| OBCCC3X |
Modified Clinical Classification Code |
Constructed/Edited |
| OBCCC4X |
Modified Clinical Classification Code |
Constructed/Edited |
Return To Table Of Contents
Flat Fee Variables
| Variable |
Description |
Source |
| FFOBTYPE |
Flat fee bundle |
Constructed |
| FFBEF09 |
Total # of visits in FF before 2009 |
FF05 |
| FFTOT10 |
Total # of visits in FF after 2009 |
FF10 |
Return To Table Of Contents
Imputed Expenditure Variables
| Variable |
Description |
Source |
| OBSF09X |
Amount paid, self/family (imputed) |
CP Section (Edited) |
| OBMR09X |
Amount paid, Medicare (imputed) |
CP Section (Edited) |
| OBMD09X |
Amount paid, Medicaid (imputed) |
CP Section (Edited) |
| OBPV09X |
Amount paid, private insurance (imputed) |
CP Section (Edited) |
| OBVA09X |
Amount paid, Veterans/CHAMPVA (imputed) |
CP Section (Edited) |
| OBTR09X |
Amount paid, TRICARE (imputed) |
CP Section (Edited) |
| OBOF09X |
Amount paid, other federal (imputed) |
CP Section (Edited) |
| OBSL09X |
Amount paid, state & local government
(imputed) |
CP Section (Edited) |
| OBWC09X |
Amount paid, workers’ compensation (imputed) |
CP Section (Edited) |
| OBOR09X |
Amount paid, other private insurance (imputed) |
Constructed |
| OBOU09X |
Amount paid, other public insurance (imputed) |
Constructed |
| OBOT09X |
Amount paid, other insurance (imputed) |
CP Section (Edited) |
| OBXP09X |
Sum of OBSF09X – OBOT09X (imputed) |
Constructed |
| OBTC09X |
Household reported total charge (imputed) |
CP Section (Edited) |
| IMPFLAG |
Imputation status |
Constructed |
Return To Table Of Contents
Weights
| Variable |
Description |
Source |
| PERWT09F |
Expenditure file person weight, 2009 |
Constructed |
| VARSTR |
Variance estimation stratum, 2009 |
Constructed |
| VARPSU |
Variance estimation PSU, 2009 |
Constructed |
Return To Table Of Contents
|
