Skip to main content
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
STATISTICAL BRIEF #543:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| July 2022 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Patricia S. Keenan, PhD and G. Edward Miller, PhD
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Highlights
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
IntroductionEmployer-sponsored insurance (ESI) is the primary source of health insurance coverage for individuals under age 65. This Statistical Brief uses data from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component (MEPS-IC) private-sector national tables to describe trends in employer coverage, premiums, and deductibles from 2008 to 2021. The MEPS-IC is an annual survey of private employers and state and local governments and is designed to be representative of all 50 states and the District of Columbia. This Statistical Brief describes trends and patterns in ESI for private-sector employees, overall and by three firm size categories: fewer than 50 employees (small firms), 50 to 99 employees (medium-sized firms), and 100 or more employees (large firms). All differences discussed in the text are at the 0.05 significance level or better. All dollar estimates are nominal (not adjusted for inflation). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
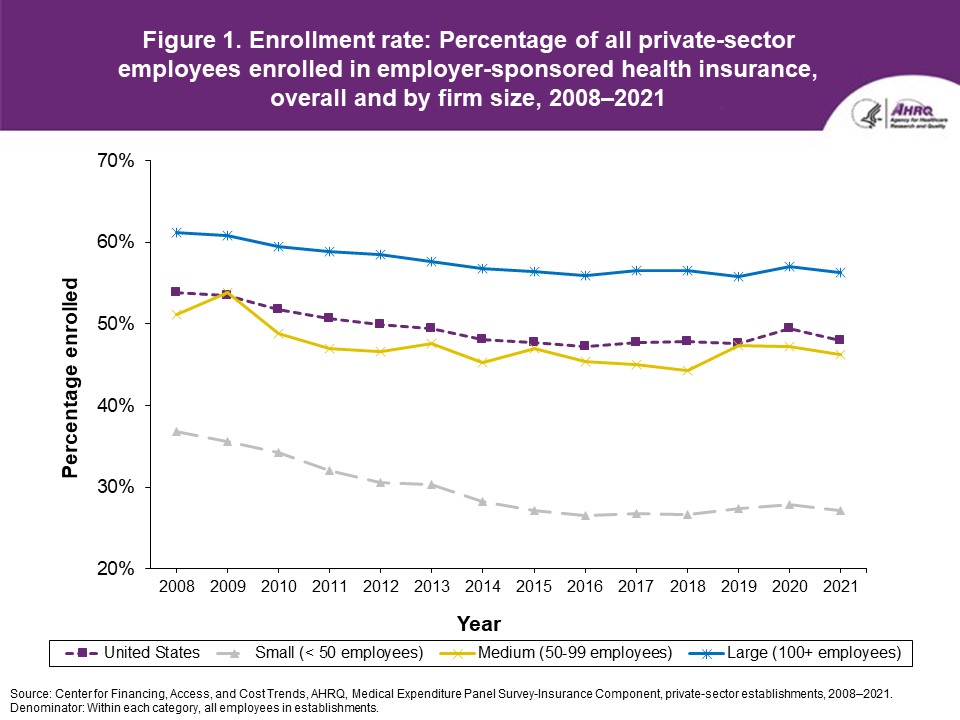
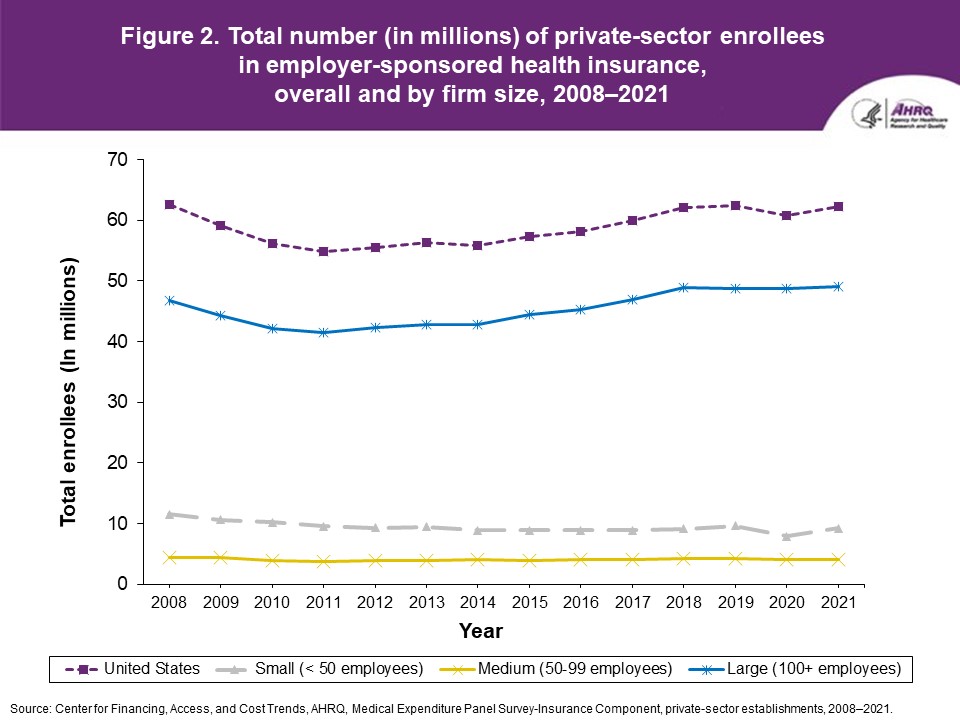
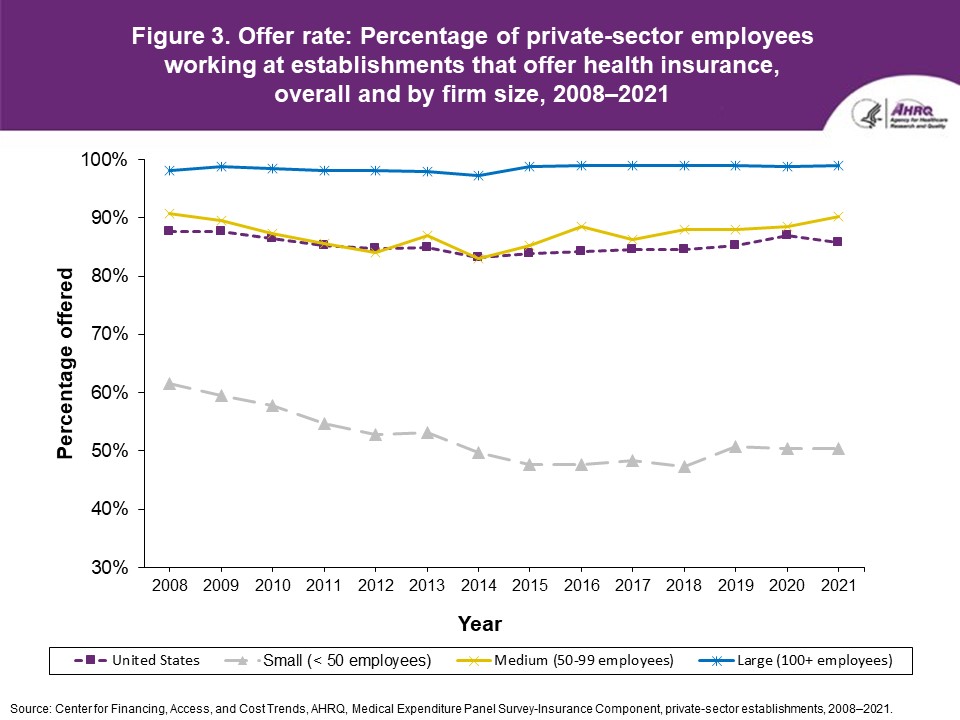
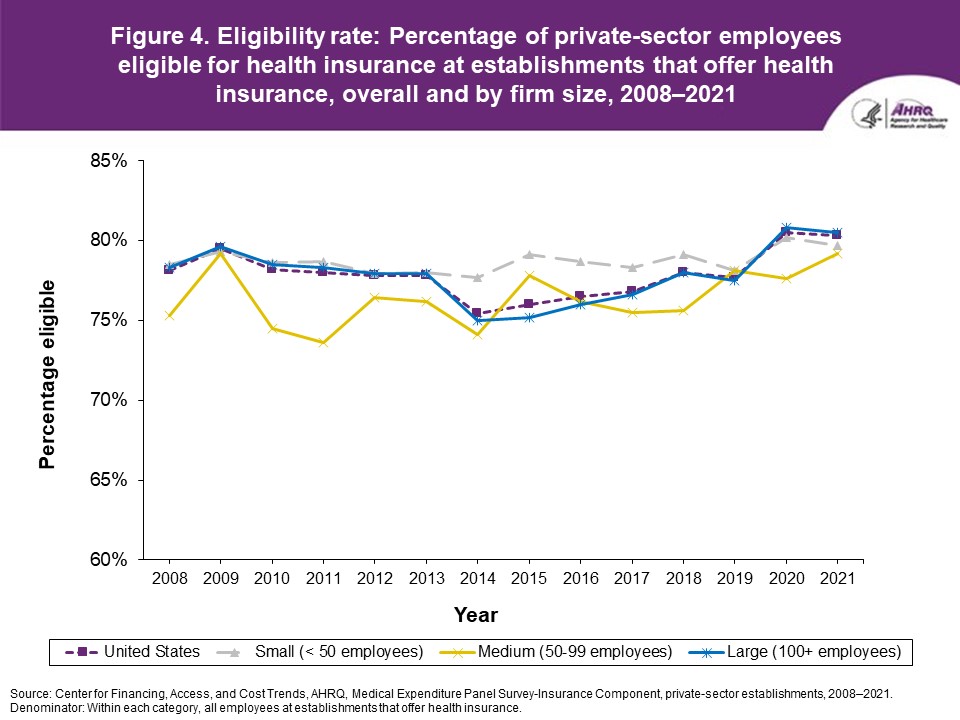
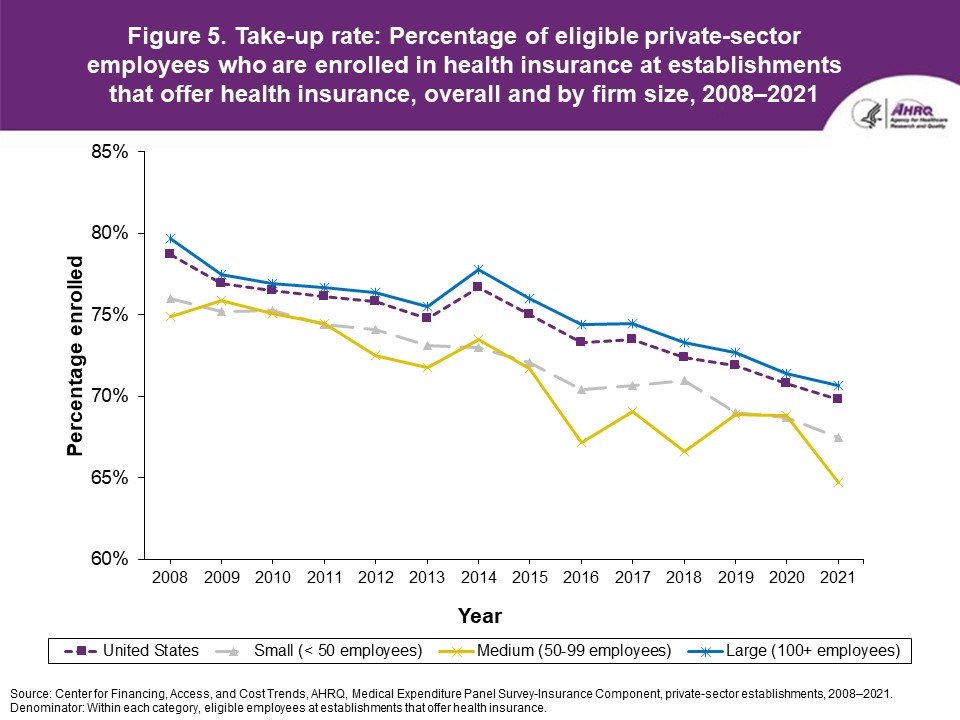
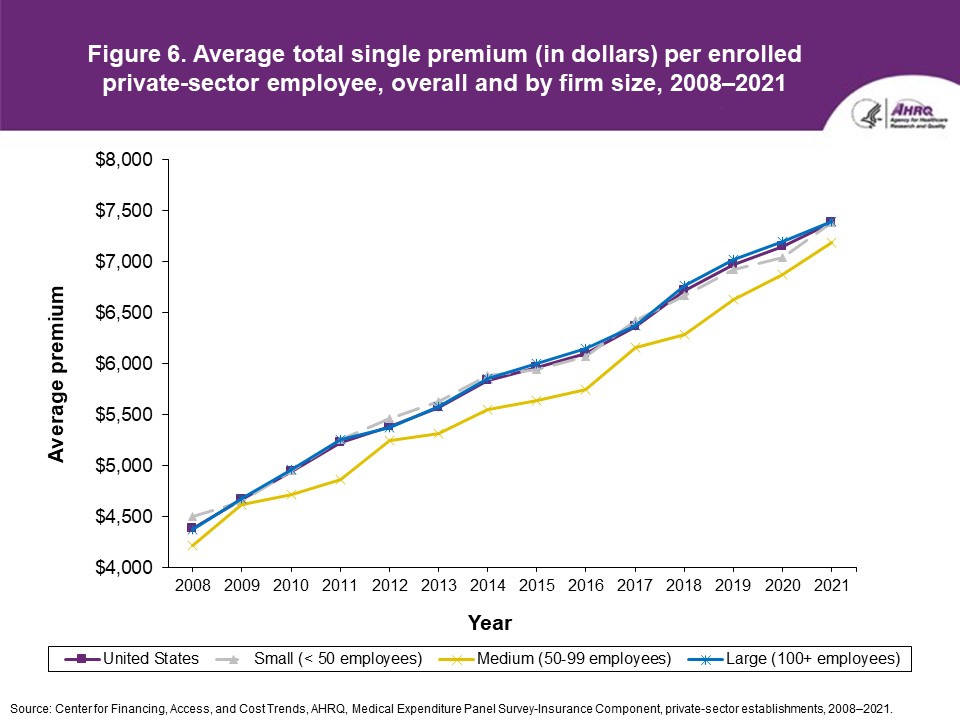
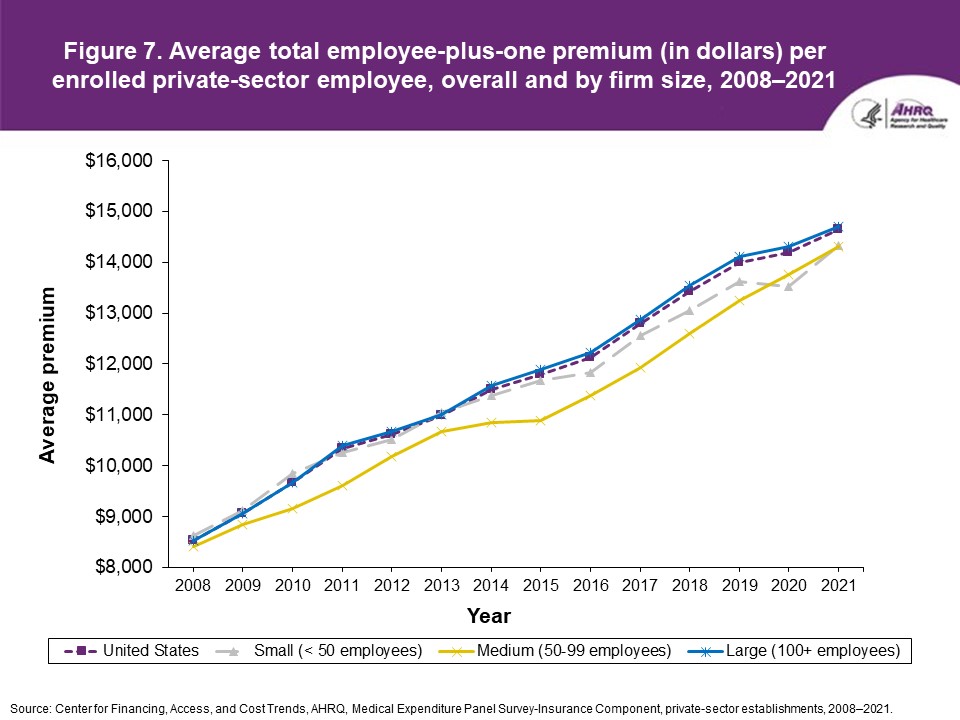
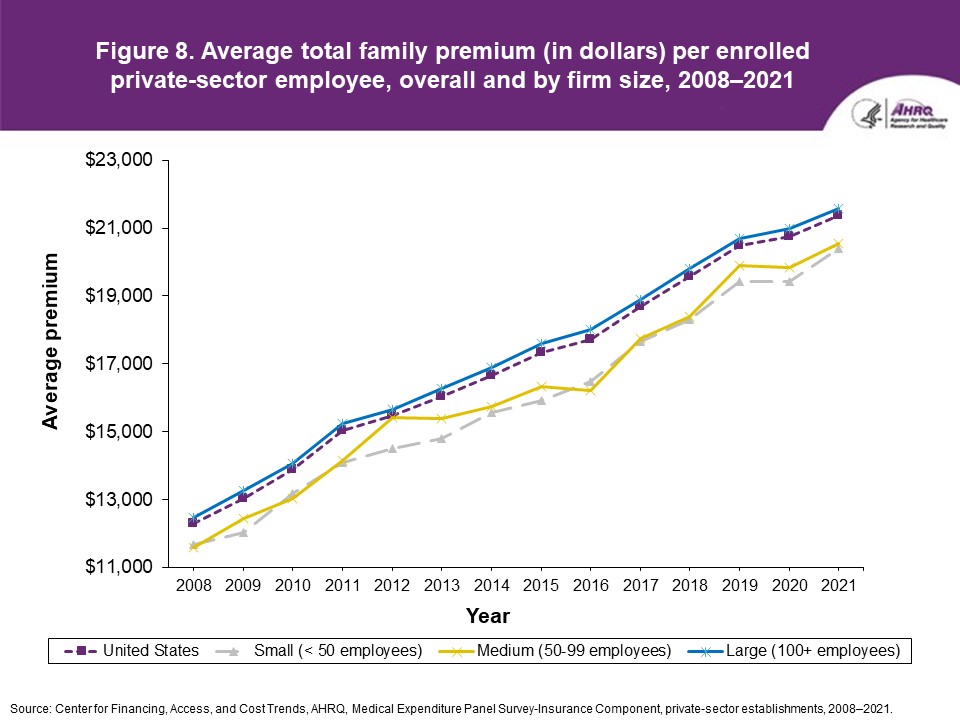
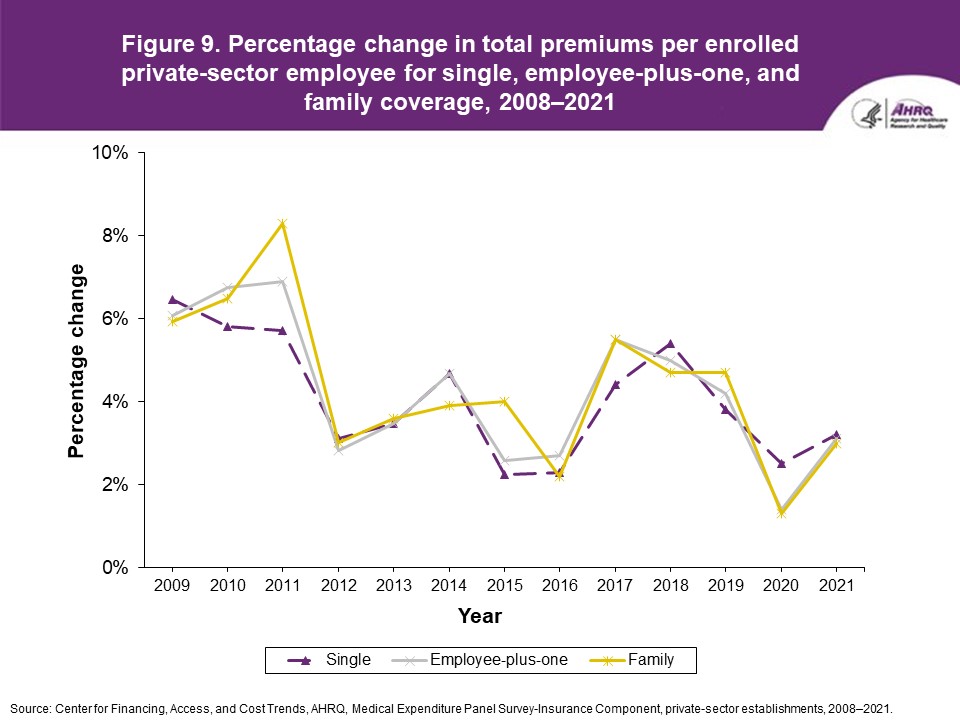
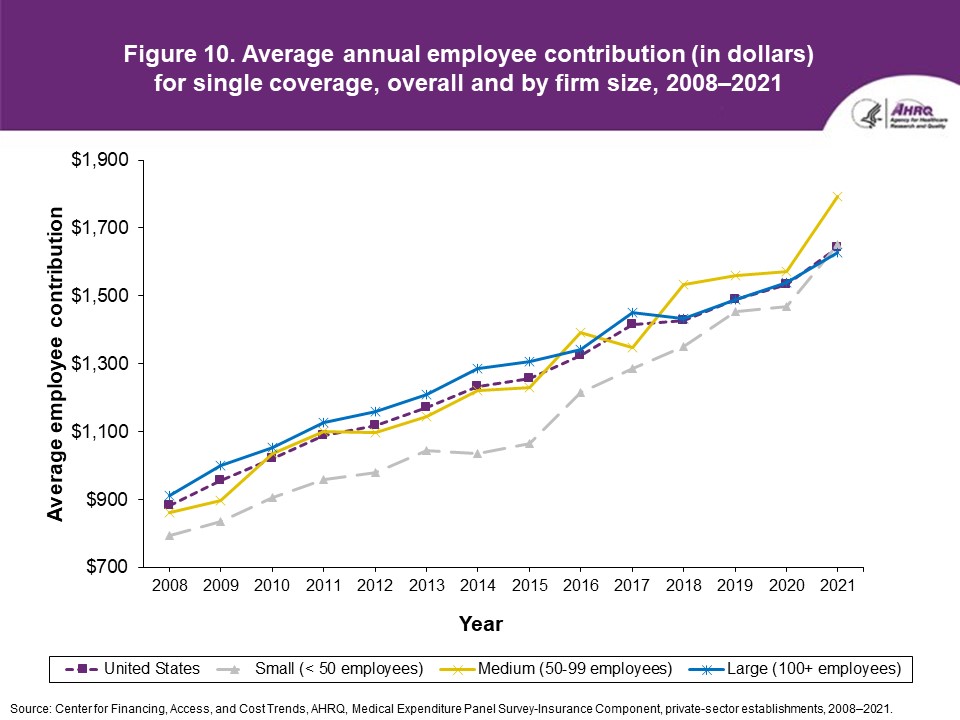
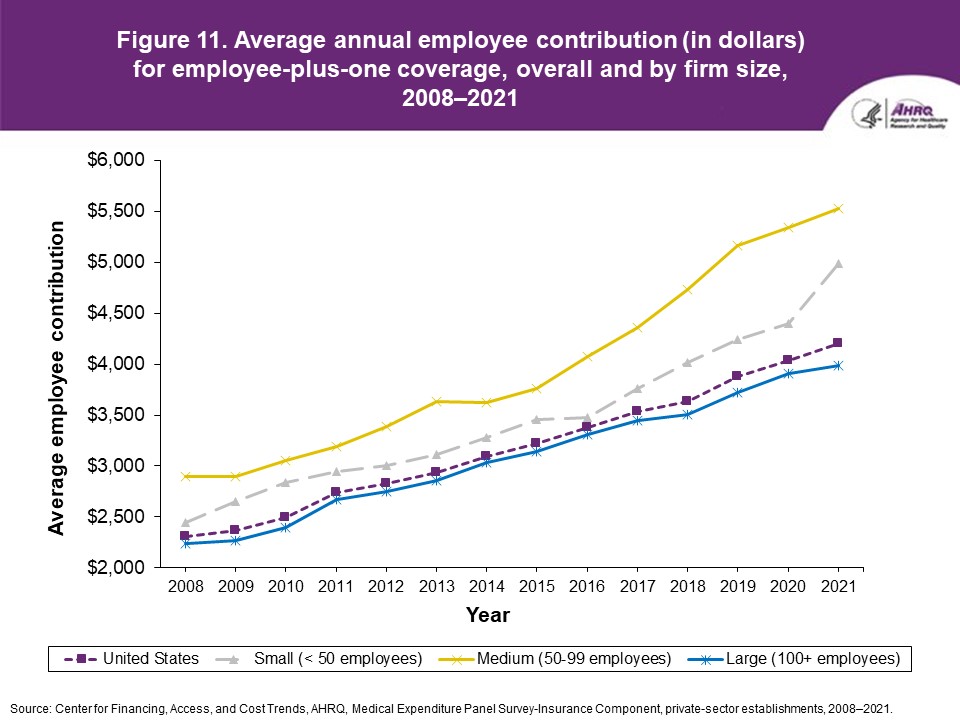
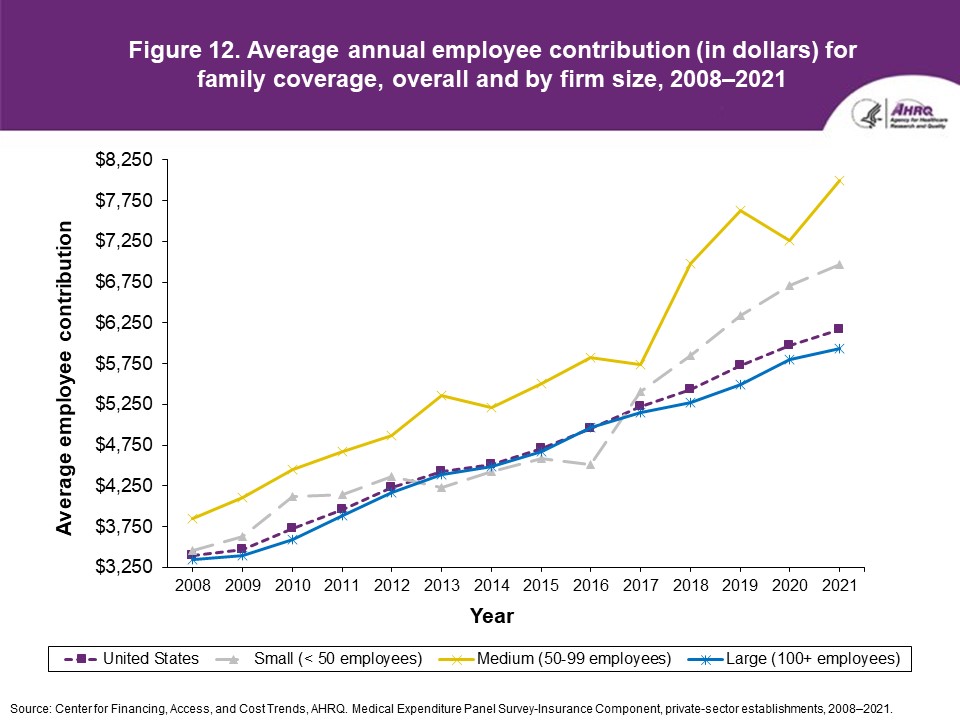
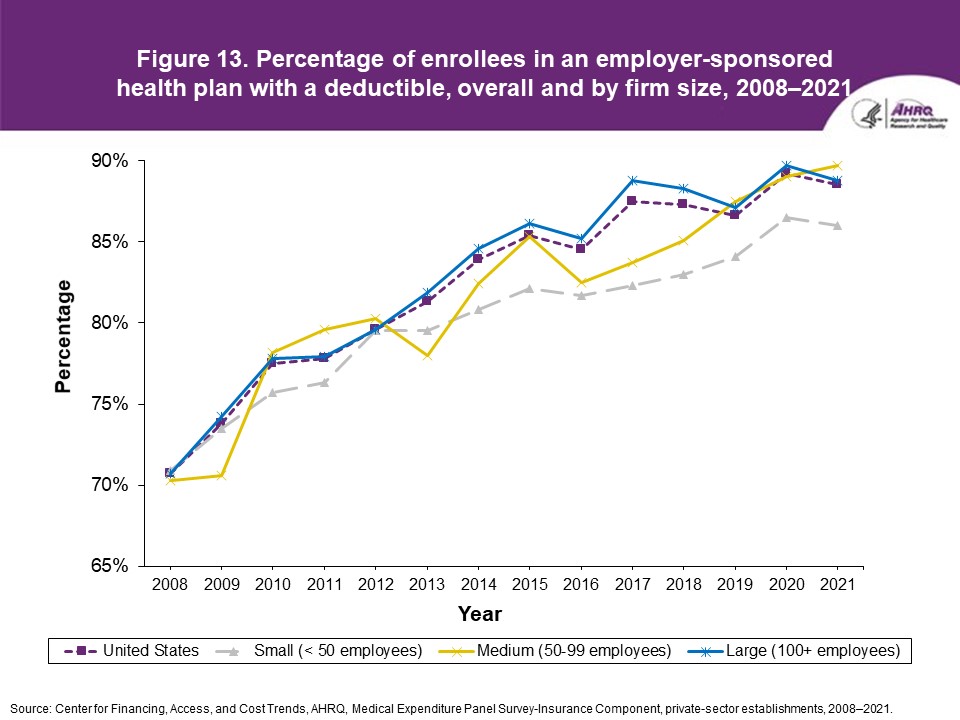
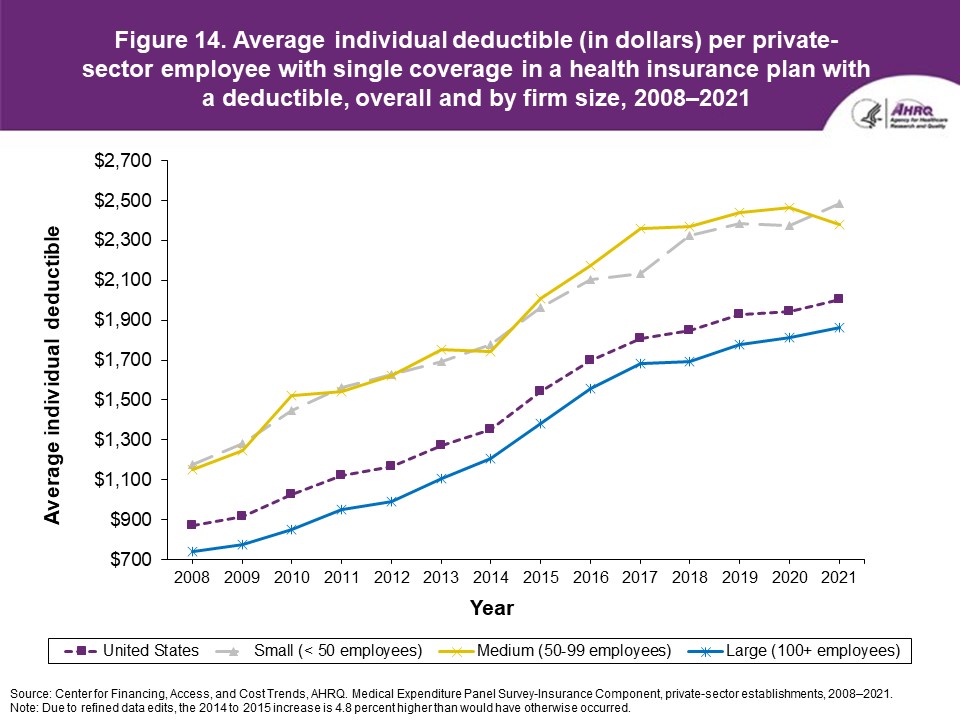
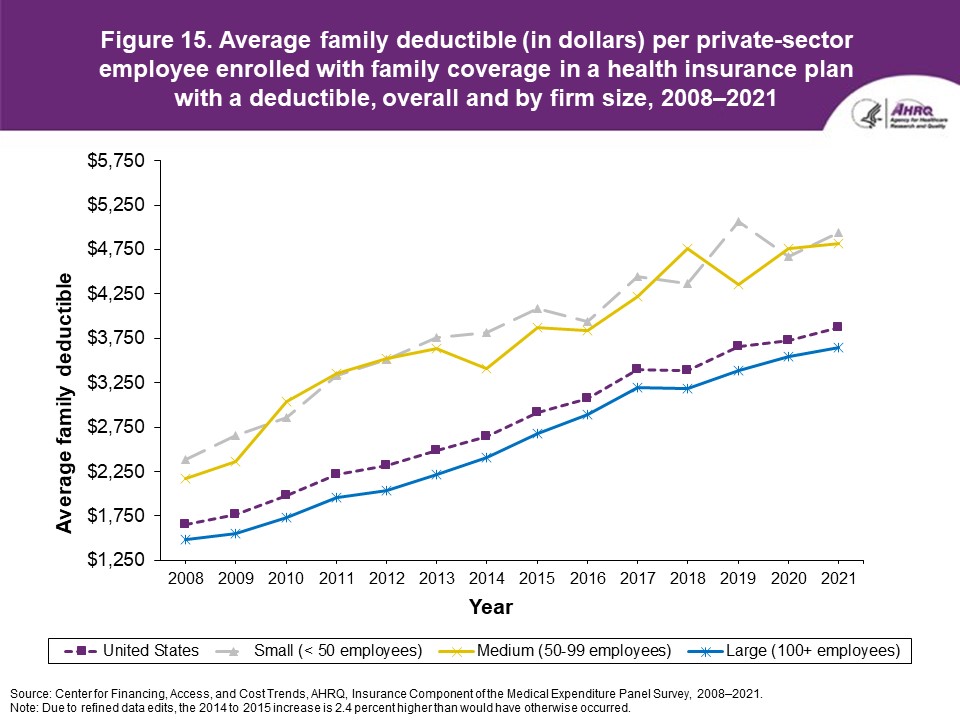
FindingsEnrollment rates and number of covered employees (figures 1-2)From 2020 to 2021, there was a decrease from 49.5 percent to 48.0 percent in the overall percentage of private-sector employees covered by a health insurance plan offered by their employers (the "enrollment rate") (figure 1). There were no significant changes, however, in the enrollment rate within any of the three firm size groups examined in this study. In 2021, the enrollment rate ranged from 27.1 percent at small employers to 56.3 percent at large employers. From 2020 to 2021, the point estimate for the total number of private-sector workers enrolled in a health insurance plan offered by their employers increased from 60.8 million to 62.2 million, but this change was not statistically significant (figure 2). Among small employers, the total number enrolled increased from 7.9 million to 9.2 million (a 15.8 percent increase, following a 17.4 percent decline between 2019 and 2020). Offer rates (figure 3)Overall, the percentage of private-sector employees working at establishments that offered insurance ("the offer rate") decreased from 86.9 percent in 2020 to 85.7 percent in 2021 (figure 3). Offer rates at small (50.4 percent), medium (90.3 percent), and large firms (98.9 percent) were unchanged from their 2020 values. The change in the overall offer rate was driven by the increase in employment among small employers. Compared to 2020, the decrease in the overall 2021 offer rate reflects an increase in the proportion of employees in small firms. Since small firms have lower offer rates than medium and large firms, the overall 2021 offer rate decreased even though offer rates within firm sizes did not change. Eligibility rates (figure 4)The overall eligibility rate for employees at private-sector establishments that offered insurance was unchanged in 2021, at 80.3 percent (versus 80.5 percent in 2020). The eligibility rates in small, medium, and large firms also were not statistically different from 2020 (79.7 percent, 79.2 percent, and 80.5 percent, respectively) (figure 4). Take-up rates (figure 5)The overall take-up rate for employees at private-sector establishments who were eligible for insurance did not show a statistically significant change from 2020 (70.8 percent) to 2021 (69.8 percent) (figure 5). Among medium employers (50-99 employees), take-up rates fell from 68.8 to 64.7 percent. The take-up rate among large firms (70.7 percent) remained higher than in medium (64.7 percent) and small firms (67.5 percent), as has been true in almost every year from 2008 through 2021. Premiums (figures 6-9)In 2021, average health insurance premiums were $7,380 for single coverage (figure 6), representing a 3.2 percent increase over 2020 (figure 9). Average premiums for employee-plus-one coverage ($14,634) and family coverage ($21,381) also increased from their 2020 levels by 3.1 and 3.0 percent, respectively. From 2020 to 2021, premiums in small and large firms increased significantly for single, employee-plus-one, and family coverage, with increases ranging from 4.8 to 5.9 percent in small firms and an increase of 2.8 percent for all coverage types in large firms (not shown). Employee premium contributionsIn 2021, average employee contributions were $1,643 for single coverage, a 7.2 percent increase from the 2020 level (figure 10). Single premium contributions increased at small (12.3 percent), medium (14.1 percent), and large firms (5.6 percent). Average employee contributions for employee-plus-one coverage were $4,199, a 4.1 percent increase (figure 11). The increase in family premium contributions, to $6,174, was not statistically significant. In 2021, average employee contributions for the two types of dependent coverage-employee-plus-one and family-were lower at large employers ($3,986 and $5,937, respectively) than at small employers ($4,984 and $6,967 respectively) and medium employers ($5,526 and $7,997, respectively). DeductiblesThe percentage of enrollees in a health insurance plan with a deductible in 2021 was not significantly different from 2020 for firms overall (88.5 percent), nor among small (86.0), medium (89.7), or large employers (88.8 percent) (figure 13). In the last 13 years, the overall percentage of enrollees with a deductible has increased by 17.8 percentage points (from 70.7 percent in 2008 to 88.5 percent in 2021). In 2021, enrollees in small firms were less likely than those in large firms to have a deductible, as has been the case in every year since 2021. From 2020 to 2021, average deductible levels for single coverage overall increased by 3.0 percent, to $2,004 (figure 14), and family coverage deductibles increased by 3.9 percent, to $3,868 (figure 15). There were no significant changes in deductible levels by firm size for single or family coverage. In the 2008 to 2021 period, single and family coverage deductibles showed overall increases in every year except 2018 and 2020. Average individual deductibles were higher in small ($2,485) and medium-sized firms ($2,378) than in large firms ($1,865) in 2021. Family deductibles were also higher in small ($4,945) and medium-sized firms ($4,816) than in large firms ($3,646) in 2021. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Data SourceThis Statistical Brief summarizes data from the 2008 through 2021 MEPS-IC. The data are available on the MEPS website at http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/survey_comp/Insurance.jsp or have been produced using special computation runs on the confidential MEPS-IC data available at the U.S. Census Bureau. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DefinitionsSingle coverageSingle coverage is health insurance that covers the employee only. Employee-plus-one coverageEmployee-plus-one coverage is health insurance that covers the employee and one other family member at a lower premium level than family coverage. If premiums differed for employee-plus-spouse and employee-plus-child coverage, information for employee-plus-child coverage was collected. Family coverageFamily coverage is health insurance that covers the employee and one or more family members (spouse and/or children as defined by the plan). For the MEPS-IC survey, family coverage is any coverage other than single and employee-plus-one. Some plans offer more than one rate for family coverage, depending on family size and composition. If more than one rate is offered, survey respondents are asked to report costs for a family of four. Enrollment rateThe enrollment rate is the percentage of all employees enrolled in their employer's health insurance at establishments both offering and not offering health insurance. Offer rateThe offer rate is the percentage of employees who work at establishments that offer health insurance. Eligible employeesEligible employees are those that are allowed to enroll in employer-sponsored coverage offered by their employer. Common eligibility criteria include a minimum number of hours worked per pay period or a minimum length of service with the employer. EmployeeAn employee is a person on the actual payroll. This definition excludes temporary and contract workers but includes the owner or manager if that person works at the firm. EstablishmentAn establishment is a single physical location of a business. Health insurance planA health insurance plan is an insurance contract that provides hospital and/or physician coverage to an employee for an agreed-upon fee (premium) for a defined benefit period. Take-up rateThe take-up rate is the percentage of eligible employees who enroll in health insurance coverage through their employer at establishments that offer insurance. DeductibleA deductible is a fixed dollar amount during the benefit period-usually a year-that an insured person pays before the insurer starts to make payments for covered medical services. The MEPS-IC collects information on deductibles for single and family coverage. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
About MEPSThe MEPS-IC is a survey of private-sector business establishments and state and local governments that collects information on employer-sponsored health insurance, such as whether insurance is offered, enrollments, types of plans, and premiums. The survey is conducted annually by the U.S. Census Bureau under the sponsorship of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). A total sample of approximately 42,000 private-sector establishments was selected for the 2021 survey, with 5.9 percent of the sample determined to be out of scope during the data collection process. The response rate for the private sector was 56.9 percent of the remaining in-scope sample units. Private-sector responses to the 2021 survey were collected from June 2021 through February 2022. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Suggested CitationKeenan, P., and Miller, G.E. Trends in Health Insurance at Private Employers, 2008-2021. Statistical Brief #543. July 2022. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. https://meps.ahrq.gov/data_files/publications/st543/stat543.shtmlAHRQ welcomes questions and comments from readers of this publication who are interested in obtaining more information about access, cost, use, financing, and quality of health care in the United States. We also invite you to tell us how you are using this Statistical Brief and other MEPS data and tools, and to share suggestions on how MEPS products might be enhanced to further meet your needs. Please email us at MEPSProjectDirector@ahrq.hhs.gov or send a letter to the address below: Joel W. Cohen, PhD, Director Center for Financing, Access and Cost Trends Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 5600 Fishers Lane, Mailstop 07W41A Rockville, MD 20857 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 1. Enrollment rate: Percentage of all private-sector employees enrolled in employer-sponsored health insurance, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 2. Total number (in millions) of private-sector enrollees in employer-sponsored health insurance, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 3. Offer rate: Percentage of private-sector employees working at establishments that offer health insurance, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 4. Eligibility rate: Percentage of private-sector employees eligible for health insurance at establishments that offer health insurance, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 5. Take-up rate: Percentage of eligible private-sector employees who are enrolled in health insurance at establishments that offer health insurance, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 6. Average total single premium (in dollars) per enrolled private-sector employee, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 7. Average total employee-plus-one premium (in dollars) per enrolled private-sector employee, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 8. Average total family premium (in dollars) per enrolled private-sector employee, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 9. Percentage change in total premiums per enrolled private-sector employee for single, employee-plus-one, and family coverage, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 10. Average annual employee contribution (in dollars) for single coverage, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 11. Average annual employee contribution (in dollars) for employee-plus-one coverage, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 12. Average annual employee contribution (in dollars) for family coverage, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 13. Percentage of enrollees in an employer-sponsored health plan with a deductible, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 14. Average individual deductible (in dollars) per private-sector employee with single coverage in a health insurance plan with a deductible, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 15. Average family deductible (in dollars) per private-sector employee enrolled with family coverage in a health insurance plan with a deductible, overall and by firm size, 2008-2021
Source: Center for Financing, Access, and Cost Trends, AHRQ. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey-Insurance Component, private-sector establishments, 2008-2021. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||